Intro
Master break-even analysis with our comprehensive guide, covering calculation, formula, and examples to help businesses achieve profitability and minimize financial risk, optimizing cost-benefit ratios and investment strategies.
Breaking even is a crucial milestone for any business, as it marks the point at which the company's revenues equal its costs. Achieving break-even point is essential for businesses to ensure their long-term sustainability and profitability. In this article, we will delve into the world of break-even analysis, exploring its importance, benefits, and steps to calculate it.
Breaking even is not just a financial concept, but a strategic tool that helps businesses make informed decisions about their operations, pricing, and investments. By understanding the break-even point, companies can identify areas for improvement, optimize their resources, and develop strategies to increase their profitability. Whether you are a small business owner, an entrepreneur, or a financial analyst, break-even analysis is an essential skill to master.
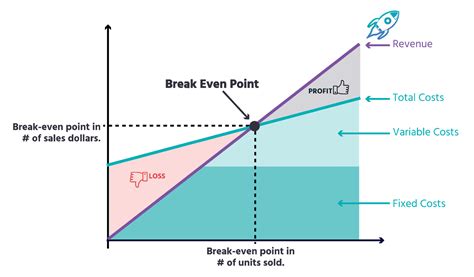
The break-even analysis is a comprehensive framework that takes into account various factors, including fixed costs, variable costs, selling price, and sales volume. It provides a clear picture of a company's financial health and helps identify the point at which the business becomes profitable. By analyzing the break-even point, businesses can determine the minimum sales required to cover their costs, make informed decisions about pricing and production, and develop strategies to increase their market share.
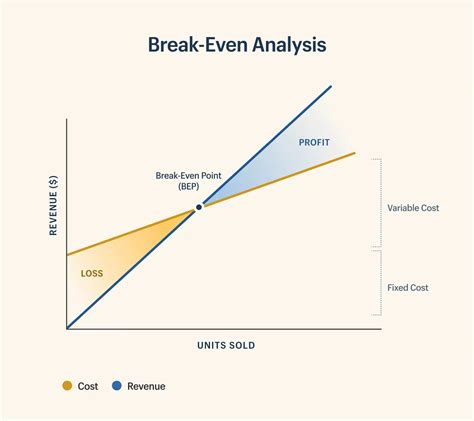
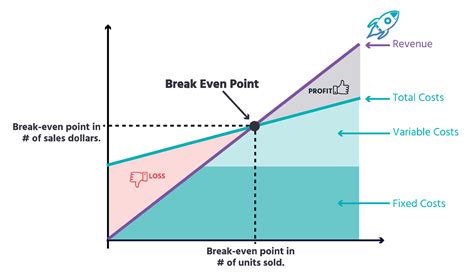
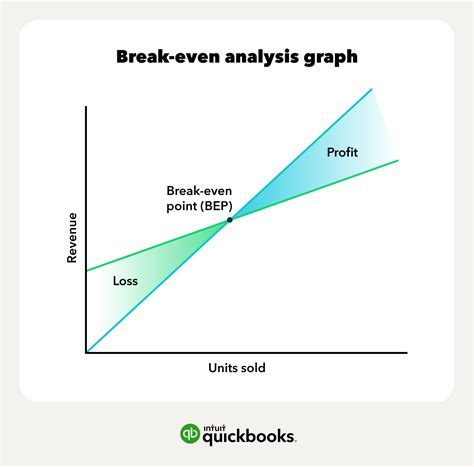
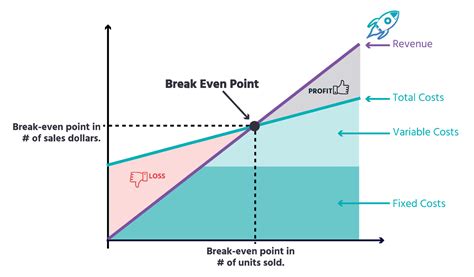
What is Break-Even Analysis?
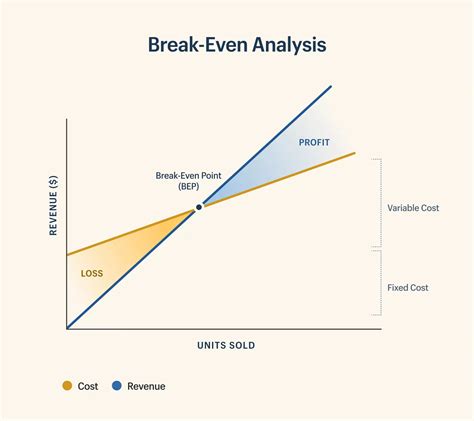
Benefits of Break-Even Analysis
The break-even analysis offers several benefits to businesses, including: * Identifying the minimum sales required to cover costs * Determining the point at which the business becomes profitable * Informing decisions about pricing and production * Helping to develop strategies to increase market share * Providing a clear picture of a company's financial healthHow to Calculate Break-Even Point
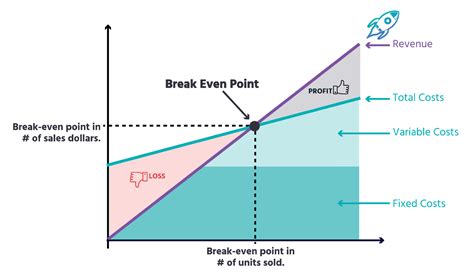
Break-Even Analysis Formula
The break-even analysis formula is: Break-Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs) Where: * Fixed Costs are the company's fixed expenses * Selling Price is the price at which the company sells its products or services * Variable Costs are the company's variable expensesExample of Break-Even Analysis
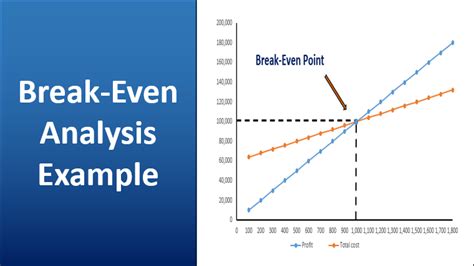
Using the break-even analysis formula, we can calculate the break-even point as follows: BEP = $10,000 / ($10 - $5) BEP = $10,000 / $5 BEP = 2,000 units
This means that the company needs to sell at least 2,000 units per month to break even.
Limitations of Break-Even Analysis
While break-even analysis is a useful tool for businesses, it has several limitations, including: * Assuming a linear relationship between sales volume and costs * Ignoring the impact of changes in market conditions and competition * Failing to account for the time value of moneyApplications of Break-Even Analysis
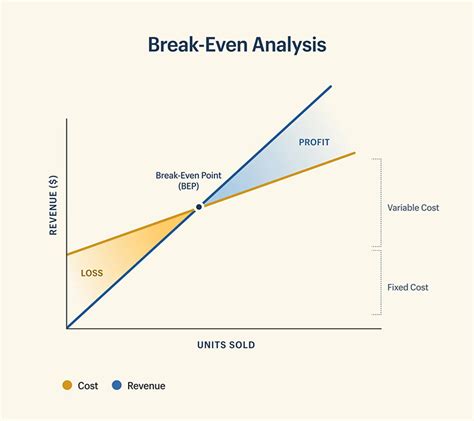
Break-Even Analysis in Different Industries
Break-even analysis is used in various industries, including: * Manufacturing: to determine the minimum production volume required to break even * Retail: to evaluate the impact of changes in pricing and inventory levels * Service: to determine the minimum number of customers required to break evenBest Practices for Break-Even Analysis
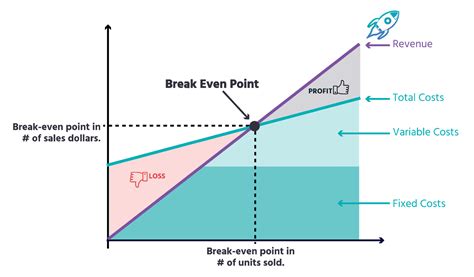
Common Mistakes in Break-Even Analysis
Common mistakes in break-even analysis include: * Failing to account for all fixed and variable costs * Ignoring the impact of changes in market conditions and competition * Using inaccurate or outdated dataBreak Even Analysis Image Gallery
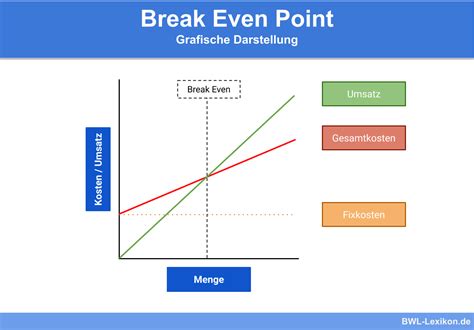

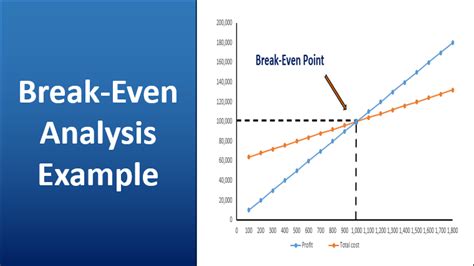
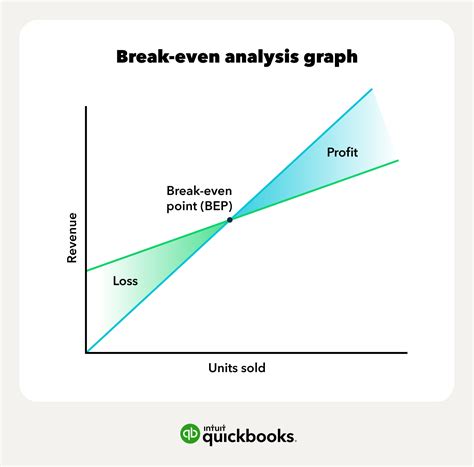

What is the purpose of break-even analysis?
+The purpose of break-even analysis is to determine the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total fixed and variable costs.
How do I calculate the break-even point?
+The break-even point can be calculated using the formula: Break-Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs)
What are the limitations of break-even analysis?
+The limitations of break-even analysis include assuming a linear relationship between sales volume and costs, ignoring the impact of changes in market conditions and competition, and failing to account for the time value of money.
How can I use break-even analysis to inform my business decisions?
+Break-even analysis can be used to inform decisions about pricing and production, identify areas for cost reduction and improvement, and develop strategies to increase market share and profitability.
What are the best practices for break-even analysis?
+Best practices for break-even analysis include regularly reviewing and updating the break-even analysis, considering multiple scenarios and sensitivity analysis, and using the break-even analysis to inform decisions about pricing and production.
In conclusion, break-even analysis is a powerful tool for businesses to determine their financial health and make informed decisions about their operations. By understanding the break-even point, companies can identify areas for improvement, optimize their resources, and develop strategies to increase their market share and profitability. Whether you are a small business owner, an entrepreneur, or a financial analyst, break-even analysis is an essential skill to master. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with break-even analysis in the comments below, and to explore our other articles and resources for more information on financial management and business planning.
