Intro
Calculate profitability with the Break Even Point Equation, analyzing fixed costs, variable costs, and revenue to determine the point of zero loss, leveraging financial metrics like contribution margin and sales volume.
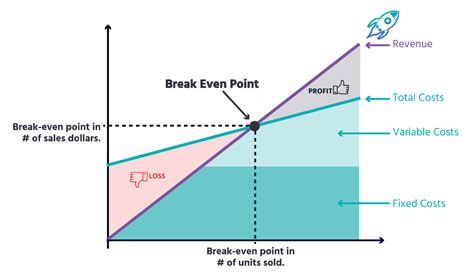
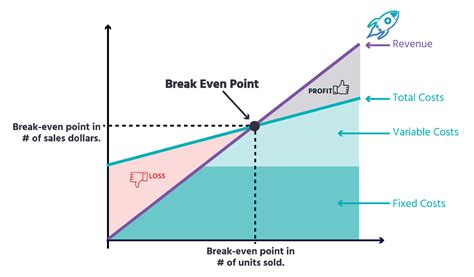
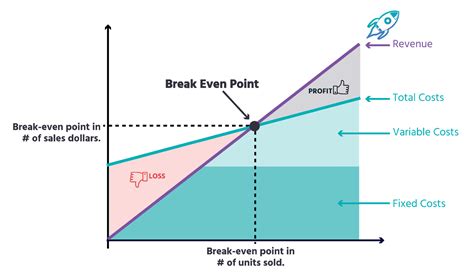
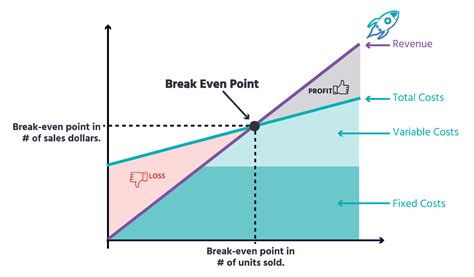
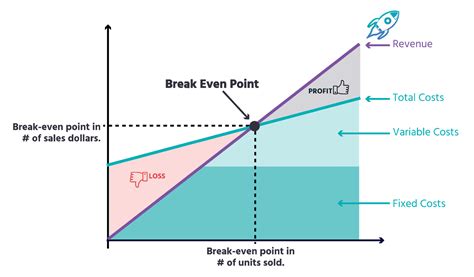
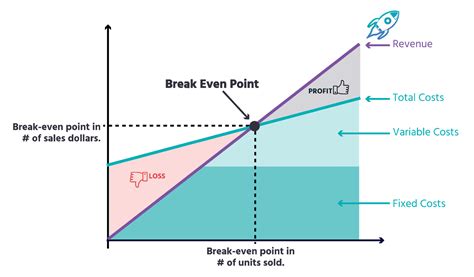
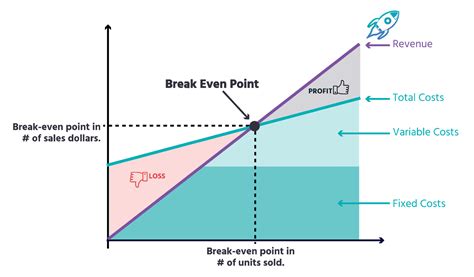
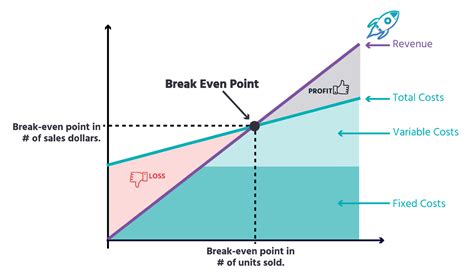
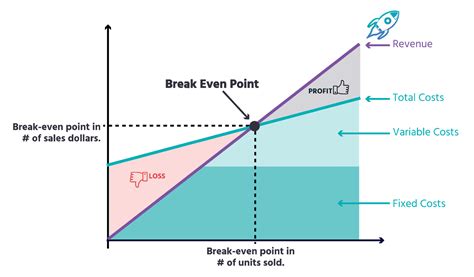
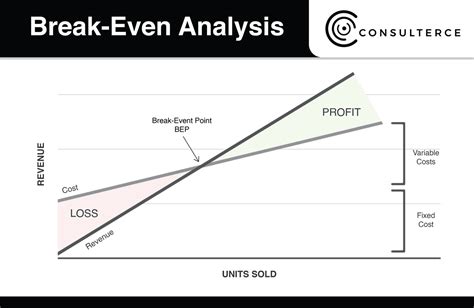
The break-even point is a crucial concept in business and finance that refers to the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total fixed and variable costs. It is the point at which a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. Understanding the break-even point is essential for businesses to determine their pricing strategies, production levels, and cost structures. In this article, we will delve into the break-even point equation, its components, and its significance in business decision-making.
The break-even point equation is a simple yet powerful tool that helps businesses calculate the point at which they become profitable. The equation is as follows: Break-Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs). This equation takes into account the fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price of a product or service to determine the break-even point. Fixed costs are expenses that remain the same even if the production level changes, such as rent, salaries, and insurance. Variable costs, on the other hand, are expenses that vary with the production level, such as raw materials, labor, and marketing expenses.
Understanding the Break-Even Point Equation
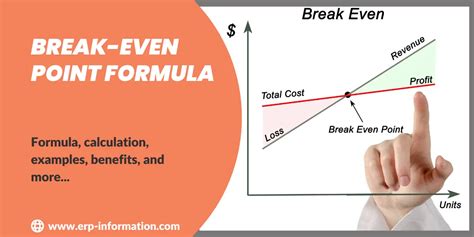
To calculate the break-even point, businesses need to know their fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price. The fixed costs are the expenses that remain the same regardless of the production level, while the variable costs are the expenses that vary with the production level. The selling price is the price at which the product or service is sold. By plugging these values into the break-even point equation, businesses can determine the point at which they become profitable.
Components of the Break-Even Point Equation
The break-even point equation consists of three main components: fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price. Fixed costs are expenses that remain the same even if the production level changes. Examples of fixed costs include rent, salaries, insurance, and depreciation. Variable costs, on the other hand, are expenses that vary with the production level. Examples of variable costs include raw materials, labor, marketing expenses, and transportation costs. The selling price is the price at which the product or service is sold.Calculating the Break-Even Point

To calculate the break-even point, businesses can follow these steps:
- Determine the fixed costs: Identify all the expenses that remain the same regardless of the production level.
- Determine the variable costs: Identify all the expenses that vary with the production level.
- Determine the selling price: Determine the price at which the product or service will be sold.
- Plug the values into the break-even point equation: BEP = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs).
Example of Calculating the Break-Even Point
Let's say a company has fixed costs of $10,000, variable costs of $5 per unit, and a selling price of $10 per unit. To calculate the break-even point, the company would plug these values into the break-even point equation: BEP = $10,000 / ($10 - $5) = $10,000 / $5 = 2,000 units. This means that the company needs to sell 2,000 units to break even.Significance of the Break-Even Point
The break-even point is a crucial concept in business decision-making. It helps businesses determine their pricing strategies, production levels, and cost structures. By knowing the break-even point, businesses can make informed decisions about their operations and finances. For example, if a company knows that it needs to sell 2,000 units to break even, it can adjust its production level and pricing strategy accordingly.
Limitations of the Break-Even Point
While the break-even point is a useful tool, it has some limitations. It assumes that the selling price and variable costs remain constant, which may not always be the case. Additionally, it does not take into account other factors that may affect profitability, such as changes in market conditions or competition.Applications of the Break-Even Point
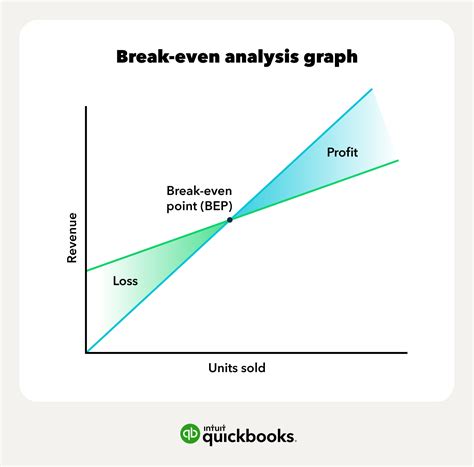
The break-even point has several applications in business and finance. It can be used to determine the viability of a new product or service, to evaluate the performance of a company, and to make informed decisions about pricing and production. Additionally, it can be used to identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized.
Real-World Examples of the Break-Even Point
The break-even point is used in various industries, including manufacturing, retail, and services. For example, a company that produces widgets may use the break-even point to determine how many widgets it needs to sell to cover its costs. A retail store may use the break-even point to determine how many units of a product it needs to sell to break even.Gallery of Break-Even Point Examples
Break-Even Point Image Gallery
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the break-even point?
+The break-even point is the point at which a company's total revenue equals its total fixed and variable costs.
How is the break-even point calculated?
+The break-even point is calculated using the formula: BEP = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs).
What are the limitations of the break-even point?
+The break-even point assumes that the selling price and variable costs remain constant, and it does not take into account other factors that may affect profitability.
In conclusion, the break-even point is a crucial concept in business and finance that helps companies determine their pricing strategies, production levels, and cost structures. By understanding the break-even point equation and its components, businesses can make informed decisions about their operations and finances. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the break-even point and its significance in business decision-making. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
