Intro
Calculate profitability with the break even point formula, understanding fixed costs, variable costs, and revenue to determine the point of zero loss, leveraging financial analysis and accounting principles for informed business decisions.
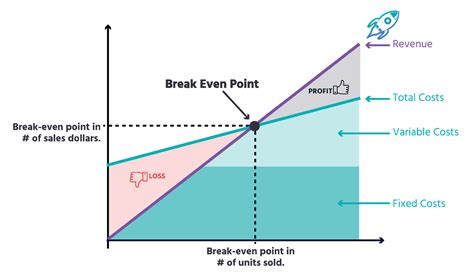
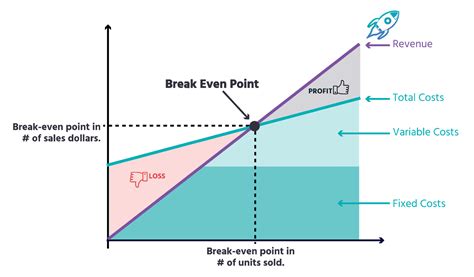
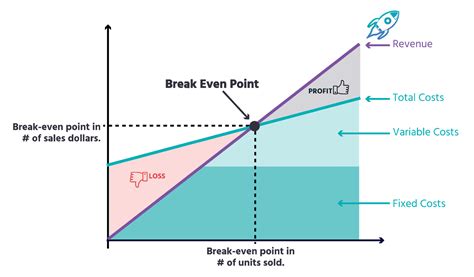
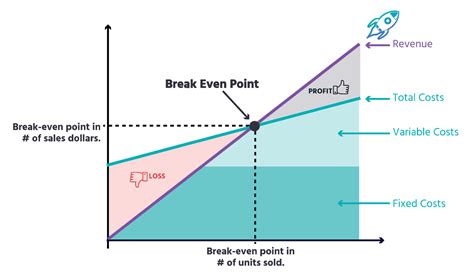
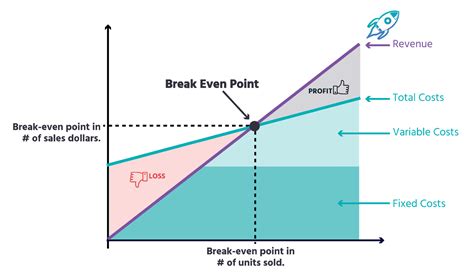
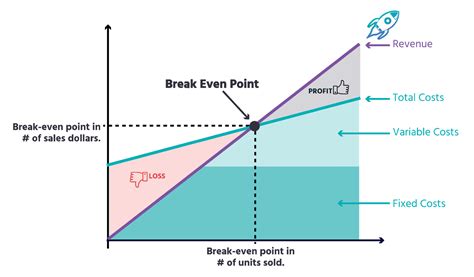
The break-even point is a crucial concept in business and finance that helps entrepreneurs and managers determine when their company will start generating profits. It is the point at which the total revenue equals the total fixed and variable costs. In other words, it is the point at which the business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. Understanding the break-even point formula is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and investment.
The break-even point is a vital metric that helps businesses to evaluate their performance and make adjustments to their strategies. It is a key indicator of a company's financial health and can be used to identify areas for improvement. By calculating the break-even point, businesses can determine the minimum amount of sales they need to generate to cover their costs and start making a profit. This information can be used to set realistic targets and make informed decisions about investments and resource allocation.
In today's competitive business environment, understanding the break-even point formula is more important than ever. With rising costs and intense competition, businesses need to be able to make accurate calculations and predictions to stay ahead of the game. The break-even point formula provides a simple and effective way to do this, and it is an essential tool for any business that wants to achieve success and profitability.
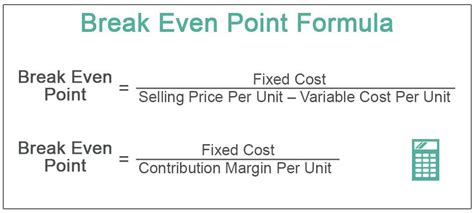
What is the Break-Even Point Formula?
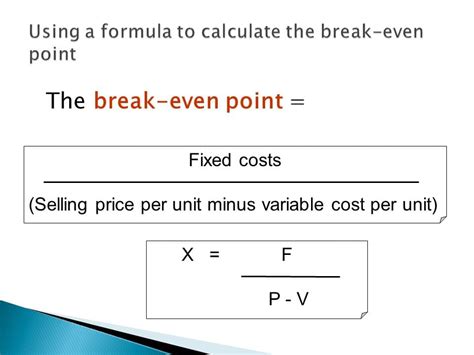
Break-Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs)
Where:
- Fixed Costs are the costs that remain the same even if the business produces more or less, such as rent, salaries, and equipment costs.
- Selling Price is the price at which the business sells its products or services.
- Variable Costs are the costs that vary depending on the level of production, such as raw materials, labor, and marketing costs.
How to Calculate the Break-Even Point
Calculating the break-even point is a simple process that involves plugging in the relevant numbers into the formula. Here are the steps to follow:- Determine the fixed costs: Identify all the fixed costs associated with the business, such as rent, salaries, and equipment costs.
- Determine the variable costs: Identify all the variable costs associated with the business, such as raw materials, labor, and marketing costs.
- Determine the selling price: Determine the price at which the business sells its products or services.
- Plug in the numbers: Plug in the fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price into the break-even point formula.
For example, let's say a business has fixed costs of $10,000 per month, variable costs of $5 per unit, and a selling price of $10 per unit. To calculate the break-even point, we would plug in the numbers as follows:
BEP = $10,000 / ($10 - $5) BEP = $10,000 / $5 BEP = 2,000 units
This means that the business needs to sell at least 2,000 units per month to break even.
Importance of the Break-Even Point
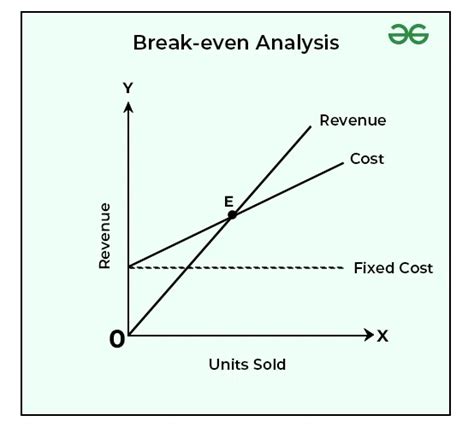
- Helps to determine pricing: The break-even point can help businesses to determine the optimal price for their products or services.
- Helps to evaluate performance: The break-even point can help businesses to evaluate their performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Helps to make informed decisions: The break-even point can help businesses to make informed decisions about investments, resource allocation, and strategy.
- Helps to manage cash flow: The break-even point can help businesses to manage their cash flow and ensure that they have enough funds to cover their costs.
Limitations of the Break-Even Point
While the break-even point is a useful metric, it has some limitations. Here are some of the limitations:- Assumes a linear relationship: The break-even point assumes a linear relationship between costs and revenue, which may not always be the case.
- Ignores other costs: The break-even point ignores other costs such as opportunity costs, sunk costs, and externalities.
- Ignores changes in the market: The break-even point ignores changes in the market, such as changes in demand, competition, and technology.
Real-World Applications of the Break-Even Point
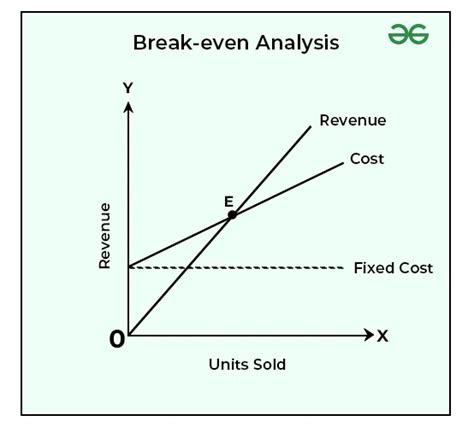
- Pricing strategy: The break-even point can be used to determine the optimal price for a product or service.
- Investment decisions: The break-even point can be used to evaluate investment opportunities and determine whether they are likely to generate a return.
- Resource allocation: The break-even point can be used to allocate resources effectively and ensure that they are being used to maximize profits.
- Strategy development: The break-even point can be used to develop a business strategy that takes into account the costs and revenue of the business.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the break-even point, there are some common mistakes to avoid. Here are some of them:- Ignoring fixed costs: Fixed costs can have a significant impact on the break-even point, so it's essential to include them in the calculation.
- Ignoring variable costs: Variable costs can also have a significant impact on the break-even point, so it's essential to include them in the calculation.
- Using incorrect numbers: Using incorrect numbers can result in an inaccurate break-even point, so it's essential to use accurate and up-to-date numbers.
Conclusion and Next Steps

Next steps for businesses that want to use the break-even point to improve their performance include:
- Calculating the break-even point regularly to track changes in costs and revenue
- Using the break-even point to evaluate investment opportunities and determine whether they are likely to generate a return
- Developing a business strategy that takes into account the costs and revenue of the business
- Continuously monitoring and adjusting the break-even point to ensure that it remains accurate and relevant.
Break Even Point Image Gallery

What is the break-even point formula?
+The break-even point formula is: Break-Even Point (BEP) = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price - Variable Costs)
Why is the break-even point important?
+The break-even point is important because it helps businesses to evaluate their performance and make informed decisions about pricing, investment, and resource allocation.
How do I calculate the break-even point?
+To calculate the break-even point, you need to determine the fixed costs, variable costs, and selling price, and then plug in the numbers into the break-even point formula.
What are the limitations of the break-even point?
+The break-even point has several limitations, including assuming a linear relationship between costs and revenue, ignoring other costs, and ignoring changes in the market.
How can I use the break-even point to improve my business?
+You can use the break-even point to evaluate investment opportunities, determine optimal pricing, and allocate resources effectively. You can also use it to develop a business strategy that takes into account the costs and revenue of the business.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the break-even point formula and its importance in business. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. Share this article with your friends and colleagues who may benefit from learning about the break-even point.
