Intro
Learn to Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio, a key metric for inventory management, using sales data and cost of goods sold, to optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency.
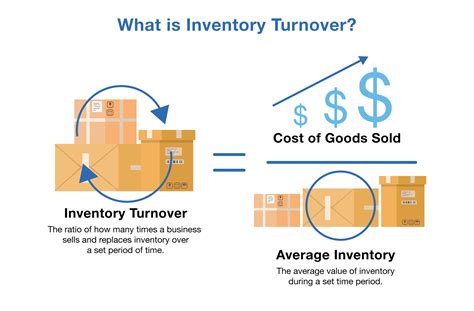
Calculating the inventory turnover ratio is crucial for businesses to understand how efficiently they are managing their inventory. This ratio provides insights into how often a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period. It's a key performance indicator that helps businesses identify areas for improvement in their inventory management strategies. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the inventory turnover ratio, its calculation, and what it signifies for businesses.
The inventory turnover ratio is a significant metric because it reflects a company's ability to manage its inventory levels, balance supply with demand, and minimize storage and handling costs. A high inventory turnover ratio indicates that a company is selling its inventory quickly, which can lead to higher profits and lower storage costs. On the other hand, a low ratio may suggest overstocking, which can result in unnecessary expenses and potential losses due to obsolete or spoiled inventory.
To calculate the inventory turnover ratio, you need to know the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the average inventory for the period. The formula for the inventory turnover ratio is: Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory. For instance, if the COGS for a year is $100,000 and the average inventory is $25,000, the inventory turnover ratio would be 4. This means the company sold and replaced its inventory four times during that year.
Understanding the Inventory Turnover Ratio
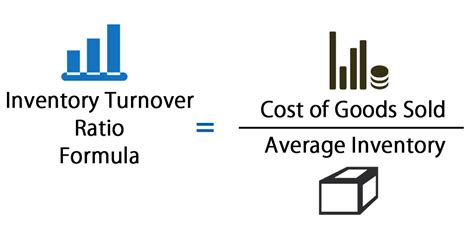
Understanding the inventory turnover ratio involves recognizing its components and how they affect the overall efficiency of inventory management. The cost of goods sold is a critical component, as it directly relates to the revenue generated from selling the inventory. Average inventory, on the other hand, gives a snapshot of the inventory levels throughout the period, taking into account both the beginning and ending inventory.
Components of the Inventory Turnover Ratio
The components of the inventory turnover ratio are essential for its calculation and interpretation. These include: - **Cost of Goods Sold (COGS):** This is the direct cost associated with producing the goods sold by a company. It includes the cost of materials, labor, and overheads directly related to the production process. - **Average Inventory:** This is the average value of inventory held by a company over a specific period. It is calculated by taking the average of the beginning and ending inventory levels.Calculating the Inventory Turnover Ratio
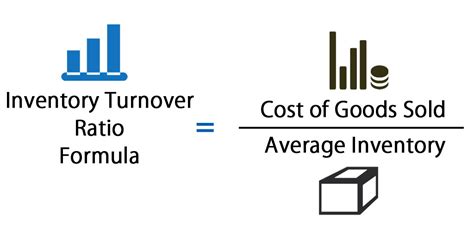
Calculating the inventory turnover ratio involves a straightforward process:
- Determine the Cost of Goods Sold: This can be found in the income statement of the company.
- Calculate the Average Inventory: Add the beginning inventory and the ending inventory, then divide by 2.
- Apply the Formula: Divide the COGS by the average inventory to get the inventory turnover ratio.
Interpreting the Inventory Turnover Ratio
Interpreting the inventory turnover ratio requires understanding what a high or low ratio signifies: - **High Inventory Turnover Ratio:** Indicates that inventory sells quickly, which can be beneficial as it suggests strong sales and efficient inventory management. However, it may also indicate that the company is not holding enough inventory, potentially leading to lost sales due to stockouts. - **Low Inventory Turnover Ratio:** Suggests that inventory is not selling as quickly as it should, which can lead to higher storage costs and potential losses due to inventory becoming obsolete or spoiled.Importance of Inventory Turnover Ratio

The inventory turnover ratio is important for several reasons:
- Efficiency Measurement: It measures how efficiently a company is using its inventory.
- Cash Flow Management: A high inventory turnover ratio can improve cash flow by reducing the amount of capital tied up in inventory.
- Decision Making: It helps in making informed decisions about inventory management, such as how much to order and when.
Factors Affecting Inventory Turnover Ratio
Several factors can affect the inventory turnover ratio, including: - **Seasonal Demand:** Businesses with seasonal demand may have varying inventory turnover ratios throughout the year. - **Inventory Management Practices:** Effective inventory management practices, such as just-in-time ordering, can significantly improve the inventory turnover ratio. - **Product Type:** The type of product can influence the inventory turnover ratio, with perishable goods typically requiring a higher turnover rate than non-perishable goods.Improving Inventory Turnover Ratio

Improving the inventory turnover ratio involves several strategies:
- Optimize Inventory Levels: Ensure that inventory levels are appropriate for the demand.
- Implement Efficient Inventory Management Systems: Use systems that can track inventory in real-time and automate reordering.
- Analyze Sales Data: Understand sales trends to predict demand accurately and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Challenges in Improving Inventory Turnover Ratio
While improving the inventory turnover ratio is beneficial, there are challenges to consider: - **Balancing Supply and Demand:** Finding the right balance to avoid overstocking or understocking. - **Investment in Technology:** Implementing advanced inventory management systems can require significant upfront investment. - **Training Personnel:** Ensuring that staff understands and can effectively use new inventory management systems.Inventory Turnover Ratio in Different Industries
The inventory turnover ratio can vary significantly across different industries:
- Retail: Typically has a high inventory turnover ratio due to the fast-moving nature of consumer goods.
- Manufacturing: May have a lower inventory turnover ratio due to the production time and the nature of the products being manufactured.
- Food Industry: Requires a high inventory turnover ratio due to the perishable nature of the products.
Industry Benchmarks
Understanding industry benchmarks for the inventory turnover ratio can help businesses assess their performance: - **Compare with Industry Averages:** To determine if the company's inventory turnover ratio is above or below the industry average. - **Set Realistic Goals:** Based on industry benchmarks and the company's specific circumstances.Gallery of Inventory Management
Inventory Management Image Gallery


What is the inventory turnover ratio?
+The inventory turnover ratio is a metric that calculates how many times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period.
How do you calculate the inventory turnover ratio?
+The inventory turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory for the period.
What does a high inventory turnover ratio indicate?
+A high inventory turnover ratio indicates that a company is selling its inventory quickly and efficiently, which can lead to higher profits and lower storage costs.
How can a company improve its inventory turnover ratio?
+A company can improve its inventory turnover ratio by optimizing inventory levels, implementing efficient inventory management systems, and analyzing sales data to predict demand accurately.
Why is the inventory turnover ratio important for businesses?
+The inventory turnover ratio is important because it measures the efficiency of a company's inventory management, helps in cash flow management, and informs decision-making regarding inventory levels and management practices.
In conclusion, calculating and understanding the inventory turnover ratio is crucial for businesses to assess their inventory management efficiency. By recognizing the factors that influence this ratio and implementing strategies to improve it, companies can enhance their overall performance, reduce costs, and increase profitability. We invite readers to share their experiences and insights on managing inventory turnover ratios and to explore more topics related to inventory management and its impact on business operations.
