Intro
Learn effective dish costing techniques, including food cost calculation, menu pricing, and recipe optimization to maximize restaurant profitability and minimize waste, with expert tips on cost control and culinary management.
The art of costing a dish effectively is a crucial aspect of the culinary world, as it directly impacts the profitability of a restaurant or food establishment. In today's competitive market, it is essential for chefs, restaurateurs, and food service providers to have a thorough understanding of the costs involved in creating a dish. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions about menu pricing, ingredient sourcing, and kitchen operations, ultimately affecting the bottom line of their business. Effective dish costing is not just about calculating the cost of ingredients, but also about considering labor costs, overheads, and other expenses that contribute to the overall cost of a dish.
As the culinary industry continues to evolve, the importance of accurate dish costing cannot be overstated. With the rise of food delivery services, meal kits, and online ordering platforms, restaurants and food establishments must be able to provide competitive pricing while maintaining profitability. Moreover, the increasing demand for sustainable and locally sourced ingredients, as well as the need to reduce food waste, requires a deeper understanding of the costs involved in creating a dish. By mastering the art of dish costing, food service providers can create menus that are not only delicious and appealing but also profitable and sustainable.
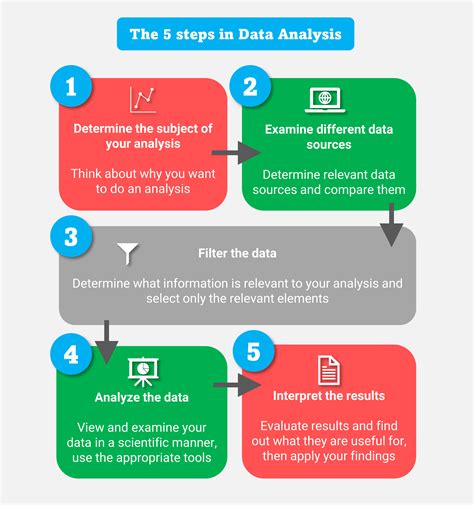
The process of costing a dish effectively involves several key steps, including calculating the cost of ingredients, determining labor costs, and considering overheads and other expenses. It also requires a deep understanding of the culinary industry, including market trends, consumer behavior, and the competitive landscape. By taking a holistic approach to dish costing, food service providers can create menus that are tailored to their target audience, while also ensuring profitability and sustainability. Whether you are a seasoned chef, a restaurateur, or a food service provider, understanding the art of costing a dish effectively is essential for success in the culinary world.
Understanding the Basics of Dish Costing
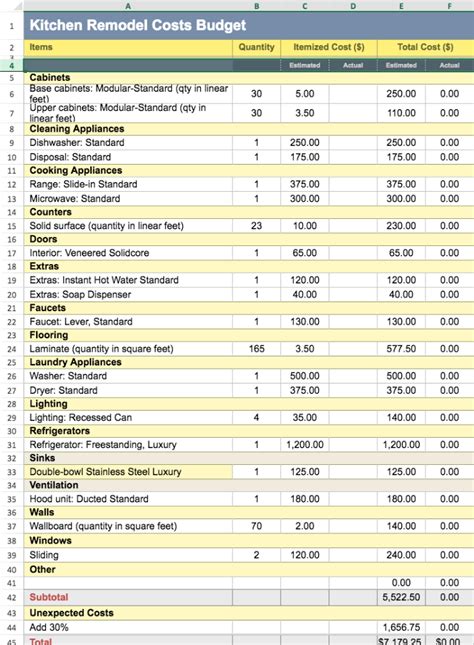
Calculating the Cost of Ingredients
Calculating the cost of ingredients is a critical step in the dish costing process. This involves determining the cost of each ingredient, including the cost of meat, produce, dairy, and pantry items. To calculate the cost of ingredients, chefs and restaurateurs can use a variety of methods, including the actual cost method, the standard cost method, and the ideal cost method. The actual cost method involves calculating the cost of ingredients based on the actual cost of the ingredients used, while the standard cost method involves calculating the cost of ingredients based on a standard cost per unit. The ideal cost method, on the other hand, involves calculating the cost of ingredients based on the ideal cost per unit, taking into account factors such as waste, spoilage, and overproduction.Determining Labor Costs

Considering Overheads and Other Expenses
Considering overheads and other expenses is also an essential step in the dish costing process. Overheads and other expenses include costs such as rent, utilities, marketing, and equipment, and can vary depending on the size and type of restaurant or food establishment. To consider overheads and other expenses, chefs and restaurateurs can use a variety of methods, including the absorption method and the allocation method. The absorption method involves allocating overheads and other expenses to each dish based on the cost of the dish, while the allocation method involves allocating overheads and other expenses to each dish based on the number of dishes sold.Menu Pricing Strategies
Creating a Profitable Menu
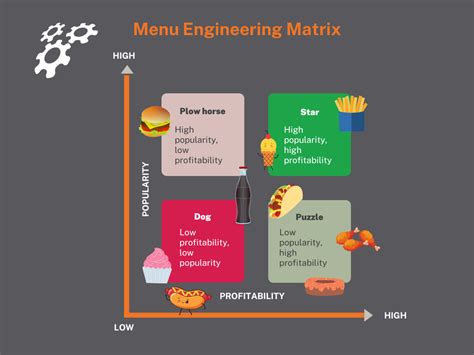
Creating a profitable menu is essential to the success of a restaurant or food establishment. By understanding the costs involved in creating a dish, chefs and restaurateurs can create menus that are not only delicious and appealing but also profitable. To create a profitable menu, chefs and restaurateurs can use a variety of techniques, including menu engineering, menu psychology, and menu pricing strategies. Menu engineering involves analyzing the menu to identify profitable and unprofitable dishes, while menu psychology involves using psychological techniques to influence customer purchasing decisions. Menu pricing strategies, on the other hand, involve using pricing techniques to maximize profitability and revenue.Sustainable and Locally Sourced Ingredients

Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste is essential to the success of a restaurant or food establishment. By reducing food waste, chefs and restaurateurs can minimize their environmental impact, reduce their costs, and create menus that are more sustainable and appealing to their target audience. To reduce food waste, chefs and restaurateurs can use a variety of techniques, including menu planning, inventory management, and food recovery. Menu planning involves planning menus that use ingredients that are in season and available, while inventory management involves managing inventory levels to minimize waste. Food recovery, on the other hand, involves recovering food that would otherwise be wasted and using it to create new dishes or donating it to those in need.Technology and Dish Costing

Using Data to Inform Menu Decisions
Using data to inform menu decisions is essential to the success of a restaurant or food establishment. By using data, chefs and restaurateurs can create menus that are more profitable, appealing, and sustainable. To use data to inform menu decisions, chefs and restaurateurs can use a variety of techniques, including data analysis, menu engineering, and customer feedback. Data analysis involves analyzing data to identify trends and patterns, while menu engineering involves using data to identify profitable and unprofitable dishes. Customer feedback, on the other hand, involves using customer feedback to inform menu decisions, including identifying dishes that are popular and unpopular.Dish Costing Image Gallery
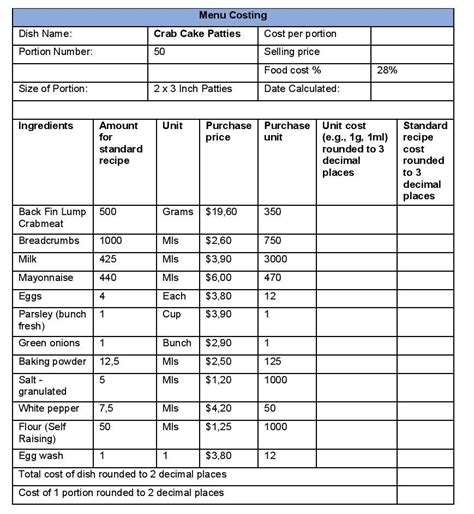






What is dish costing and why is it important?
+Dish costing is the process of calculating the cost of a dish, including the cost of ingredients, labor, and overheads. It is essential to the success of a restaurant or food establishment, as it enables chefs and restaurateurs to create menus that are profitable, appealing, and sustainable.
How do I calculate the cost of ingredients?
+To calculate the cost of ingredients, you can use a variety of methods, including the actual cost method, the standard cost method, and the ideal cost method. The actual cost method involves calculating the cost of ingredients based on the actual cost of the ingredients used, while the standard cost method involves calculating the cost of ingredients based on a standard cost per unit.
What are some common menu pricing strategies?
+There are several common menu pricing strategies, including the cost-plus method, the competitive pricing method, and the value-based pricing method. The cost-plus method involves adding a markup to the cost of the dish to determine the selling price, while the competitive pricing method involves pricing dishes based on the prices of similar dishes at competing restaurants.
How can I reduce food waste in my restaurant or food establishment?
+To reduce food waste, you can use a variety of techniques, including menu planning, inventory management, and food recovery. Menu planning involves planning menus that use ingredients that are in season and available, while inventory management involves managing inventory levels to minimize waste.
What role does technology play in dish costing?
+Technology plays a significant role in dish costing, as it enables chefs and restaurateurs to streamline their operations, reduce their costs, and create menus that are more profitable and appealing to their target audience. There are several technologies that can be used in dish costing, including recipe management software, inventory management software, and point-of-sale systems.
In
Final Thoughts

