Intro
Discover 5 ways to work with CSV in Excel, including import, export, and data management techniques, using formulas, pivot tables, and data analysis tools for efficient spreadsheet management and data visualization.
Importing and exporting data between CSV (Comma Separated Values) files and Excel is a common task for many users, given the widespread use of Excel for data analysis and the versatility of CSV files for data exchange. Excel, being a powerful spreadsheet program, offers several methods to work with CSV files, each with its own advantages. Understanding these methods can significantly enhance your productivity when dealing with data in both formats. Here's an overview of 5 ways to work with CSV files in Excel, including importing, exporting, and managing data efficiently.
The ability to easily move data between Excel and CSV is crucial for data analysis, reporting, and collaboration. CSV files are simple text files that contain tabular data, with each line representing a data record and each value separated by a comma. This format is widely supported by various applications and systems, making it an ideal choice for data exchange. Excel, with its robust data manipulation and analysis capabilities, is often the preferred tool for working with data from CSV files.
Excel's flexibility and the simplicity of CSV files make them a perfect pair for data management tasks. Whether you're importing data from a CSV file into Excel for analysis, exporting data from Excel to a CSV file for sharing, or simply managing and manipulating data, understanding the best practices and methods can streamline your workflow. This article delves into the specifics of working with CSV files in Excel, covering the basics of importing and exporting, as well as more advanced techniques for data manipulation and management.
Understanding CSV and Excel

Before diving into the methods of working with CSV files in Excel, it's essential to understand the basics of both formats. CSV files are plain text files that contain data separated by commas, making them easily readable by humans and machines. Excel, on the other hand, is a spreadsheet program that can store, organize, and analyze data. The compatibility between CSV and Excel allows for seamless data transfer, enabling users to leverage the strengths of both formats for their data management needs.
Importing CSV Files into Excel

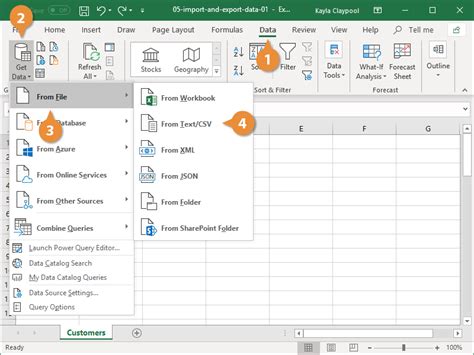
Importing a CSV file into Excel can be done in several ways, but one of the most straightforward methods is using the "Data" tab in Excel. By clicking on "From Text/CSV" and selecting your CSV file, Excel will guide you through the import process, allowing you to specify how the data should be imported, such as delimiter selection and data type specification for each column. This method provides a high degree of control over the import process, ensuring that your data is correctly formatted and ready for analysis.
Step-by-Step Import Guide
- Open Excel: Start by opening a new or existing Excel workbook.
- Navigate to the Data Tab: Click on the "Data" tab in the ribbon.
- Select From Text/CSV: Click on "From Text/CSV" in the "Get & Transform Data" group.
- Choose Your CSV File: Browse to the location of your CSV file and select it.
- Import: Follow the Text Import Wizard to specify how you want to import the file, including delimiter and data type settings.
- Load: Once the settings are configured, click "Load" to import the data into Excel.
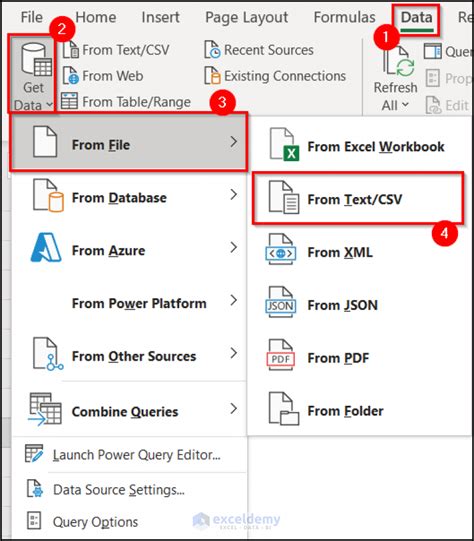
Exporting Excel Data to CSV
Exporting data from Excel to a CSV file is equally straightforward. By using the "Save As" option and selecting "CSV (Comma delimited)" as the file type, you can quickly export your Excel data into a format that's easily shared or imported into other applications. This method is useful for creating data backups, sharing data with others who may not have Excel, or preparing data for import into databases or other software systems.
Exporting Tips
- Select the Right Data: Ensure you've selected the data range you wish to export.
- Use Save As: Go to "File" > "Save As" and choose the location for your CSV file.
- Choose CSV Format: In the "Save as type" dropdown, select "CSV (Comma delimited)".
- Consider Settings: Depending on your Excel version, you might have options to adjust settings like the delimiter used in the CSV file.
Working with Large CSV Files
Large CSV files can pose challenges due to their size, which can exceed Excel's capacity or slow down the import process. For such files, using the Power Query feature in Excel can be beneficial. Power Query allows you to connect to a CSV file, select the data you need, and then load it into Excel, providing a more efficient way to handle large datasets.
Power Query Basics
- Access Power Query: Go to the "Data" tab and click on "From Text/CSV" or use "New Query" to access Power Query.
- Connect to CSV: Select your CSV file and follow the prompts to connect to it.
- Transform Data: Use Power Query's tools to filter, sort, and transform your data as needed.
- Load Data: Once your data is prepared, click "Load" to bring it into Excel.
Advanced Data Management

For more advanced data management tasks, such as merging data from multiple CSV files, performing complex data analysis, or automating repetitive tasks, Excel's built-in functions and add-ins like Power Query, Power Pivot, and VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) can be incredibly powerful. These tools allow you to manipulate data in sophisticated ways, create interactive dashboards, and automate workflows, significantly enhancing your productivity and the insights you can derive from your data.
Advanced Techniques
- Use Power Query for Merging: Combine data from multiple CSV files using Power Query's merge feature.
- Leverage VBA for Automation: Write macros to automate repetitive tasks, such as data import and formatting.
- Power Pivot for Analysis: Use Power Pivot to create data models that enable advanced analysis and reporting.
Gallery of CSV and Excel Images
CSV and Excel Image Gallery
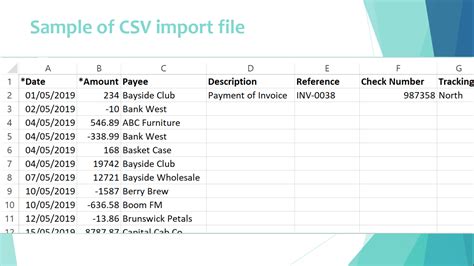
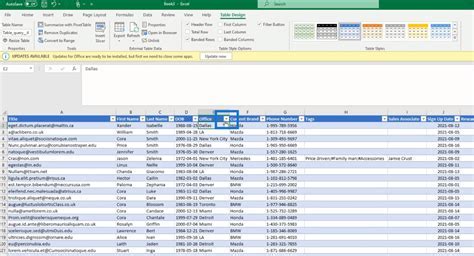

Frequently Asked Questions
How do I import a CSV file into Excel?
+To import a CSV file, go to the "Data" tab, click "From Text/CSV", select your file, and follow the import wizard.
Can I export Excel data to a CSV file?
+Yes, you can export Excel data to a CSV file by using the "Save As" option and selecting "CSV (Comma delimited)" as the file type.
What is Power Query and how does it help with CSV files?
+Power Query is a feature in Excel that allows you to connect to, manipulate, and load data from various sources, including CSV files, enabling efficient data management and analysis.
In conclusion, working with CSV files in Excel is a fundamental skill for anyone involved in data analysis, management, or exchange. By understanding the various methods of importing and exporting CSV files, leveraging advanced tools like Power Query, and mastering techniques for data manipulation and analysis, you can significantly enhance your productivity and the insights you derive from your data. Whether you're dealing with small datasets or large, complex files, Excel's flexibility and the simplicity of CSV files make them an indispensable combination for data management tasks. We invite you to share your experiences, tips, and questions about working with CSV files in Excel, and to explore how these skills can be applied to real-world scenarios to drive better decision-making and outcomes.
