Intro
Manage diverticulitis symptoms with a tailored diet. Discover 7 expert-backed diverticulitis diet tips, including low-fiber foods, gut-friendly nutrition, and digestive health strategies to alleviate pain and prevent flare-ups.
Diverticulitis is a gastrointestinal condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. While there is no cure for diverticulitis, a well-planned diet can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore seven diverticulitis diet tips that can help individuals with this condition navigate their dietary needs and make informed choices.
The importance of a diverticulitis-friendly diet cannot be overstated. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups, while a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can exacerbate the condition. By understanding the role of diet in managing diverticulitis, individuals can take control of their health and make positive changes to their lifestyle.
A well-planned diverticulitis diet should be tailored to an individual's specific needs and health status. For example, some people may need to follow a low-fiber diet during acute flare-ups, while others may require a high-fiber diet to help regulate bowel movements. By working with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian, individuals can develop a personalized diet plan that meets their unique needs and promotes overall health and well-being.
Understanding Diverticulitis
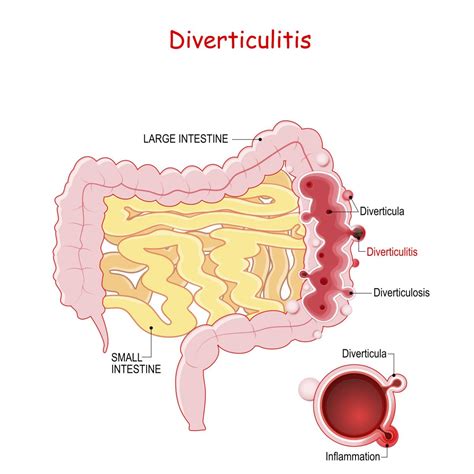
Factors That Contribute to Diverticulitis
Several factors can contribute to the development of diverticulitis, including: * A low-fiber diet * Obesity * Lack of physical activity * Age (diverticulitis is more common in people over 40) * Family history * Certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)Dietary Recommendations for Diverticulitis
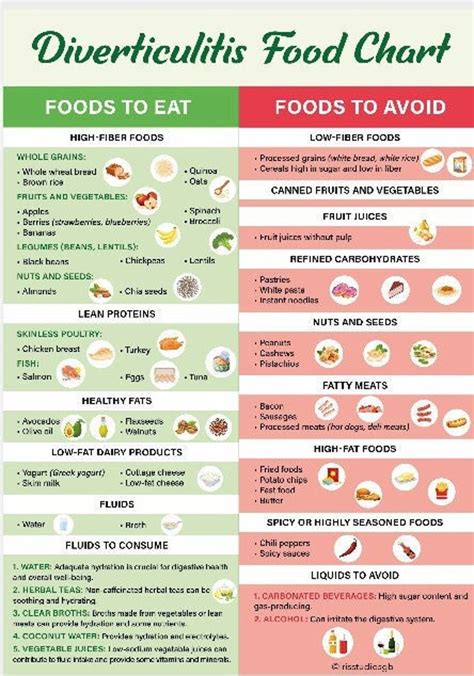
Foods to Eat and Avoid
The following foods can help alleviate diverticulitis symptoms: * Fruits: berries, citrus fruits, apples, and bananas * Vegetables: leafy greens, broccoli, bell peppers, and carrots * Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and whole grain pasta * Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans * Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, fish, and tofu Foods to avoid or limit include: * Processed meats: hot dogs, sausages, and bacon * Fried foods: french fries, fried chicken, and doughnuts * High-sugar foods: candy, cookies, and cakes * Dairy products: milk, cheese, and ice cream (for some individuals with lactose intolerance)7 Diverticulitis Diet Tips

Additional Tips for Managing Diverticulitis
In addition to following a diverticulitis-friendly diet, the following tips can help manage symptoms and prevent complications: * Exercise regularly: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress, promote regular bowel movements, and improve overall health. * Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. * Get enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can help reduce stress and promote healing.Gallery of Diverticulitis Diet Foods
Diverticulitis Diet Foods Gallery


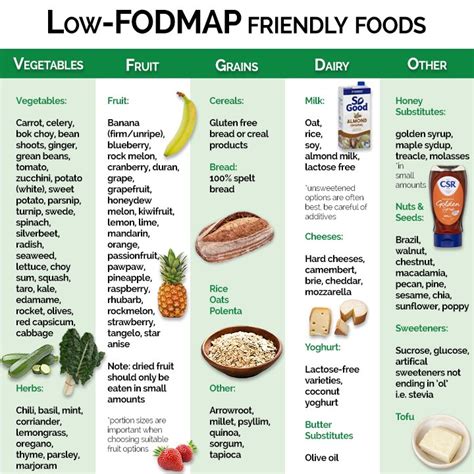
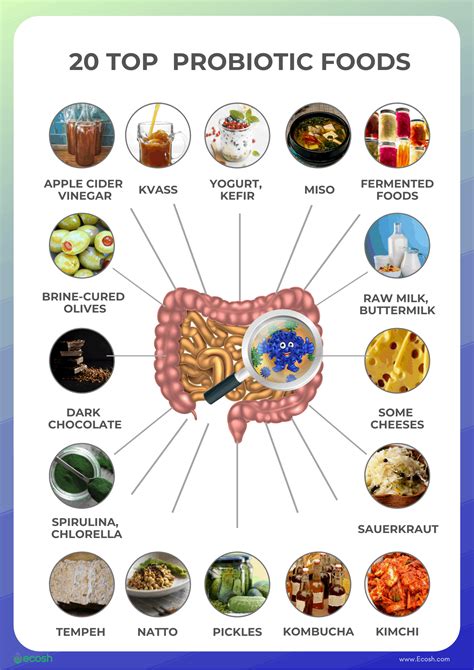






Frequently Asked Questions
What is diverticulitis?
+Diverticulitis is a gastrointestinal condition characterized by the formation of small, bulging pouches (diverticula) in the digestive tract, typically in the colon.
What are the symptoms of diverticulitis?
+Symptoms of diverticulitis may include abdominal pain, bloating, changes in bowel habits, and fever.
How can I manage diverticulitis symptoms through diet?
+A well-planned diet that is high in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can help manage diverticulitis symptoms. Avoiding trigger foods, staying hydrated, and incorporating probiotics can also help alleviate symptoms.
Can diverticulitis be prevented?
+While diverticulitis cannot be completely prevented, a healthy diet and lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing the condition. Eating a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly can help promote overall health and reduce the risk of diverticulitis.
What are the complications of diverticulitis?
+Complications of diverticulitis may include abscesses, perforation, and peritonitis. In severe cases, diverticulitis can lead to life-threatening complications, such as sepsis and organ failure.
In conclusion, a well-planned diverticulitis diet can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall quality of life. By following the seven diverticulitis diet tips outlined in this article and incorporating a healthy lifestyle, individuals with diverticulitis can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing diverticulitis symptoms through diet and lifestyle changes. By working together, we can promote awareness and understanding of this condition and help individuals with diverticulitis live healthy, fulfilling lives.
