Intro
Master General Ledger Accounting Basics with our guide, covering ledger accounts, journal entries, and financial reporting, to streamline accounting processes and ensure accurate financial statements.
The world of accounting can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those who are new to the field. However, understanding the basics of general ledger accounting is essential for any business or individual looking to manage their finances effectively. In this article, we will delve into the world of general ledger accounting, exploring its importance, key components, and practical applications. Whether you are a seasoned accountant or just starting out, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of general ledger accounting basics.
General ledger accounting is the foundation of any accounting system, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of all financial transactions. It is a centralized ledger that contains all the accounts of a business, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. The general ledger is used to prepare financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, which provide stakeholders with a clear picture of a company's financial health. By understanding general ledger accounting basics, businesses can make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
The importance of general ledger accounting cannot be overstated. It provides a transparent and accurate record of all financial transactions, enabling businesses to track their financial performance, identify trends, and make predictions about future financial outcomes. General ledger accounting also helps businesses to manage their cash flow, reduce errors, and prevent fraud. Furthermore, it provides a framework for financial reporting, enabling businesses to communicate their financial position to stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
Introduction to General Ledger Accounting
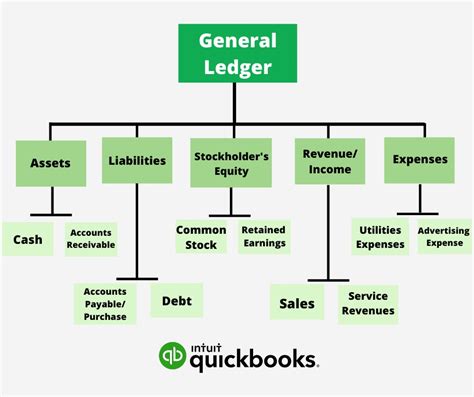
General ledger accounting involves the use of a chart of accounts, which is a list of all the accounts used by a business to record financial transactions. The chart of accounts is typically organized into categories, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. Each account has a unique account number and name, making it easy to identify and track. The general ledger also includes a journal, which is a record of all financial transactions, including debits and credits. The journal is used to record transactions as they occur, and the information is then posted to the general ledger.
Key Components of General Ledger Accounting
The key components of general ledger accounting include: * Chart of accounts: A list of all the accounts used by a business to record financial transactions. * General ledger: A centralized ledger that contains all the accounts of a business. * Journal: A record of all financial transactions, including debits and credits. * Debits and credits: The basic elements of accounting, used to record financial transactions. * Financial statements: The balance sheet and income statement, which provide stakeholders with a clear picture of a company's financial health.Understanding Debits and Credits
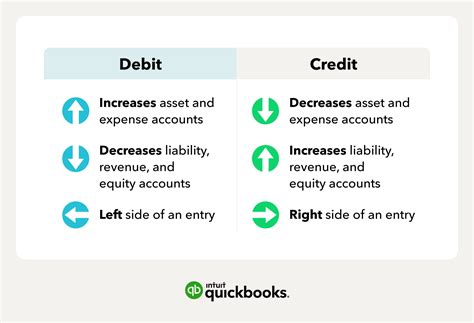
Debits and credits are the basic elements of accounting, used to record financial transactions. A debit is an entry that increases an asset account or decreases a liability or equity account. A credit is an entry that decreases an asset account or increases a liability or equity account. The accounting equation, assets = liabilities + equity, is used to ensure that debits and credits are balanced. For every debit entry, there must be a corresponding credit entry, and vice versa. Understanding debits and credits is essential for accurate financial recording and reporting.
Types of Accounts in General Ledger Accounting
There are several types of accounts in general ledger accounting, including: * Asset accounts: Accounts that represent the resources owned or controlled by a business, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. * Liability accounts: Accounts that represent the debts or obligations of a business, such as accounts payable and loans payable. * Equity accounts: Accounts that represent the ownership interest in a business, such as common stock and retained earnings. * Revenue accounts: Accounts that represent the income earned by a business, such as sales and service revenue. * Expense accounts: Accounts that represent the costs incurred by a business, such as salaries and wages, rent, and utilities.Preparing Financial Statements
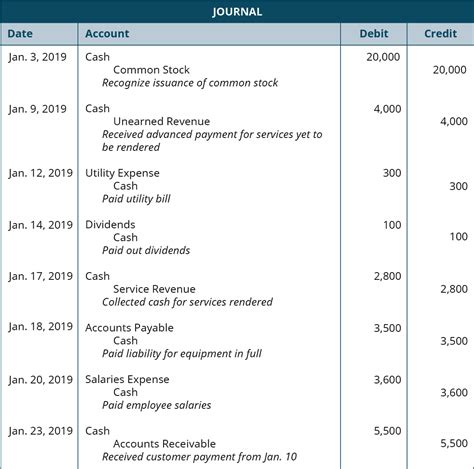
Financial statements are the end product of general ledger accounting, providing stakeholders with a clear picture of a company's financial health. The two main financial statements are the balance sheet and the income statement. The balance sheet presents a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific point in time, including its assets, liabilities, and equity. The income statement presents a summary of a company's revenues and expenses over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. Other financial statements, such as the statement of cash flows and the statement of changes in equity, provide additional information about a company's financial performance.
Best Practices for General Ledger Accounting
To ensure accurate and effective general ledger accounting, businesses should follow best practices, such as: * Regularly reviewing and reconciling accounts to ensure accuracy and completeness. * Using a standardized chart of accounts to ensure consistency and comparability. * Implementing internal controls to prevent errors and fraud. * Providing ongoing training and support to accounting staff to ensure they are knowledgeable and skilled. * Using technology, such as accounting software, to streamline and automate accounting processes.Common Challenges in General Ledger Accounting

Despite its importance, general ledger accounting can be challenging, especially for small businesses or those with limited accounting expertise. Common challenges include:
- Inaccurate or incomplete financial recording and reporting.
- Insufficient internal controls, leading to errors and fraud.
- Inadequate training and support for accounting staff.
- Inefficient use of technology, leading to manual errors and wasted time.
- Non-compliance with regulatory requirements, leading to penalties and fines.
Solutions to Common Challenges
To overcome common challenges in general ledger accounting, businesses can: * Implement a standardized chart of accounts and accounting procedures. * Provide ongoing training and support to accounting staff. * Use technology, such as accounting software, to streamline and automate accounting processes. * Regularly review and reconcile accounts to ensure accuracy and completeness. * Implement internal controls to prevent errors and fraud.Future of General Ledger Accounting
The future of general ledger accounting is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing. These technologies have the potential to automate and streamline accounting processes, improve accuracy and efficiency, and provide real-time financial insights. Additionally, the increasing demand for sustainability and social responsibility reporting is likely to drive the development of new accounting standards and practices.
Emerging Trends in General Ledger Accounting
Emerging trends in general ledger accounting include: * The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate accounting processes. * The adoption of blockchain technology to improve the security and transparency of financial transactions. * The increasing use of cloud computing to provide real-time financial insights and improve collaboration. * The development of new accounting standards and practices to support sustainability and social responsibility reporting.General Ledger Accounting Image Gallery









What is general ledger accounting?
+General ledger accounting is the foundation of any accounting system, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of all financial transactions.
What are the key components of general ledger accounting?
+The key components of general ledger accounting include the chart of accounts, general ledger, journal, debits and credits, and financial statements.
What are the benefits of general ledger accounting?
+The benefits of general ledger accounting include accurate and efficient financial recording and reporting, improved decision-making, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
How can businesses overcome common challenges in general ledger accounting?
+Businesses can overcome common challenges in general ledger accounting by implementing a standardized chart of accounts and accounting procedures, providing ongoing training and support to accounting staff, and using technology to streamline and automate accounting processes.
What is the future of general ledger accounting?
+The future of general ledger accounting is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing, which will automate and streamline accounting processes, improve accuracy and efficiency, and provide real-time financial insights.
In conclusion, general ledger accounting is a critical component of any accounting system, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of all financial transactions. By understanding general ledger accounting basics, businesses can make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. As technology continues to evolve, the future of general ledger accounting is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with general ledger accounting in the comments below, and to explore the resources and tools available to support their accounting needs. Whether you are a seasoned accountant or just starting out, we hope this article has provided a valuable introduction to the world of general ledger accounting.
