Intro
Discover the GI Food Chart Printable, a valuable resource for managing blood sugar with glycemic index, glucose control, and healthy eating guides, perfect for diet planning and nutrition management.
The importance of maintaining a healthy diet cannot be overstated, and one key aspect of achieving this is understanding the glycemic index (GI) of various foods. The GI is a measure of how quickly the carbohydrates in a particular food raise blood sugar levels after consumption. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, while those with a low GI result in a more gradual increase. For individuals managing conditions like diabetes, or for those simply looking to maintain optimal health, a GI food chart can be an invaluable tool. This article will delve into the details of the GI food chart, its benefits, how it works, and provide practical examples to help readers make informed dietary choices.
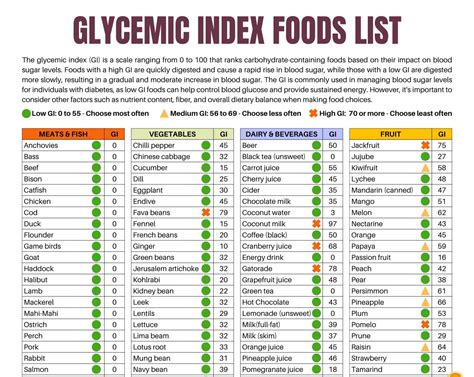
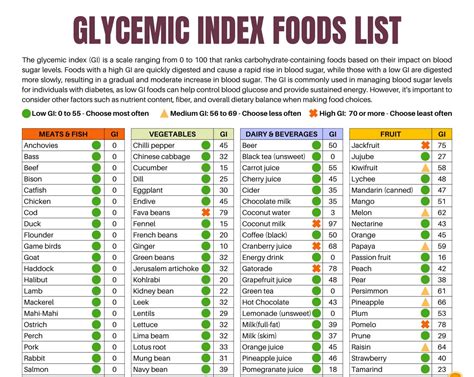
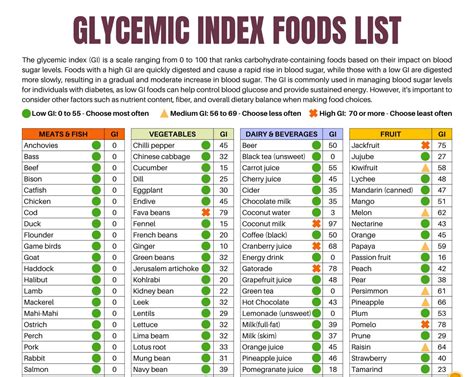
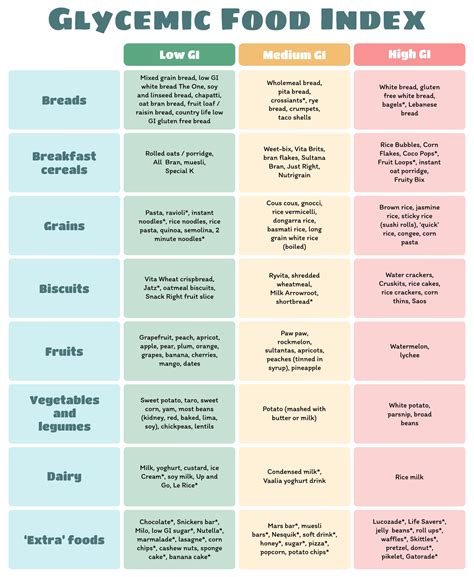
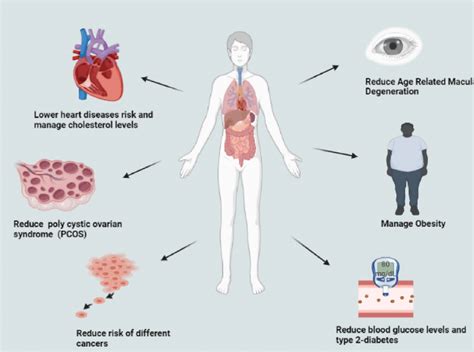
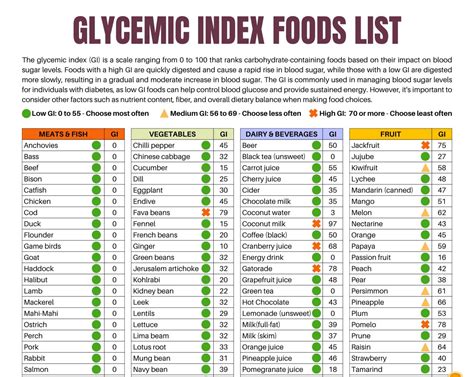
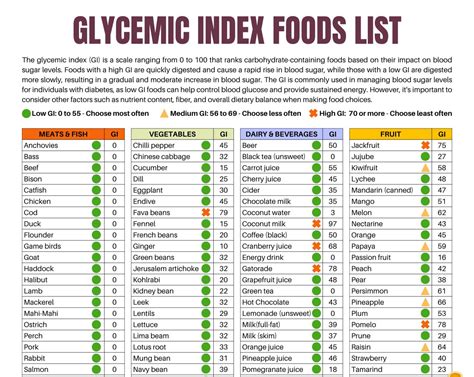
Understanding the GI scale is crucial. It ranks foods from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. Foods are categorized as low GI (0-55), medium GI (56-69), and high GI (70 and above). A low GI diet has been associated with numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar control, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. By incorporating a GI food chart into meal planning, individuals can make conscious decisions about the foods they eat, aiming to balance their diet with a variety of low to medium GI foods.
The working mechanism of the GI is relatively straightforward. When carbohydrates are digested, they are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The speed at which this occurs varies significantly between different types of carbohydrates. For instance, white bread and sugary snacks have a high GI because they are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to a rapid increase in blood glucose levels. On the other hand, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables tend to have a lower GI due to their higher fiber content, which slows down digestion and absorption, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar.
Benefits of Using a GI Food Chart
Steps to Implement a GI Diet
To start benefiting from a GI diet, follow these simple steps: - **Identify Low GI Foods**: Familiarize yourself with the GI values of common foods. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. - **Plan Your Meals**: Use a GI food chart to plan your meals. Aim for a balance of low to medium GI foods at each meal. - **Read Labels**: When purchasing packaged foods, check the ingredient list and nutrition label for added sugars and refined carbohydrates, which are typically high in GI. - **Cook at Home**: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and cooking methods, making it easier to maintain a low GI diet.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Key Foods and Their GI Values
Here are some common foods and their GI values: - **Bread**: White bread (70-80), whole wheat bread (30-40) - **Fruits**: Apple (38), banana (51), orange (40) - **Vegetables**: Broccoli (10), carrot (41), potato (70-110) - **Grains**: Brown rice (50), quinoa (35), white rice (80)Challenges and Considerations
Tips for Overcoming Challenges
- **Start Slow**: Gradually introduce low GI foods into your diet to give yourself time to adjust. - **Explore Recipes**: Find recipes that incorporate low GI ingredients to keep meals interesting and varied. - **Consult a Professional**: For personalized advice, consider consulting a dietitian or nutritionist who can help tailor a GI diet to your specific needs and preferences.Conclusion and Future Directions

Gallery of GI Food Chart Examples
GI Food Chart Image Gallery





What is the glycemic index, and how does it affect my diet?
+The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. Choosing foods with a low GI can help manage blood sugar levels, aid in weight loss, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
How can I incorporate a GI food chart into my daily meal planning?
+Start by identifying low GI foods and planning your meals around them. Use a GI food chart to guide your choices, and consider consulting a dietitian or nutritionist for personalized advice. Gradually introduce low GI foods into your diet, and explore recipes to keep meals interesting and varied.
What are some common low GI foods that I can easily incorporate into my diet?
+Common low GI foods include whole grains like brown rice and quinoa, most fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Examples of specific foods and their GI values include apples (38), broccoli (10), and whole wheat bread (30-40). Incorporating these foods into your meals can help you maintain a balanced and healthy diet.
We invite you to share your experiences with incorporating a GI food chart into your diet, and to ask any questions you may have about getting started. Whether you're looking to manage a health condition or simply want to improve your overall well-being, the journey towards a healthier you begins with informed choices about the foods you eat. Share this article with friends and family who might benefit from learning more about the glycemic index and its role in a healthy diet. Together, let's take the first steps towards a healthier, happier life.
