Intro
Master blood sugar control with our Glycemic Food List Printable Guide, featuring low GI foods, carbohydrate tracking, and healthy meal planning for diabetes management and weight loss.
The concept of glycemic index has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly among individuals who are mindful of their dietary choices and their impact on health. Understanding the glycemic index of foods can be a powerful tool for managing blood sugar levels, improving overall health, and even supporting weight management. For those looking to make informed decisions about their diet, having a glycemic food list printable guide can be incredibly valuable. This guide can serve as a quick reference, helping individuals choose foods that fit within their dietary goals and preferences.
The importance of managing blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. High blood sugar can lead to a range of health issues, including diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. By choosing foods that are low on the glycemic index, individuals can help regulate their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of these and other health problems. Furthermore, a diet rich in low-glycemic foods can provide sustained energy, improve mood, and support overall well-being.
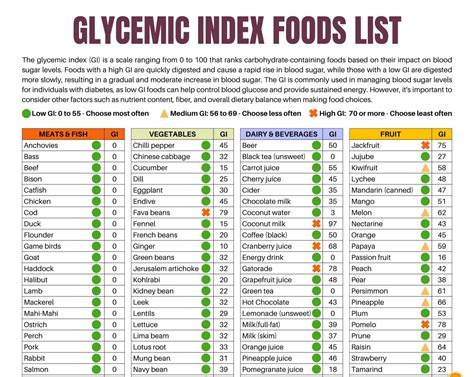
For those new to the concept of glycemic index, it's essential to understand that it's a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) are quickly digested and absorbed, causing a rapid increase in blood sugar. In contrast, foods with a low GI are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar. Knowing the GI of common foods can help individuals make better choices, whether they're aiming to manage a health condition or simply improve their diet.
Introduction to Glycemic Index
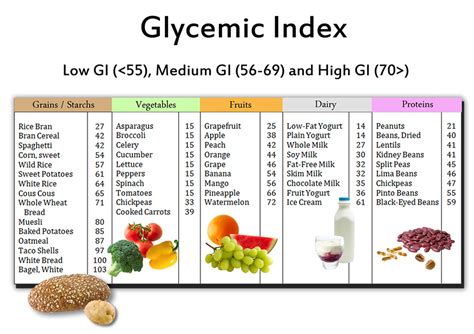
Understanding the glycemic index is the first step in using it as a tool for dietary management. The GI is not just about the type of carbohydrate in a food but also about how that carbohydrate is structured and how it's prepared. For example, whole, unprocessed foods tend to have a lower GI than processed foods. This is because processing can break down the natural barriers to carbohydrate digestion, making the carbs more readily available and thus increasing the food's GI.
Benefits of a Low-Glycemic Diet
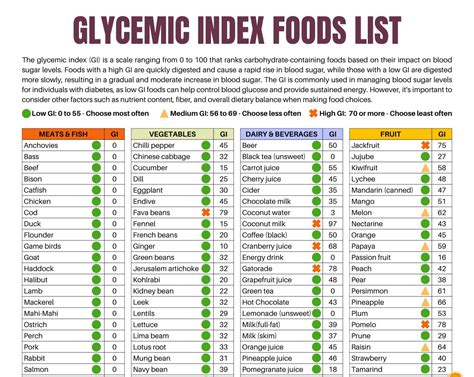
Adopting a low-glycemic diet can have numerous health benefits. It can help regulate blood sugar levels, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. A low-glycemic diet can also aid in weight management. By choosing foods that are digested slowly, individuals can feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Additionally, low-glycemic diets tend to be rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and low in unhealthy fats and added sugars, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Key Components of a Low-Glycemic Diet
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains over refined or processed grains. Whole grains have a lower GI and are richer in fiber and nutrients.
- Vegetables: Most vegetables are low in carbohydrates and have a minimal effect on blood sugar. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Fruits: While fruits are natural sources of sugar, many have a low to moderate GI. Portion control is key, as larger servings can significantly impact blood sugar.
- Proteins and Fats: Foods high in protein and fat, such as meats, poultry, fish, eggs, nuts, and seeds, have little to no effect on blood sugar levels.
Creating a Glycemic Food List Printable Guide
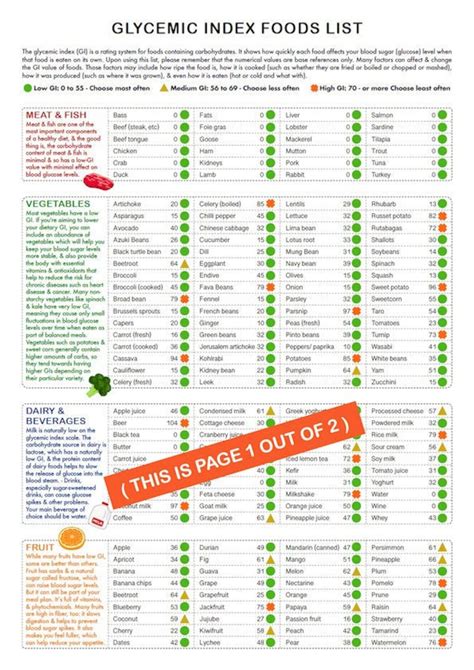
Creating a personalized glycemic food list printable guide involves researching the GI of various foods and organizing them in a way that's easy to reference. Here are some steps to follow:
- Research GI Values: Look up the GI values of common foods. There are many online resources and books that provide comprehensive lists of foods and their GI values.
- Categorize Foods: Divide foods into categories (e.g., grains, vegetables, fruits, proteins) to make the list more manageable.
- Include Portion Sizes: The GI of a food can vary based on the portion size. Include standard serving sizes to help with meal planning.
- Consider Meal Ideas: Include some meal ideas or combinations of foods that are low in GI to help with planning.
Sample Glycemic Food List
- Grains:
- Whole wheat bread (GI: 30-40)
- Brown rice (GI: 50)
- Quinoa (GI: 35)
- Vegetables:
- Broccoli (GI: 10)
- Carrots (GI: 41)
- Spinach (GI: 1)
- Fruits:
- Apple (GI: 38)
- Banana (GI: 51)
- Berries (GI: 32)
Practical Applications of a Glycemic Food List

Having a glycemic food list can be incredibly practical for daily meal planning. It can help individuals make informed choices at the grocery store, reduce the risk of spikes in blood sugar, and contribute to a balanced diet. For those with specific dietary needs or restrictions, such as diabetes, a glycemic food list can be particularly valuable, serving as a guide for managing blood sugar levels through diet.
Tips for Using Your Glycemic Food List
- Plan Ahead: Use your list to plan meals for the week, ensuring you have low-GI foods on hand.
- Read Labels: When shopping, read food labels to identify added sugars and refined carbohydrates, which can increase a food's GI.
- Be Mindful of Portion Sizes: Even low-GI foods can cause a spike in blood sugar if consumed in large quantities.
Gallery of Glycemic Index Foods
Glycemic Index Foods Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the glycemic index?
+The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels.
Why is it important to manage blood sugar levels?
+Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing health issues like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
How can I use a glycemic food list?
+You can use a glycemic food list to plan meals, make informed grocery choices, and manage blood sugar levels through dietary choices.
In conclusion, having a glycemic food list printable guide can be a valuable tool for anyone looking to manage their blood sugar levels, improve their diet, and enhance their overall health. By understanding the glycemic index of foods and making informed choices, individuals can take a proactive approach to their health and well-being. We invite you to share your experiences with using glycemic food lists, ask questions, or provide tips on how you incorporate the glycemic index into your dietary planning. Together, we can support each other in making healthier, more informed choices.
