Intro
Learn 5 essential inventory ratio formulas to optimize stock levels, including turnover, days inventory outstanding, and more, to improve supply chain management and inventory control with key performance indicators.
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business, particularly those in the retail, manufacturing, and distribution sectors. Effective inventory management helps companies to minimize costs, maximize profits, and ensure that they have the right products in stock to meet customer demand. One way to measure the effectiveness of inventory management is by using inventory ratio formulas. These formulas provide insights into various aspects of inventory management, such as inventory turnover, inventory levels, and the efficiency of inventory management. In this article, we will explore five essential inventory ratio formulas that businesses can use to optimize their inventory management.
Inventory management involves balancing the need to have enough inventory on hand to meet customer demand with the need to minimize inventory costs. Inventory costs can be significant, and they include the cost of purchasing or producing inventory, storing and handling inventory, and the cost of inventory that becomes obsolete or is damaged. By using inventory ratio formulas, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their inventory management.
Inventory ratio formulas are useful tools for businesses to evaluate their inventory management performance. These formulas help businesses to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in their inventory management. By analyzing inventory ratios, businesses can determine whether they are holding too much or too little inventory, whether their inventory is turning over quickly enough, and whether their inventory management practices are efficient. In the following sections, we will delve into five essential inventory ratio formulas that businesses can use to optimize their inventory management.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
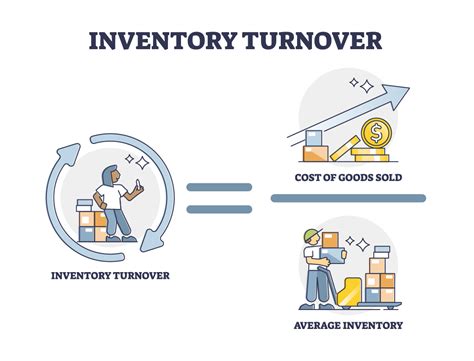
To calculate the inventory turnover ratio, businesses can use the following formula: Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory For example, if a business has a cost of goods sold of $100,000 and an average inventory level of $20,000, its inventory turnover ratio would be 5. This means that the business sells and replaces its inventory five times per year.
Inventory Days Ratio
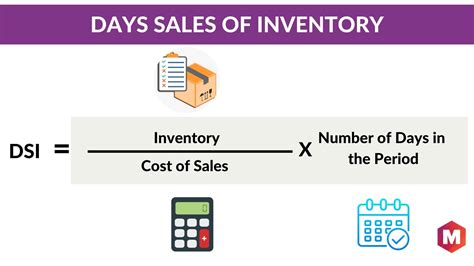
To calculate the inventory days ratio, businesses can use the following formula: Inventory Days Ratio = Average Inventory / (Cost of Goods Sold / 365) For example, if a business has an average inventory level of $20,000 and a cost of goods sold of $100,000 per year, its inventory days ratio would be 73 days. This means that the business takes an average of 73 days to sell its inventory.
Inventory to Sales Ratio

To calculate the inventory to sales ratio, businesses can use the following formula: Inventory to Sales Ratio = Average Inventory / Average Daily Sales For example, if a business has an average inventory level of $20,000 and an average daily sales of $1,000, its inventory to sales ratio would be 20. This means that the business is holding 20 days' worth of inventory in relation to its sales.
Gross Margin Return on Inventory (GMROI) Ratio

To calculate the GMROI ratio, businesses can use the following formula: GMROI Ratio = Gross Margin / Average Inventory For example, if a business has a gross margin of $50,000 and an average inventory level of $20,000, its GMROI ratio would be 2.5. This means that the business is generating $2.50 in gross margin for every dollar of inventory it holds.
Inventory Obsolete Ratio
To calculate the inventory obsolete ratio, businesses can use the following formula: Inventory Obsolete Ratio = Value of Obsolete Inventory / Total Inventory Value For example, if a business has a value of obsolete inventory of $5,000 and a total inventory value of $50,000, its inventory obsolete ratio would be 0.10 or 10%. This means that 10% of the business's inventory is obsolete and no longer saleable.
Gallery of Inventory Management
Inventory Management Image Gallery




What is the purpose of inventory ratio formulas?
+The purpose of inventory ratio formulas is to measure the effectiveness of inventory management and identify areas for improvement.
How do I calculate the inventory turnover ratio?
+To calculate the inventory turnover ratio, divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory level.
What is the difference between the inventory days ratio and the inventory turnover ratio?
+The inventory days ratio measures the average number of days that inventory remains in stock, while the inventory turnover ratio measures how quickly a business sells and replaces its inventory.
How can I use inventory ratio formulas to improve my inventory management?
+By analyzing inventory ratios, you can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in your inventory management, and make data-driven decisions to optimize your inventory management practices.
What are some common inventory management challenges that businesses face?
+Common inventory management challenges include inventory obsolescence, stockouts, overstocking, and inefficient inventory tracking and management systems.
In conclusion, inventory ratio formulas are essential tools for businesses to evaluate their inventory management performance and identify areas for improvement. By using these formulas, businesses can optimize their inventory management practices, reduce costs, and improve profitability. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the five essential inventory ratio formulas and how to use them to improve your inventory management. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from it.
