Intro
Learn about Inventory Turnover Ratio, a key metric for measuring stock efficiency, including calculation, analysis, and optimization techniques for effective inventory management and supply chain control.
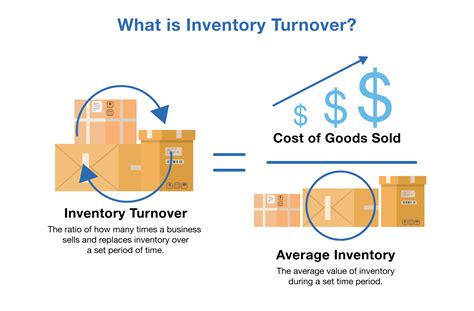
The inventory turnover ratio is a crucial metric in the business world, particularly for companies that deal with physical products. It measures the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period, typically a year. This ratio is essential for businesses to evaluate their inventory management efficiency, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about production, pricing, and inventory levels. In this article, we will delve into the world of inventory turnover, exploring its importance, calculation, and interpretation, as well as providing practical examples and tips for improvement.
The inventory turnover ratio is a key performance indicator (KPI) that helps businesses assess their ability to manage inventory levels, reduce waste, and optimize production. A high inventory turnover ratio indicates that a company is selling and replacing its inventory quickly, which can be beneficial in several ways. For instance, it can help reduce storage costs, minimize the risk of inventory becoming obsolete, and improve cash flow. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover ratio may suggest that a company is holding onto inventory for too long, which can lead to increased storage costs, waste, and reduced profitability.
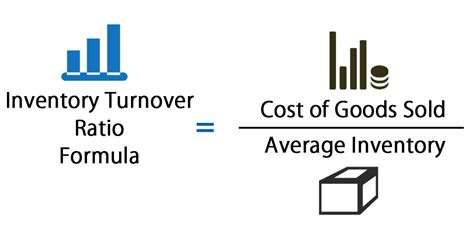
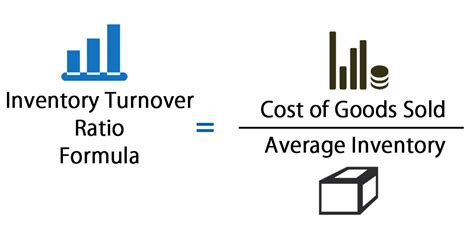
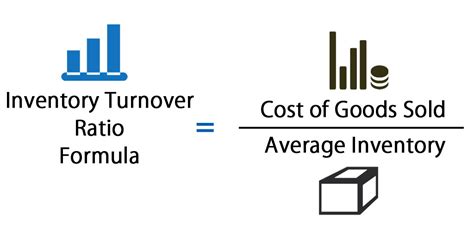
To calculate the inventory turnover ratio, businesses need to divide the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value. The COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing and selling a company's products, while the average inventory value is the total value of inventory held by the company during a given period. The formula for calculating the inventory turnover ratio is: Inventory Turnover Ratio = COGS / Average Inventory Value. For example, if a company has a COGS of $100,000 and an average inventory value of $20,000, its inventory turnover ratio would be 5, indicating that it sells and replaces its inventory five times a year.
Understanding Inventory Turnover Ratio
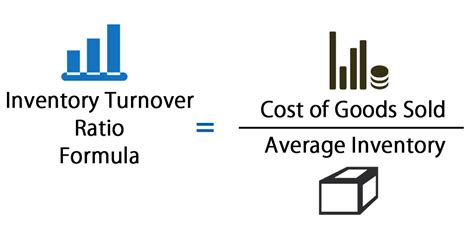
Understanding the inventory turnover ratio is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their inventory management strategies. A high inventory turnover ratio can be beneficial, but it can also indicate that a company is not holding enough inventory to meet demand. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover ratio may suggest that a company is holding too much inventory, which can lead to waste and reduced profitability. To interpret the inventory turnover ratio effectively, businesses need to consider several factors, including industry benchmarks, market trends, and their own operational efficiency.
Importance of Inventory Turnover Ratio
The inventory turnover ratio is essential for businesses to evaluate their inventory management efficiency and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing the inventory turnover ratio, companies can determine whether they are holding too much or too little inventory, which can help them optimize production, reduce waste, and improve cash flow. Additionally, the inventory turnover ratio can help businesses assess their pricing strategies, as a high inventory turnover ratio may indicate that prices are too low, while a low inventory turnover ratio may suggest that prices are too high.
Calculating Inventory Turnover Ratio
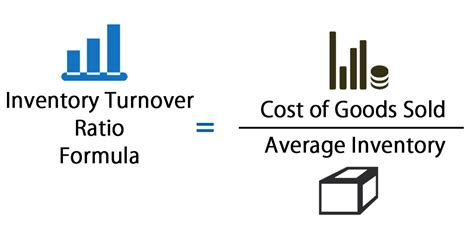
Calculating the inventory turnover ratio is a straightforward process that involves dividing the COGS by the average inventory value. However, businesses need to ensure that they are using accurate and up-to-date data to calculate the ratio. Additionally, companies should consider using weighted average inventory values to account for changes in inventory levels over time. By using the correct calculation method and accurate data, businesses can obtain a reliable inventory turnover ratio that reflects their inventory management efficiency.
Interpreting Inventory Turnover Ratio
Interpreting the inventory turnover ratio requires careful consideration of several factors, including industry benchmarks, market trends, and operational efficiency. A high inventory turnover ratio may indicate that a company is selling and replacing its inventory quickly, but it can also suggest that the company is not holding enough inventory to meet demand. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover ratio may indicate that a company is holding too much inventory, which can lead to waste and reduced profitability. By analyzing the inventory turnover ratio in conjunction with other metrics, such as gross margin and cash flow, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their inventory management efficiency.
Improving Inventory Turnover Ratio

Improving the inventory turnover ratio requires a combination of strategies, including optimizing production, reducing waste, and improving cash flow. Businesses can achieve this by implementing just-in-time (JIT) production, which involves producing and delivering products just in time to meet customer demand. Additionally, companies can reduce waste by implementing lean manufacturing techniques, such as kaizen and total productive maintenance (TPM). By improving the inventory turnover ratio, businesses can reduce storage costs, minimize the risk of inventory becoming obsolete, and improve profitability.
Inventory Turnover Ratio and Industry Benchmarks

The inventory turnover ratio can vary significantly across industries, and businesses should compare their ratio to industry benchmarks to assess their performance. For example, the inventory turnover ratio for the retail industry may be higher than that of the manufacturing industry, due to the faster turnover of inventory in retail. By comparing their inventory turnover ratio to industry benchmarks, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to optimize their inventory management.
Common Mistakes in Inventory Turnover Ratio Calculation

Calculating the inventory turnover ratio can be prone to errors, and businesses should be aware of common mistakes to avoid. One common mistake is using incorrect or outdated data, which can result in an inaccurate inventory turnover ratio. Additionally, businesses may fail to account for changes in inventory levels over time, which can affect the accuracy of the ratio. By using accurate and up-to-date data, and considering weighted average inventory values, businesses can avoid common mistakes and obtain a reliable inventory turnover ratio.
Inventory Turnover Ratio and Cash Flow

The inventory turnover ratio is closely linked to cash flow, as a high inventory turnover ratio can improve cash flow by reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of inventory becoming obsolete. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover ratio can reduce cash flow by increasing storage costs and reducing profitability. By analyzing the inventory turnover ratio in conjunction with cash flow metrics, such as days inventory outstanding (DIO) and days sales outstanding (DSO), businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their cash flow management.
Gallery of Inventory Turnover Ratio
Inventory Turnover Ratio Image Gallery





What is the inventory turnover ratio?
+The inventory turnover ratio is a metric that measures the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period.
How is the inventory turnover ratio calculated?
+The inventory turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value.
What are the benefits of a high inventory turnover ratio?
+A high inventory turnover ratio can improve cash flow, reduce storage costs, and minimize the risk of inventory becoming obsolete.
How can businesses improve their inventory turnover ratio?
+Businesses can improve their inventory turnover ratio by optimizing production, reducing waste, and improving cash flow management.
What are the common mistakes in inventory turnover ratio calculation?
+Common mistakes in inventory turnover ratio calculation include using incorrect or outdated data, and failing to account for changes in inventory levels over time.
In conclusion, the inventory turnover ratio is a vital metric for businesses to evaluate their inventory management efficiency and identify areas for improvement. By understanding the calculation, interpretation, and importance of the inventory turnover ratio, businesses can develop strategies to optimize their inventory management, reduce waste, and improve cash flow. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on inventory turnover ratio in the comments section below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your network to help others improve their inventory management skills.
