Intro
Boost efficiency with 5 inventory turnover ratios, including stock turnover, inventory days, and sell-through rates, to optimize supply chain management and improve cash flow with effective inventory control and management techniques.
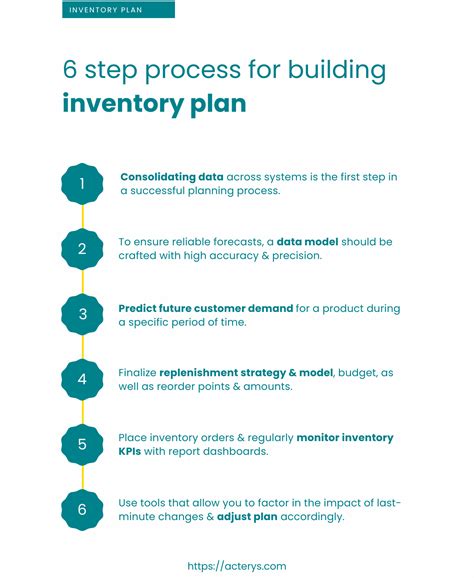
The importance of inventory management cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts a company's profitability and efficiency. One key metric used to evaluate inventory management is the inventory turnover ratio. This ratio measures how many times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period. In this article, we will delve into the world of inventory turnover ratios, exploring their significance, calculation methods, and the benefits of maintaining a healthy inventory turnover rate.
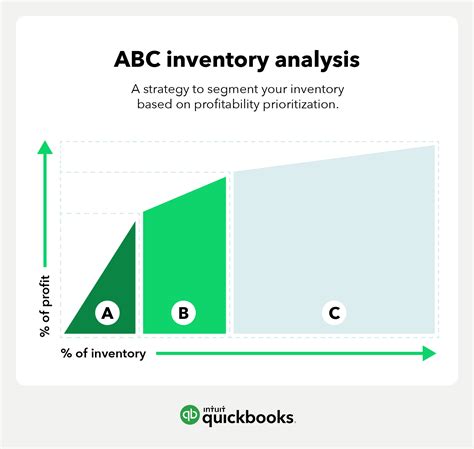
Inventory turnover ratios are crucial for businesses, as they provide insights into inventory management practices, helping companies identify areas for improvement. By analyzing inventory turnover ratios, businesses can determine whether they are holding too much inventory, which can lead to waste and unnecessary storage costs, or if they are not holding enough, resulting in lost sales opportunities. Understanding inventory turnover ratios is essential for making informed decisions about inventory management, ultimately affecting a company's bottom line.
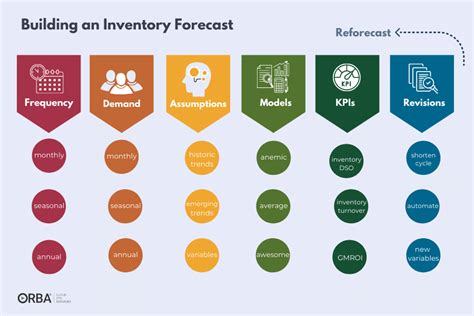
Effective inventory management is a delicate balance between meeting customer demand and minimizing inventory costs. Companies must ensure they have sufficient inventory to fulfill orders, but excessive inventory can lead to waste, obsolescence, and unnecessary expenses. Inventory turnover ratios help businesses strike this balance by providing a clear picture of their inventory management performance. By regularly monitoring and analyzing inventory turnover ratios, companies can identify trends, optimize their inventory levels, and improve their overall operational efficiency.
What is Inventory Turnover Ratio?
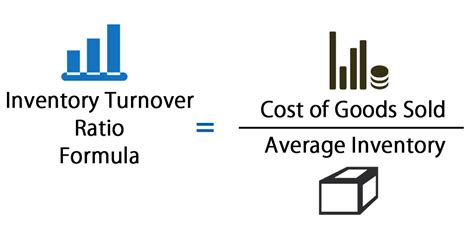
Types of Inventory Turnover Ratios
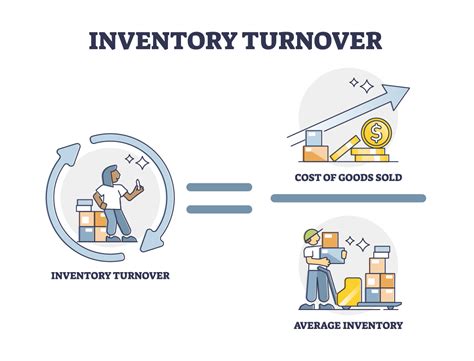
Benefits of Inventory Turnover Ratios

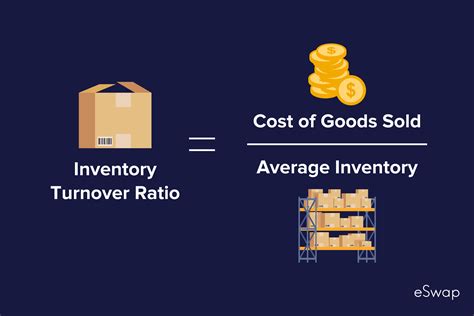
How to Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio
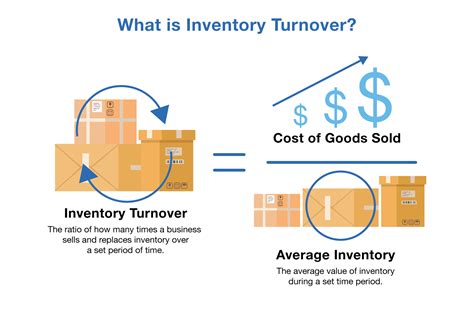
Example of Inventory Turnover Ratio
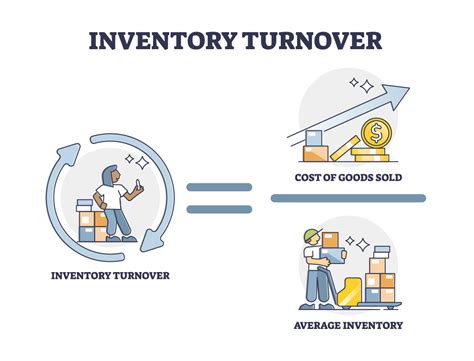
Importance of Inventory Turnover Ratio
Gallery of Inventory Turnover Ratios
Inventory Turnover Ratio Image Gallery


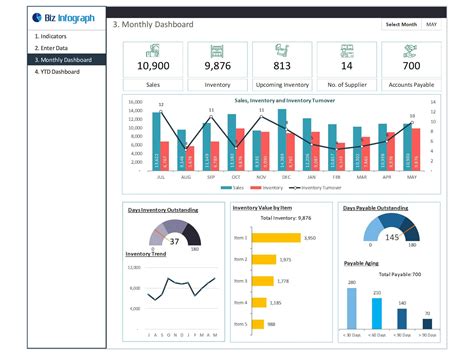
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of inventory turnover ratio?
+The purpose of inventory turnover ratio is to measure the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period.
How is inventory turnover ratio calculated?
+Inventory turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory value.
What does a high inventory turnover ratio indicate?
+A high inventory turnover ratio indicates that a company is selling and replacing its inventory quickly, which can be beneficial for reducing inventory costs and minimizing the risk of inventory becoming obsolete.
What does a low inventory turnover ratio indicate?
+A low inventory turnover ratio may suggest that a company is holding too much inventory, which can lead to waste and unnecessary expenses.
Why is inventory turnover ratio important for businesses?
+Inventory turnover ratio is important for businesses because it provides insights into inventory management practices, helping companies identify areas for improvement and optimize their inventory levels.
In conclusion, inventory turnover ratios are a vital metric for businesses, providing insights into inventory management practices and helping companies optimize their inventory levels. By regularly monitoring and analyzing inventory turnover ratios, businesses can identify trends, reduce inventory costs, and improve their overall operational efficiency. Whether you're a seasoned business owner or just starting out, understanding inventory turnover ratios is essential for making informed decisions about inventory management and driving your company's success. We encourage you to share your thoughts on inventory turnover ratios in the comments below and explore our other articles on inventory management for more insights and expertise.
