Intro
Explore Americas history with a printable map of 13 colonies, featuring original states, colonial regions, and historical territories for educational purposes.
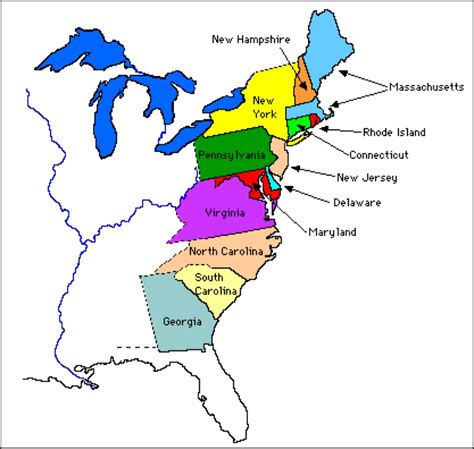
The history of the United States is deeply rooted in the 13 colonies that declared independence from British rule, paving the way for the formation of a new nation. Understanding the geography and layout of these colonies is essential for grasping the historical context of the American Revolution and the early development of the United States. A printable map of the 13 colonies can be a valuable tool for educators, students, and history enthusiasts alike, providing a visual representation of the colonies' locations, boundaries, and relationships to one another.
The 13 original colonies were divided into three main groups based on their geographical locations and economic characteristics: the New England colonies, the Middle colonies, and the Southern colonies. Each group had its unique culture, economy, and political system, which played significant roles in shaping the course of American history. A printable map can help illustrate these distinctions and provide a clearer understanding of how the colonies interacted and influenced one another.
Introduction to the 13 Colonies
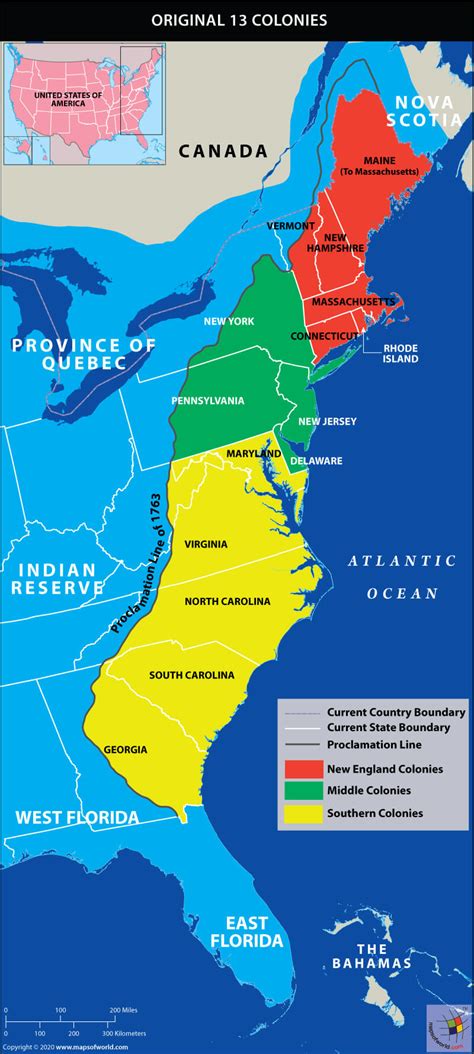
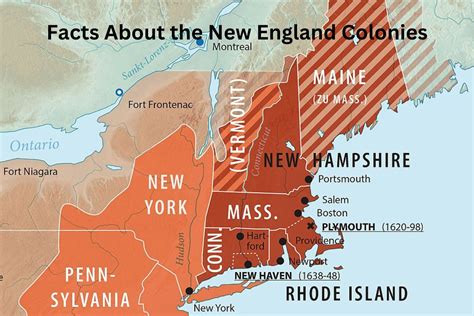
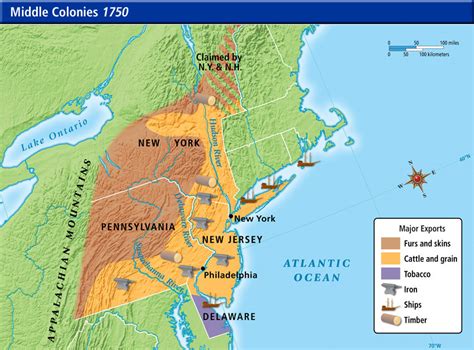
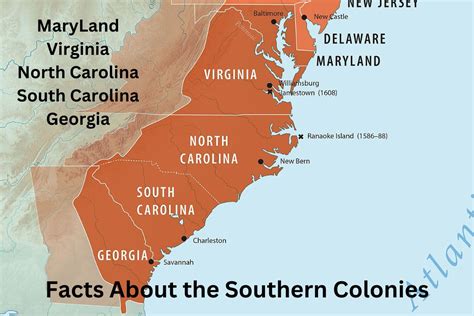
The New England colonies, consisting of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Connecticut, were primarily focused on trade and commerce. The Middle colonies, which included New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, were characterized by their diverse economies and cultures, with significant contributions from European immigrants. The Southern colonies, comprising Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, were largely agricultural, with economies based on plantation farming and slavery.
Geography and Climate of the 13 Colonies
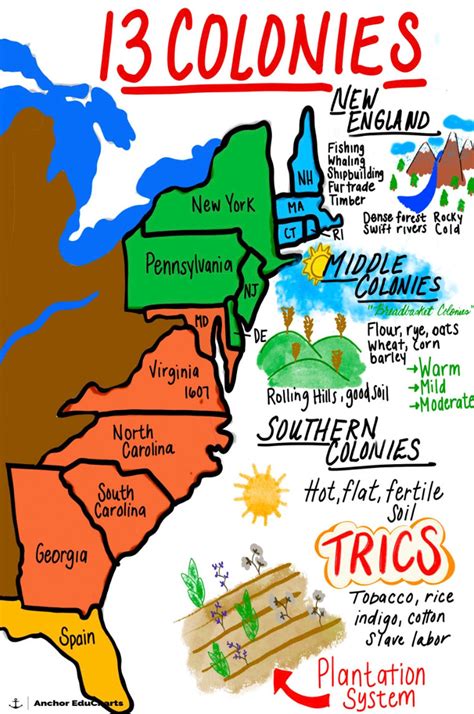
The geography and climate of the 13 colonies played crucial roles in their development and the daily lives of their inhabitants. The colonies' locations along the eastern coast of North America exposed them to the Atlantic Ocean, facilitating trade and communication with Europe. The varied landscapes, ranging from the rugged mountains of New England to the fertile plains of the Southern colonies, influenced the types of economies and settlements that could be established.
Regional Characteristics
The regional characteristics of the 13 colonies are a testament to the diversity and complexity of early American history. Each region had its unique challenges and opportunities, shaped by its geography, climate, and the cultural backgrounds of its inhabitants. Understanding these regional characteristics is essential for appreciating the evolution of the United States from a collection of distinct colonies to a unified nation.Economic Systems of the 13 Colonies
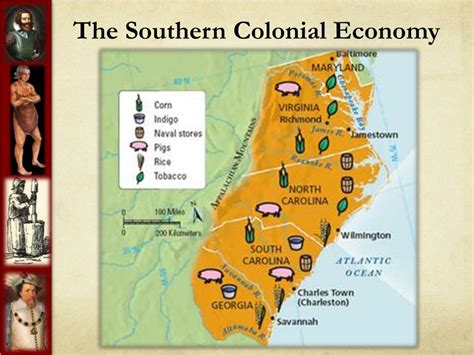
The economic systems of the 13 colonies were as diverse as their geography and cultures. From the mercantile economy of the New England colonies, which relied heavily on trade and shipping, to the plantation economy of the Southern colonies, which was based on agriculture and slavery, each region developed economic strategies that suited its resources and population. The Middle colonies, with their mixed economies, served as a bridge between the North and South, facilitating trade and exchange between the two.
Trade and Commerce
Trade and commerce were vital components of the colonial economy, with the 13 colonies engaging in extensive trade with Britain and other European countries. The colonies exported goods such as tobacco, cotton, and furs, while importing manufactured goods, textiles, and other necessities. The triangular trade, which involved the exchange of goods, slaves, and raw materials between Europe, Africa, and the Americas, played a significant role in the economic development of the colonies.Social and Political Structures

The social and political structures of the 13 colonies were shaped by their histories, cultures, and economic systems. Each colony had its own system of government, ranging from the democratic town meetings of New England to the aristocratic plantation societies of the South. The colonies also developed distinct social hierarchies, with divisions based on wealth, race, and occupation.
Colonial Governance
The governance of the 13 colonies was a complex issue, with power divided between the British monarchy, colonial assemblies, and local governments. The colonies had a significant degree of autonomy, with their own legislative bodies and legal systems. However, the British government also exerted control through laws and policies, such as the Navigation Acts, which regulated trade and commerce.Historical Significance of the 13 Colonies
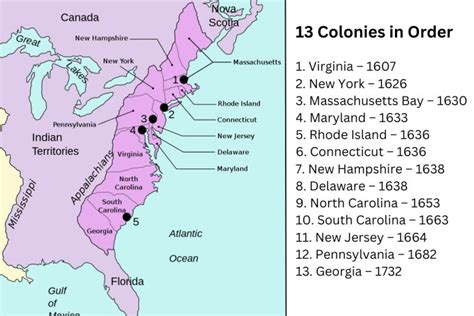
The 13 colonies hold a profound historical significance, as they laid the foundation for the United States of America. The colonial experience shaped American political, social, and economic institutions, influencing the country's development and growth. The struggles and achievements of the colonies, from their early settlements to their declaration of independence, continue to inspire and inform American society today.
Legacy of the 13 Colonies
The legacy of the 13 colonies can be seen in the modern United States, with its democratic system of government, diverse economy, and multicultural society. The colonies' experiences with self-governance, trade, and cultural exchange have contributed to America's position as a global leader. Moreover, the historical events and figures associated with the 13 colonies, such as the American Revolution and the Founding Fathers, remain essential parts of American identity and heritage.13 Colonies Image Gallery






What were the original 13 colonies?
+The original 13 colonies were Virginia, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Maryland, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Delaware, North Carolina, South Carolina, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Georgia.
Why were the 13 colonies established?
+The 13 colonies were established for a variety of reasons, including economic opportunities, religious freedom, and the desire for a new life in the Americas.
What was the significance of the 13 colonies in American history?
+The 13 colonies played a crucial role in American history, as they laid the foundation for the United States of America and shaped the country's political, social, and economic institutions.
How did the 13 colonies declare independence from Britain?
+The 13 colonies declared independence from Britain through the American Revolution, which began in 1775 and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
What were the main differences between the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies?
+The main differences between the New England, Middle, and Southern colonies were their economies, cultures, and geographical locations. New England colonies were focused on trade and commerce, Middle colonies had diverse economies, and Southern colonies were primarily agricultural.
In conclusion, the 13 colonies were a pivotal part of American history, shaping the country's development and growth. Understanding the geography, economy, and social structures of the colonies is essential for appreciating the complexities of American society today. By exploring the historical significance of the 13 colonies, we can gain a deeper understanding of the United States and its place in the world. We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of the 13 colonies in American history and how their legacy continues to influence contemporary society.
