Intro
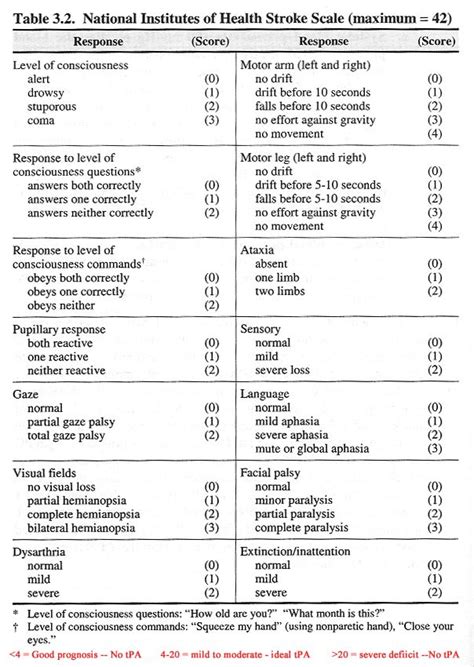
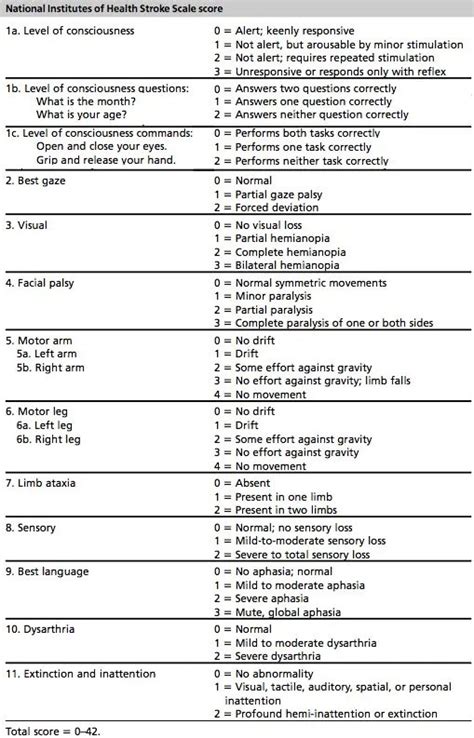
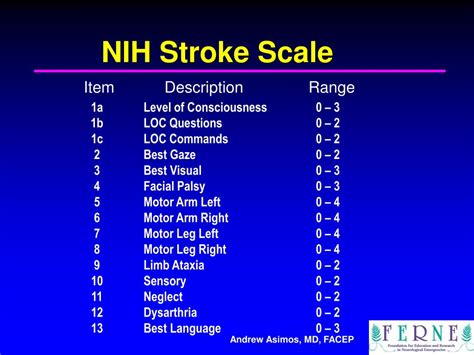
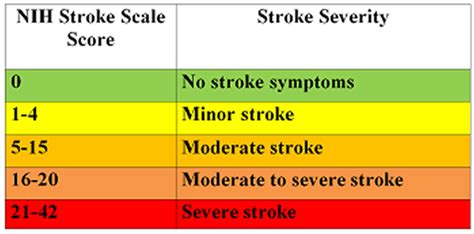
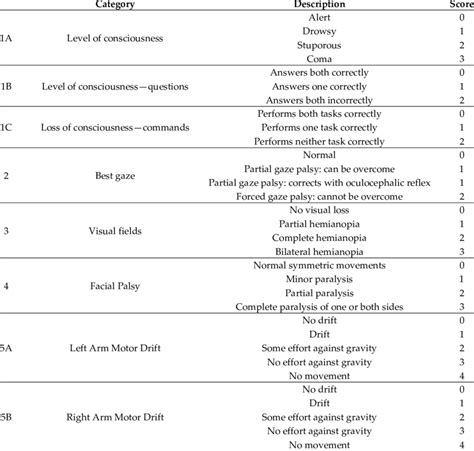
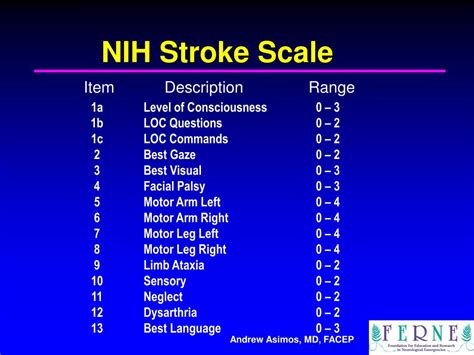
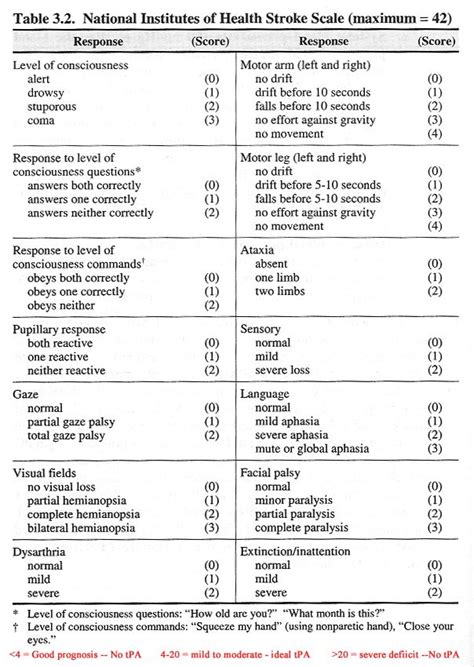
The NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a systematic assessment tool that healthcare professionals use to evaluate the effects of acute cerebral infarction on the levels of consciousness, visual-field loss, extraocular movement, motor strength, ataxia, dysarthria, and language. It is a crucial tool in the initial assessment and ongoing management of patients with stroke. The NIHSS is composed of 11 items, each of which scores a specific aspect of neurological function. The scores from each item are summed to give a total score that ranges from 0 to 42, with higher scores indicating more severe neurological deficits.
The importance of the NIH Stroke Scale lies in its ability to provide a standardized and reliable assessment of stroke severity. This information is critical for guiding treatment decisions, predicting patient outcomes, and facilitating communication among healthcare providers. The scale is widely used in clinical practice and research, and its application has been shown to improve patient care and outcomes. Given its significance, having access to an NIH Stroke Scale printable form can be invaluable for healthcare professionals, allowing them to quickly and accurately assess patients and make informed decisions about their care.
Understanding the NIH Stroke Scale

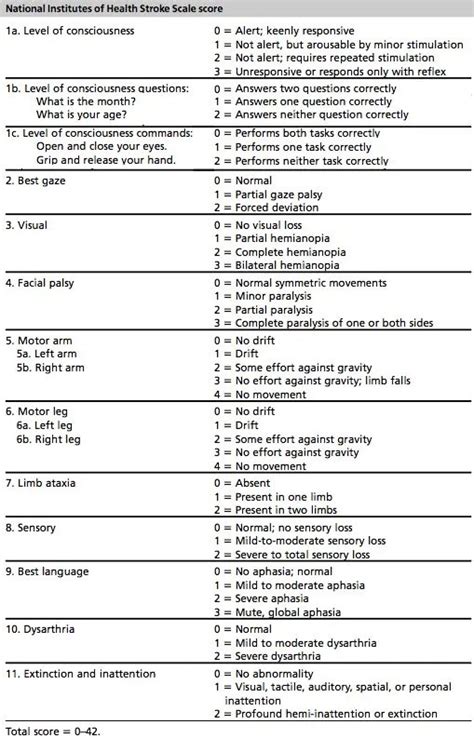
To fully understand the NIH Stroke Scale, it is essential to break down its components and scoring system. The scale assesses levels of consciousness, including the patient's ability to respond to verbal commands and their level of alertness. It also evaluates visual-field loss, extraocular movement, and motor strength in the face, arm, and leg. Additionally, the scale assesses ataxia, which refers to a lack of muscle coordination, and dysarthria, which is difficulty speaking due to problems with muscle control. Language is also evaluated, including the patient's ability to understand and express themselves through speech.
Each item on the NIHSS is scored based on the patient's performance, with specific criteria for determining the score. For example, the item assessing levels of consciousness awards a score of 0 for a patient who is alert and fully responsive, while a patient who is unresponsive receives a score of 3. Similarly, the motor strength assessment awards a score of 0 for normal strength and up to 4 for no movement.
Components of the NIH Stroke Scale
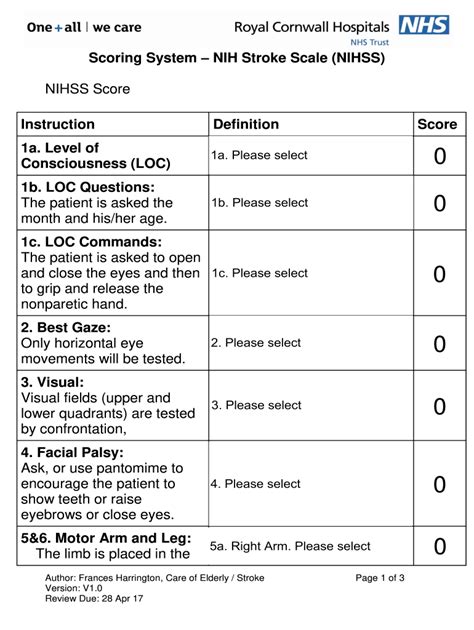
The components of the NIH Stroke Scale are designed to provide a comprehensive assessment of neurological function. These components include:
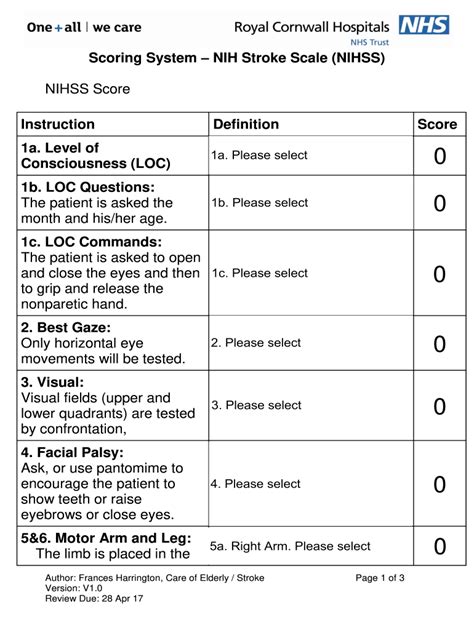
- Level of Consciousness (LOC): This assesses the patient's level of alertness and ability to respond to verbal commands.
- Best Gaze: This evaluates the patient's ability to move their eyes in response to verbal commands.
- Visual-Field Loss: This assesses the patient's ability to see objects or movements in their visual field.
- Facial Palsy: This evaluates the patient's facial strength and symmetry.
- Motor Arm and Leg: These assess the patient's strength and ability to move their arms and legs.
- Limb Ataxia: This evaluates the patient's coordination and ability to perform movements smoothly.
- Sensory: This assesses the patient's ability to feel sensations such as touch and pain.
- Best Language: This evaluates the patient's ability to understand and express language.
- Dysarthria: This assesses the patient's speech clarity and articulation.
- Extinction and Inattention: This evaluates the patient's ability to perceive and respond to stimuli on both sides of their body.
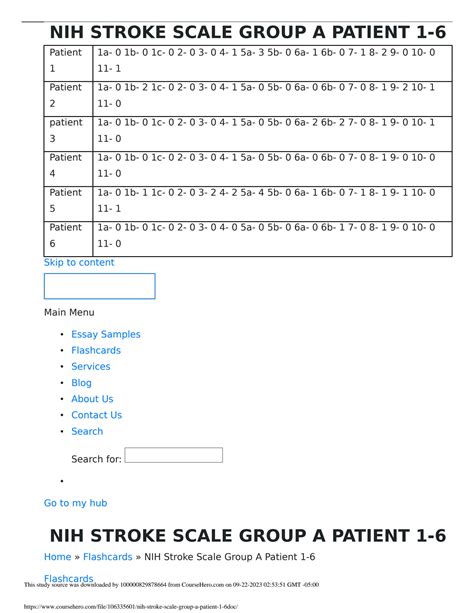
Each component is scored based on specific criteria, and these scores are summed to give a total NIHSS score.
Benefits of Using the NIH Stroke Scale

The benefits of using the NIH Stroke Scale are numerous. It provides a standardized and reliable method for assessing stroke severity, which is crucial for guiding treatment decisions. The scale is also useful for predicting patient outcomes, as higher scores are associated with worse outcomes. Additionally, the NIHSS facilitates communication among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the patient's care team are aware of their neurological status and any changes that may occur.
The use of the NIH Stroke Scale has been shown to improve patient care and outcomes. By providing a clear and comprehensive assessment of neurological function, the scale helps healthcare providers to identify areas of deficit and tailor their treatment approach accordingly. This can lead to more effective management of stroke and its complications, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Steps for Administering the NIH Stroke Scale
Administering the NIH Stroke Scale requires careful attention to detail and adherence to the specific criteria for each item. The steps for administering the scale include:
- Preparation: Before administering the scale, ensure that the patient is in a comfortable and quiet environment. This will help to minimize distractions and ensure that the patient can focus on the assessment.
- Introduction: Introduce yourself to the patient and explain the purpose of the assessment. This helps to establish trust and ensures that the patient understands what is expected of them.
- Assessment: Begin the assessment by evaluating the patient's level of consciousness. Ask the patient to respond to verbal commands and assess their level of alertness.
- Component Evaluation: Evaluate each component of the NIHSS in turn, using the specific criteria for each item to determine the score.
- Scoring: Score each item based on the patient's performance, and sum these scores to give a total NIHSS score.
- Documentation: Document the patient's score and any notable findings or deficits. This information is crucial for guiding treatment decisions and predicting patient outcomes.
By following these steps, healthcare providers can ensure that the NIH Stroke Scale is administered accurately and effectively, providing valuable information for the management of patients with stroke.
Practical Applications of the NIH Stroke Scale
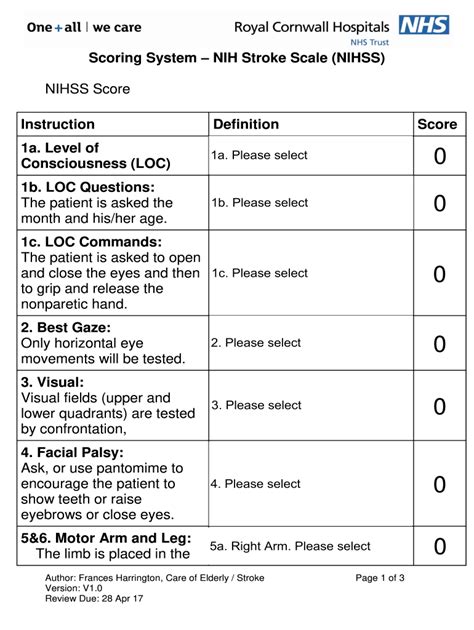
The NIH Stroke Scale has numerous practical applications in clinical practice and research. It is widely used in emergency departments and stroke units to assess patients with suspected stroke and guide initial management. The scale is also used in research studies to evaluate the effectiveness of new treatments for stroke and to predict patient outcomes.
In addition to its use in acute stroke care, the NIHSS can be used to monitor patients' progress over time and adjust their treatment plan as needed. This can help to optimize patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
The practical applications of the NIH Stroke Scale include:
- Initial Assessment: The scale is used to assess patients with suspected stroke and guide initial management.
- Ongoing Monitoring: The scale is used to monitor patients' progress over time and adjust their treatment plan as needed.
- Research: The scale is used in research studies to evaluate the effectiveness of new treatments for stroke and to predict patient outcomes.
- Communication: The scale facilitates communication among healthcare providers, ensuring that all members of the patient's care team are aware of their neurological status and any changes that may occur.
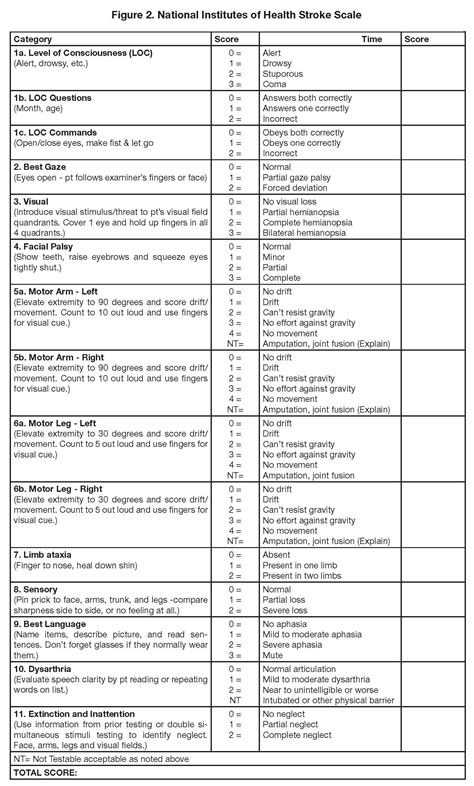
Gallery of NIH Stroke Scale Images
NIH Stroke Scale Image Gallery
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the NIH Stroke Scale?
+The NIH Stroke Scale is a systematic assessment tool used to evaluate the effects of acute cerebral infarction on the levels of consciousness, visual-field loss, extraocular movement, motor strength, ataxia, dysarthria, and language.
How is the NIH Stroke Scale administered?
+The NIH Stroke Scale is administered by a healthcare professional who evaluates the patient's neurological function using the specific criteria for each item on the scale.
What are the benefits of using the NIH Stroke Scale?
+The benefits of using the NIH Stroke Scale include providing a standardized and reliable method for assessing stroke severity, guiding treatment decisions, predicting patient outcomes, and facilitating communication among healthcare providers.
How is the NIH Stroke Scale scored?
+The NIH Stroke Scale is scored by summing the scores from each item on the scale, with higher scores indicating more severe neurological deficits.
What are the practical applications of the NIH Stroke Scale?
+The practical applications of the NIH Stroke Scale include initial assessment, ongoing monitoring, research, and communication among healthcare providers.
In conclusion, the NIH Stroke Scale is a valuable tool for assessing stroke severity and guiding treatment decisions. Its ability to provide a standardized and reliable assessment of neurological function makes it an essential component of stroke care. By understanding the components, benefits, and practical applications of the NIH Stroke Scale, healthcare providers can optimize patient outcomes and improve the management of stroke. We encourage readers to share their experiences with the NIH Stroke Scale and to explore the resources provided in this article to learn more about this important tool. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply interested in learning more about stroke care, we hope that this article has provided you with valuable insights and information.
