Intro
Medication aides play a vital role in the healthcare system, assisting patients with their medication needs and ensuring they take the right dose at the right time. As the demand for healthcare services continues to grow, the importance of medication aides cannot be overstated. In this article, we will delve into the world of medication aides, exploring their role, responsibilities, and the skills required to excel in this profession. We will also provide valuable tips for medication aides to improve their performance and provide better care for their patients.
The role of a medication aide is multifaceted, involving not only the administration of medication but also monitoring patient health, reporting any changes or concerns to healthcare professionals, and maintaining accurate records. Medication aides work in various settings, including nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and hospitals, and their duties may vary depending on the specific needs of their patients. With the increasing complexity of medication regimens and the growing number of patients with chronic conditions, the need for skilled and knowledgeable medication aides has never been greater.
Effective medication management is crucial for patient health and well-being, and medication aides are at the forefront of this effort. By understanding the medications they administer, their potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to prescribed regimens, medication aides can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. Moreover, medication aides often develop close relationships with their patients, providing emotional support and reassurance, which can have a profound impact on patient satisfaction and overall quality of life. As we explore the tips and strategies for medication aides, it is essential to remember the critical role they play in the healthcare system and the positive impact they can have on patient care.
Understanding Medication Administration
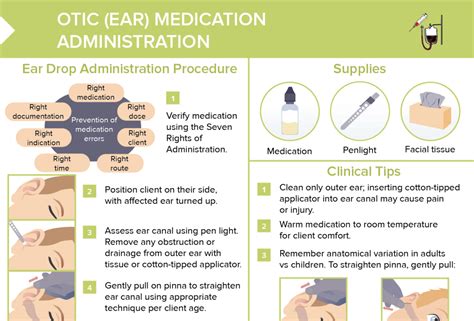
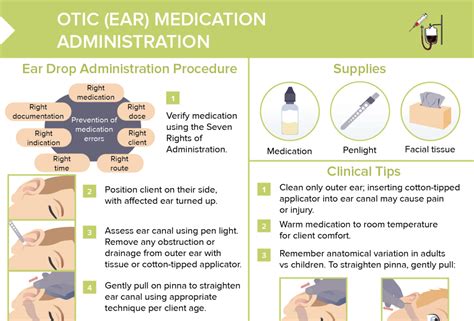
Key Principles of Medication Administration
Medication aides should adhere to the following key principles of medication administration: * Verify the patient's identity and the medication order before administering any medication * Use the "five rights" of medication administration: right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, and right time * Monitor patient response to medication and report any adverse effects or concerns to healthcare professionals * Maintain accurate and up-to-date records of medication administrationDeveloping Effective Communication Skills

Strategies for Effective Communication
Medication aides can use the following strategies to improve their communication skills: * Use clear and simple language when explaining medication regimens and instructions * Listen actively to patient concerns and respond in a empathetic and understanding manner * Ask open-ended questions to encourage patient engagement and understanding * Use non-verbal communication, such as body language and facial expressions, to convey empathy and supportManaging Medication Errors

Strategies for Managing Medication Errors
Medication aides can use the following strategies to manage medication errors: * Use a systematic approach to medication administration, including verification of patient identity and medication orders * Stay focused and alert during medication administration, avoiding distractions and minimizing interruptions * Report any errors or concerns to healthcare professionals promptly, and participate in efforts to investigate and prevent future errorsStaying Organized and Managing Time Effectively

Strategies for Staying Organized
Medication aides can use the following strategies to stay organized and manage their time effectively: * Use a planner or calendar to schedule medication administration and other tasks * Prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance, focusing on the most critical tasks first * Minimize distractions and interruptions, such as turning off notifications and finding a quiet workspaceContinuing Education and Professional Development

Resources for Continuing Education
Medication aides can use the following resources to support their continuing education and professional development: * Online training and certification programs, such as those offered by the American Association of Medication Aides * Conferences and workshops, such as the annual conference of the National Association of Health Care Assistants * Mentorship programs, which pair experienced medication aides with newer professionals for guidance and supportMedication Aide Image Gallery






What are the key responsibilities of a medication aide?
+The key responsibilities of a medication aide include administering medications, monitoring patient response, and reporting any adverse effects or concerns to healthcare professionals.
How can medication aides prevent medication errors?
+Medication aides can prevent medication errors by verifying patient identity and medication orders, using barcode scanning and other technologies, and staying focused and alert during medication administration.
What are the benefits of continuing education for medication aides?
+The benefits of continuing education for medication aides include staying current with new medications and technologies, improving patient care and safety, and enhancing career development and advancement opportunities.
How can medication aides develop effective communication skills?
+Medication aides can develop effective communication skills by using clear and simple language, listening actively to patient concerns, and asking open-ended questions to encourage patient engagement and understanding.
What are the most common causes of medication errors?
+The most common causes of medication errors include distractions, fatigue, and inadequate training, as well as poor communication and lack of verification of patient identity and medication orders.
In conclusion, medication aides play a vital role in the healthcare system, and their skills and knowledge are essential for providing high-quality patient care. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, medication aides can improve their performance, prevent medication errors, and enhance patient safety and satisfaction. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on this topic, and to explore the resources and references provided for further learning and professional development. By working together, we can promote excellence in medication administration and improve health outcomes for patients everywhere.
