Intro
Explore 5 detailed plant cell diagrams, illustrating cell structure, organelles, and functions, including chloroplasts, mitochondria, and nuclei, for a deeper understanding of plant biology and cellular processes.
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants, and understanding their structure is essential for botany and biology. The plant cell diagram is a visual representation of the different components that make up a plant cell. In this article, we will explore the importance of plant cell diagrams, their components, and provide examples of different types of plant cell diagrams.
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning their DNA is enclosed within a nucleus. They are also surrounded by a cell wall, which provides structural support and protection. The cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. Plant cells also have large vacuoles, which are used for storage and waste management. The vacuoles are surrounded by a tonoplast membrane, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the vacuole.
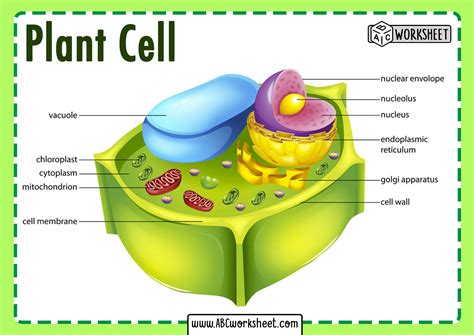
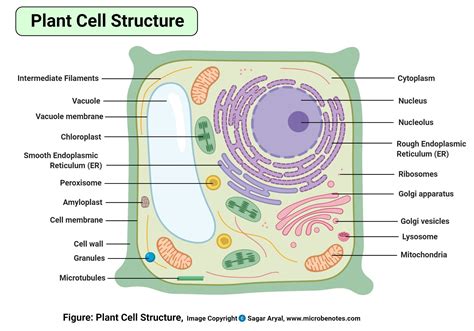
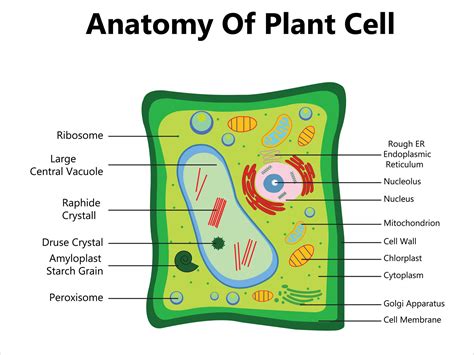
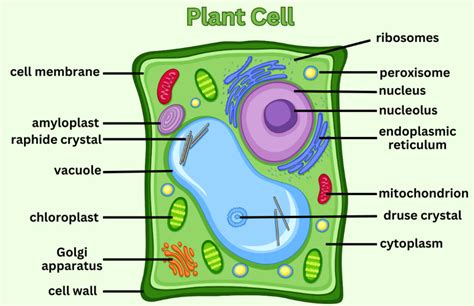
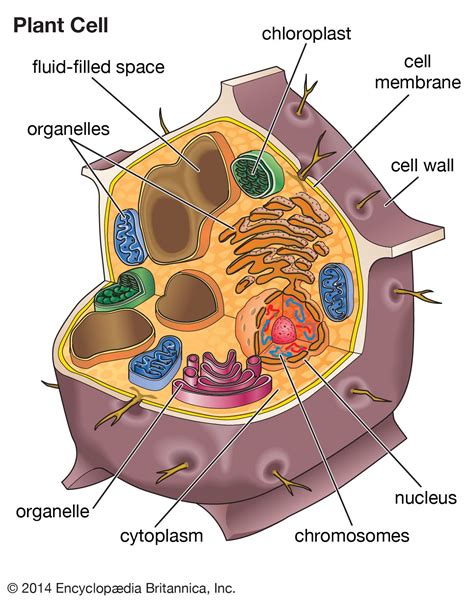
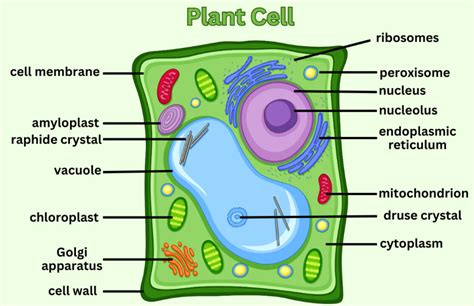
The plant cell diagram is a useful tool for understanding the structure and function of plant cells. It shows the different components of the cell, including the cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. The diagram also illustrates the relationships between these components and how they work together to maintain the cell's overall function.
Introduction to Plant Cell Diagrams
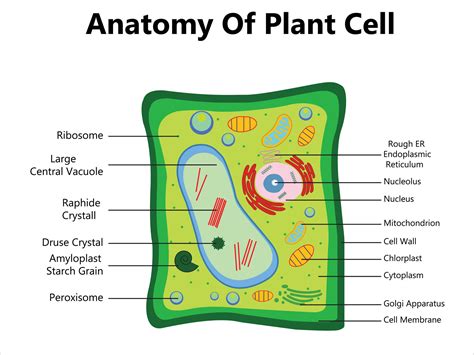
Plant cell diagrams are essential for students of botany and biology, as they provide a visual representation of the cell's structure and function. The diagrams show the different components of the cell, including the cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. They also illustrate the relationships between these components and how they work together to maintain the cell's overall function.
Plant cell diagrams can be used to teach students about the different parts of a plant cell and their functions. They can also be used to illustrate the differences between plant cells and animal cells. For example, plant cells have a cell wall, which provides structural support and protection, while animal cells do not.
Components of a Plant Cell Diagram
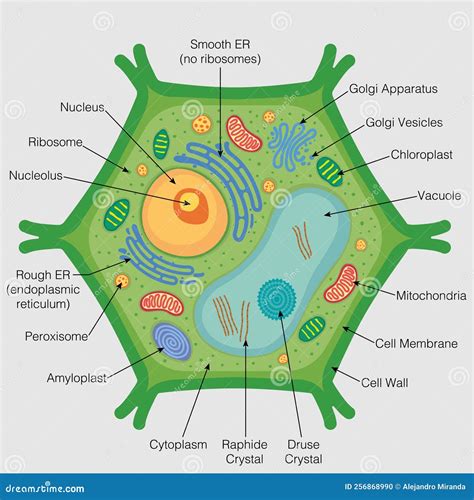
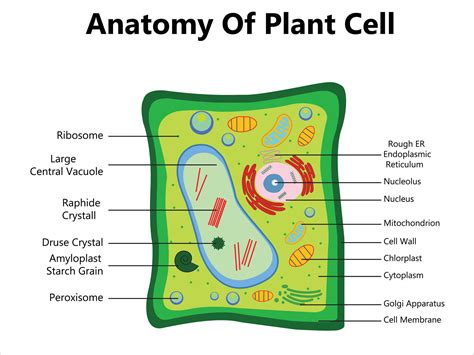
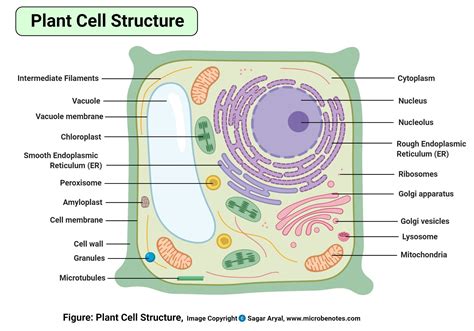
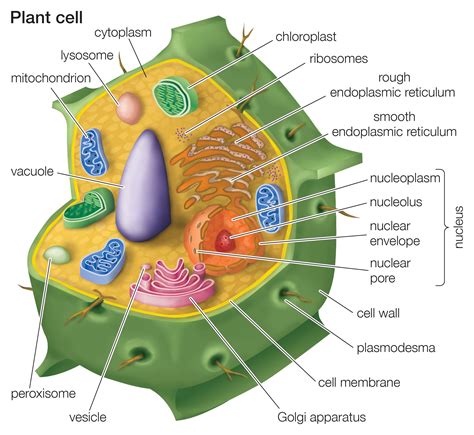
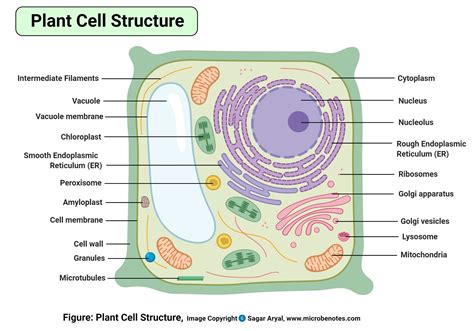
A plant cell diagram typically includes the following components:
- Cell wall: The cell wall is the outermost layer of the plant cell. It provides structural support and protection to the cell.
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell's DNA and is responsible for regulating the cell's growth and reproduction.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell. They generate energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
- Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Vacuoles: Vacuoles are used for storage and waste management. They are surrounded by a tonoplast membrane, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the vacuole.
These components work together to maintain the cell's overall function. For example, the mitochondria generate energy for the cell, which is then used by the chloroplasts to perform photosynthesis.
Types of Plant Cell Diagrams
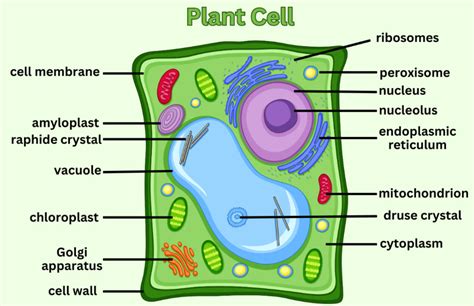
There are several types of plant cell diagrams, including:
- Labeled diagrams: These diagrams show the different components of the plant cell and their functions.
- Unlabeled diagrams: These diagrams show the different components of the plant cell, but do not include labels.
- Diagrams with arrows: These diagrams show the relationships between the different components of the plant cell.
- Diagrams with colors: These diagrams use different colors to highlight the different components of the plant cell.
Each type of diagram has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, labeled diagrams are useful for students who are new to plant cell biology, while unlabeled diagrams are useful for students who want to test their knowledge.
Benefits of Plant Cell Diagrams
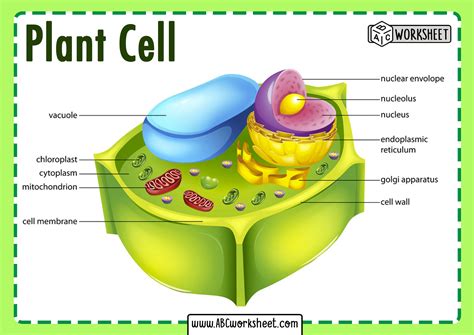
Plant cell diagrams have several benefits, including:
- They provide a visual representation of the plant cell's structure and function.
- They help students understand the relationships between the different components of the plant cell.
- They are useful for teaching students about the different parts of a plant cell and their functions.
- They can be used to illustrate the differences between plant cells and animal cells.
Overall, plant cell diagrams are an essential tool for students of botany and biology. They provide a visual representation of the plant cell's structure and function, and help students understand the relationships between the different components of the plant cell.
Practical Applications of Plant Cell Diagrams
Plant cell diagrams have several practical applications, including:
- They are used in botanical research to study the structure and function of plant cells.
- They are used in agriculture to develop new crops and improve crop yields.
- They are used in medicine to develop new treatments for diseases.
- They are used in biotechnology to develop new products and technologies.
These applications demonstrate the importance of plant cell diagrams in different fields. They are not only useful for teaching students about plant cell biology, but also have practical applications in various industries.
Gallery of Plant Cell Diagrams
Plant Cell Diagrams Image Gallery
What is the function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
+The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the plant cell.
What is the role of chloroplasts in a plant cell?
+Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
What is the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell?
+Plant cells have a cell wall, which provides structural support and protection, while animal cells do not.
What is the function of the nucleus in a plant cell?
+The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell's DNA and regulating the cell's growth and reproduction.
What is the role of vacuoles in a plant cell?
+Vacuoles are used for storage and waste management, surrounded by a tonoplast membrane that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the vacuole.
In conclusion, plant cell diagrams are an essential tool for understanding the structure and function of plant cells. They provide a visual representation of the different components of the plant cell, including the cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. Plant cell diagrams are useful for teaching students about the different parts of a plant cell and their functions, and they have practical applications in various industries. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of plant cell diagrams and their importance in botany and biology. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about plant cell biology, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
