Intro
Optimize inventory management with the 5 Ways Reorder Point Formula, leveraging demand forecasting, lead time, and safety stock to minimize stockouts and overstocking, ensuring efficient supply chain operations and maximizing profitability.
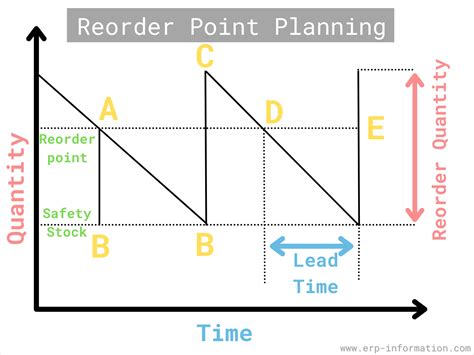
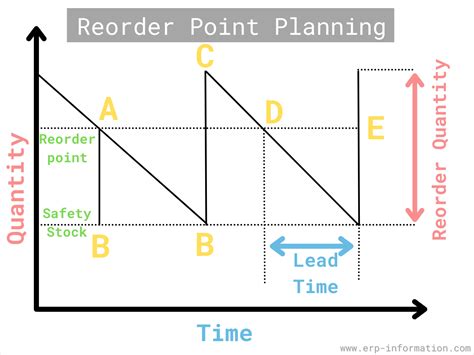
The reorder point formula is a crucial tool for businesses to determine when to replenish their inventory levels. It helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, ensuring that the right amount of products is available to meet customer demand. In this article, we will delve into the world of reorder point formulas, exploring five different methods to calculate the optimal reorder point.
Reorder point formulas are essential for businesses that deal with inventory management. By using these formulas, companies can minimize the risk of running out of stock, reduce inventory holding costs, and improve customer satisfaction. The reorder point formula takes into account factors such as lead time, demand, and safety stock to determine the optimal time to reorder inventory. In the following sections, we will discuss five different reorder point formulas, their benefits, and how to apply them in real-world scenarios.
Introduction to Reorder Point Formulas
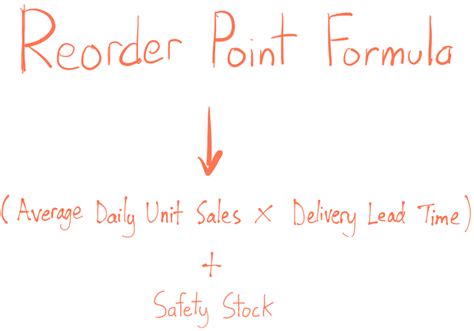
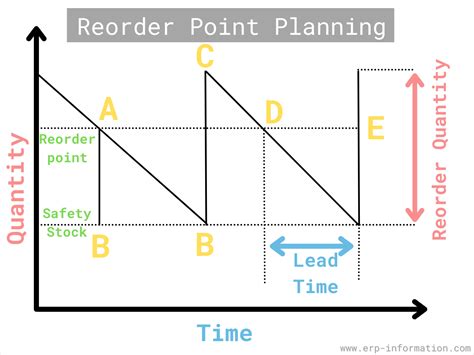
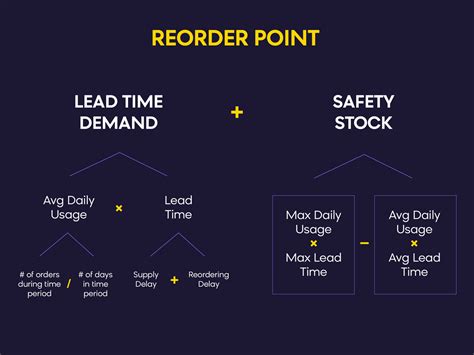
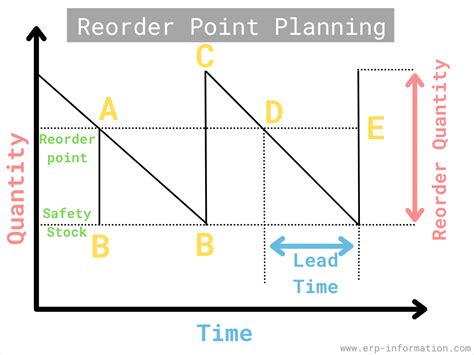
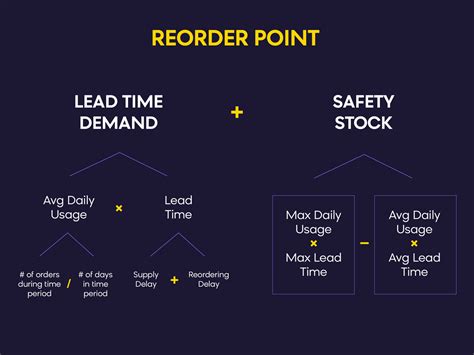
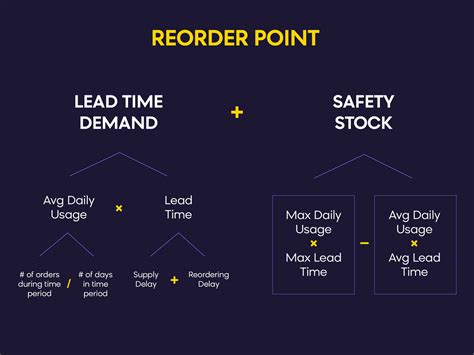
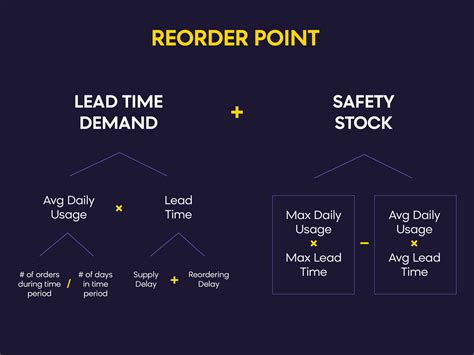
The reorder point formula is a mathematical equation that helps businesses determine when to reorder inventory. It considers factors such as lead time, demand, and safety stock to calculate the optimal reorder point. The formula is typically represented as:
Reorder Point = Lead Time Demand + Safety Stock
Where:
- Lead Time Demand is the amount of inventory required to meet customer demand during the lead time period.
- Safety Stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties such as changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Reorder Point Formula 1: Basic Reorder Point Formula

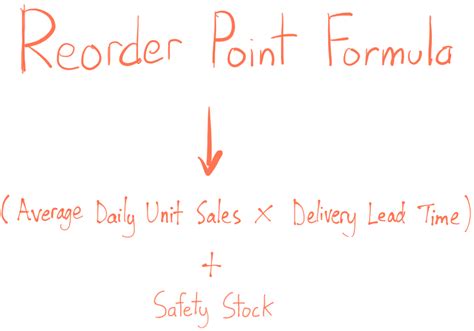
The basic reorder point formula is the most straightforward method to calculate the reorder point. It uses the following equation:
Reorder Point = Average Daily Demand x Lead Time + Safety Stock
Where:
- Average Daily Demand is the average amount of inventory sold per day.
- Lead Time is the time it takes to receive inventory after placing an order.
- Safety Stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties.
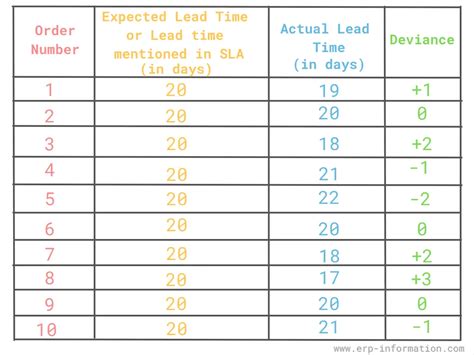
For example, let's say a company has an average daily demand of 100 units, a lead time of 5 days, and a safety stock of 200 units. Using the basic reorder point formula, the reorder point would be:
Reorder Point = 100 units/day x 5 days + 200 units = 700 units
Reorder Point Formula 2: Reorder Point Formula with Seasonal Demand

The reorder point formula with seasonal demand takes into account fluctuations in demand due to seasonal changes. It uses the following equation:
Reorder Point = Average Daily Demand x Lead Time x Seasonal Index + Safety Stock
Where:
- Average Daily Demand is the average amount of inventory sold per day.
- Lead Time is the time it takes to receive inventory after placing an order.
- Seasonal Index is a factor that represents the change in demand due to seasonal fluctuations.
- Safety Stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties.
For example, let's say a company has an average daily demand of 100 units, a lead time of 5 days, a safety stock of 200 units, and a seasonal index of 1.2 during peak season. Using the reorder point formula with seasonal demand, the reorder point would be:
Reorder Point = 100 units/day x 5 days x 1.2 + 200 units = 920 units
Reorder Point Formula 3: Reorder Point Formula with Vendor Lead Time
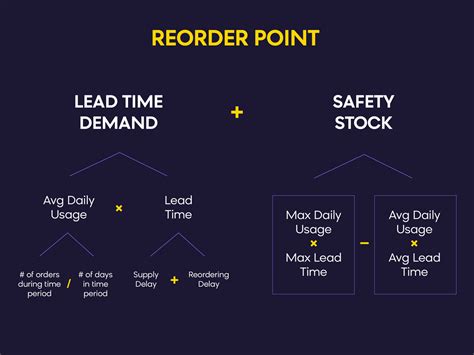
The reorder point formula with vendor lead time takes into account the time it takes for the vendor to deliver inventory. It uses the following equation:
Reorder Point = Average Daily Demand x (Lead Time + Vendor Lead Time) + Safety Stock
Where:
- Average Daily Demand is the average amount of inventory sold per day.
- Lead Time is the time it takes to receive inventory after placing an order.
- Vendor Lead Time is the time it takes for the vendor to deliver inventory.
- Safety Stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties.
For example, let's say a company has an average daily demand of 100 units, a lead time of 5 days, a vendor lead time of 3 days, and a safety stock of 200 units. Using the reorder point formula with vendor lead time, the reorder point would be:
Reorder Point = 100 units/day x (5 days + 3 days) + 200 units = 1,000 units
Reorder Point Formula 4: Reorder Point Formula with Service Level
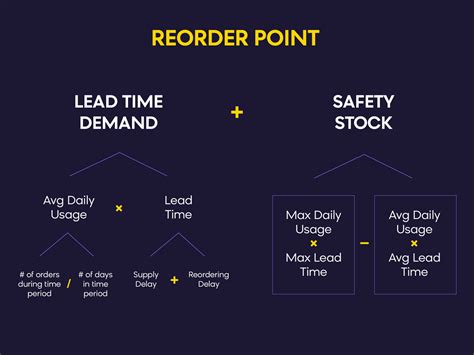
The reorder point formula with service level takes into account the desired service level, which represents the percentage of time that inventory is available to meet customer demand. It uses the following equation:
Reorder Point = Average Daily Demand x Lead Time x Service Level + Safety Stock
Where:
- Average Daily Demand is the average amount of inventory sold per day.
- Lead Time is the time it takes to receive inventory after placing an order.
- Service Level is the desired percentage of time that inventory is available to meet customer demand.
- Safety Stock is the additional inventory held to buffer against uncertainties.
For example, let's say a company has an average daily demand of 100 units, a lead time of 5 days, a service level of 95%, and a safety stock of 200 units. Using the reorder point formula with service level, the reorder point would be:
Reorder Point = 100 units/day x 5 days x 0.95 + 200 units = 745 units
Reorder Point Formula 5: Reorder Point Formula with Economic Order Quantity
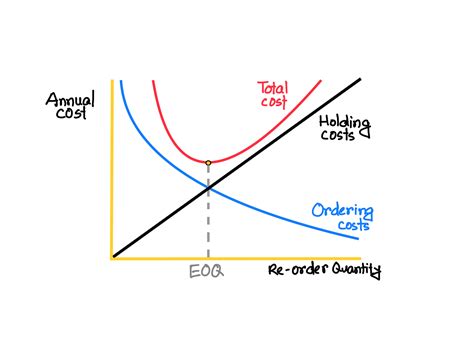
The reorder point formula with economic order quantity takes into account the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. It uses the following equation:
Reorder Point = Economic Order Quantity / 2
Where:
- Economic Order Quantity is the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs.
For example, let's say a company has an economic order quantity of 1,000 units. Using the reorder point formula with economic order quantity, the reorder point would be:
Reorder Point = 1,000 units / 2 = 500 units
Gallery of Reorder Point Formulas
Reorder Point Formulas Image Gallery
What is the purpose of the reorder point formula?
+The purpose of the reorder point formula is to determine when to reorder inventory to prevent stockouts and overstocking.
How do I calculate the reorder point using the basic reorder point formula?
+To calculate the reorder point using the basic reorder point formula, you need to multiply the average daily demand by the lead time and add the safety stock.
What is the difference between the reorder point formula with seasonal demand and the basic reorder point formula?
+The reorder point formula with seasonal demand takes into account fluctuations in demand due to seasonal changes, while the basic reorder point formula does not.
How do I determine the optimal order quantity using the economic order quantity formula?
+To determine the optimal order quantity using the economic order quantity formula, you need to calculate the square root of the total annual demand divided by the cost per unit.
What is the importance of safety stock in the reorder point formula?
+Safety stock is essential in the reorder point formula as it helps to buffer against uncertainties such as changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
In conclusion, the reorder point formula is a crucial tool for businesses to determine when to replenish their inventory levels. By using one of the five reorder point formulas discussed in this article, companies can minimize the risk of running out of stock, reduce inventory holding costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Whether you are using the basic reorder point formula or a more advanced formula that takes into account seasonal demand or economic order quantity, the key is to find the optimal reorder point that meets your business needs. We encourage you to share your experiences with reorder point formulas in the comments section below and explore how these formulas can be applied in real-world scenarios to improve inventory management.
