Intro
Master General Ledger Accounting Basics with our guide, covering ledger accounts, journal entries, and financial reporting, to streamline accounting processes and ensure accurate financial statements.
The general ledger is a fundamental component of any accounting system, serving as the central repository for all financial transactions within an organization. Understanding general ledger accounting basics is crucial for businesses, accountants, and financial professionals to ensure accurate and efficient financial management. In this article, we will delve into the world of general ledger accounting, exploring its importance, key components, and practical applications.
The general ledger is often referred to as the "book of final entry" because it contains a comprehensive record of all financial transactions, including income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. This ledger provides a clear picture of a company's financial position at any given time, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning. Whether you are a seasoned accountant or just starting to learn about accounting principles, grasping the basics of general ledger accounting is essential for success in the financial realm.
As we explore the intricacies of general ledger accounting, it becomes apparent that this system is the backbone of financial management. The general ledger is used to prepare financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, which are essential tools for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies. By understanding how to navigate and maintain a general ledger, organizations can ensure compliance with accounting standards, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Introduction to General Ledger Accounting
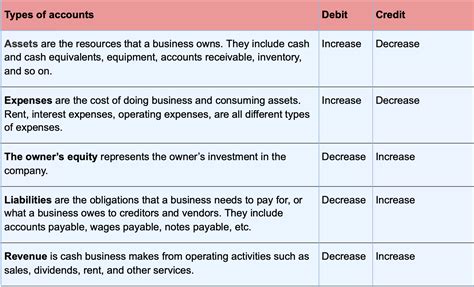
General ledger accounting is based on a set of principles and rules that govern how financial transactions are recorded and reported. The accounting equation, which states that assets equal liabilities plus equity, is the foundation of general ledger accounting. This equation is represented as A = L + E, where A represents assets, L represents liabilities, and E represents equity. Understanding this equation is vital for maintaining a balanced general ledger and ensuring that financial statements accurately reflect a company's financial position.
Key Components of General Ledger Accounting
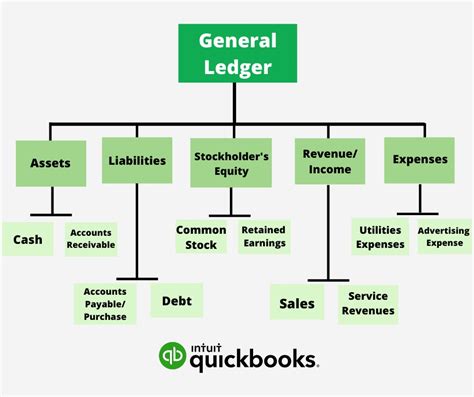
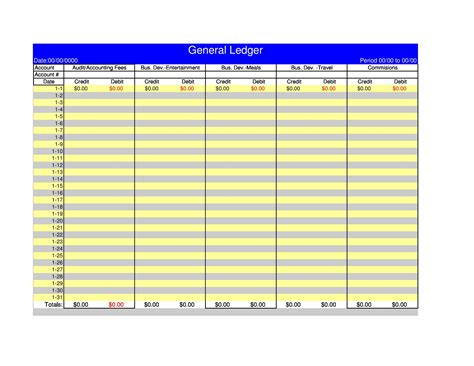
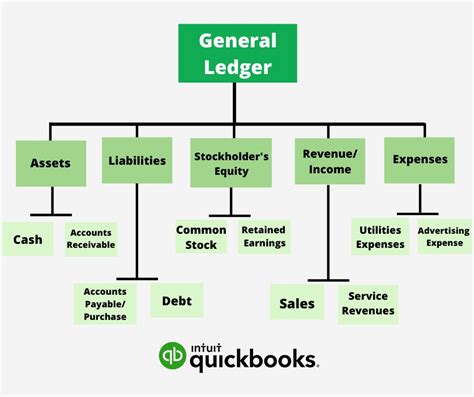
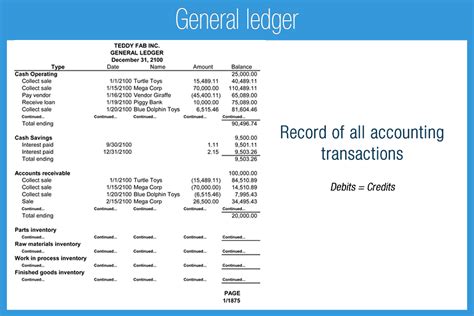
The general ledger consists of several key components, including accounts, journals, and ledgers. Accounts are the individual records within the general ledger that track specific types of transactions, such as cash, accounts payable, or sales revenue. Journals are used to record transactions in chronological order, while ledgers are used to group related accounts together. The chart of accounts, which is a list of all accounts used by an organization, is a critical component of the general ledger, as it provides a framework for categorizing and tracking financial transactions.Understanding General Ledger Accounts
General ledger accounts can be categorized into several types, including asset accounts, liability accounts, equity accounts, revenue accounts, and expense accounts. Asset accounts, such as cash and accounts receivable, represent the resources owned or controlled by an organization. Liability accounts, such as accounts payable and loans payable, represent the amounts owed by an organization to its creditors. Equity accounts, such as common stock and retained earnings, represent the ownership interest in an organization.
Recording Transactions in the General Ledger
Recording transactions in the general ledger involves several steps, including identifying the transaction, determining the accounts affected, and posting the transaction to the general ledger. The accounting equation is used to ensure that the transaction is recorded in a way that maintains the balance of the general ledger. For example, when a company purchases office supplies on credit, the transaction would be recorded as a debit to office supplies expense and a credit to accounts payable.General Ledger Accounting Principles
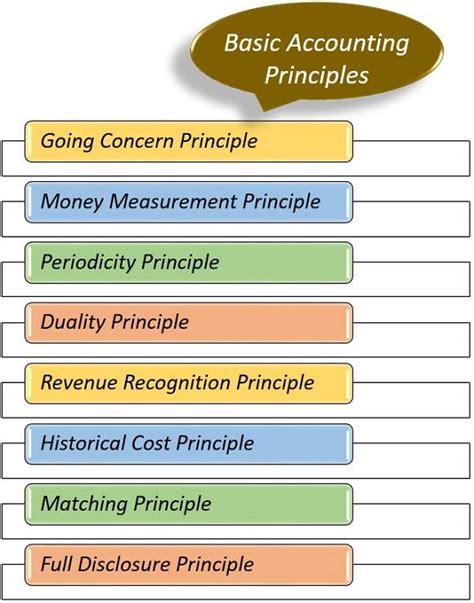
General ledger accounting is based on several key principles, including the accrual principle, the matching principle, and the materiality principle. The accrual principle states that revenues and expenses should be recognized when earned, regardless of when cash is received or paid. The matching principle states that expenses should be matched with the revenues they help to generate. The materiality principle states that financial information is material if its omission or misstatement could influence the decisions of stakeholders.
Benefits of General Ledger Accounting
The benefits of general ledger accounting are numerous, including improved financial management, enhanced decision-making, and increased transparency. By providing a comprehensive and accurate picture of an organization's financial position, the general ledger enables stakeholders to make informed decisions about investments, lending, and other business activities. Additionally, the general ledger helps organizations to identify areas for improvement, such as inefficient operations or inadequate cash management.General Ledger Accounting Software
General ledger accounting software is designed to streamline and automate the accounting process, providing a range of tools and features to support financial management. These systems typically include modules for accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, and financial reporting, as well as tools for budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis. By leveraging general ledger accounting software, organizations can reduce errors, increase efficiency, and improve financial visibility.
Best Practices for General Ledger Accounting
Best practices for general ledger accounting include maintaining a chart of accounts, reconciling accounts regularly, and performing periodic audits. Additionally, organizations should establish clear policies and procedures for accounting and financial reporting, as well as provide ongoing training and support for accounting staff. By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that their general ledger accounting system is accurate, reliable, and effective.Common General Ledger Accounting Errors
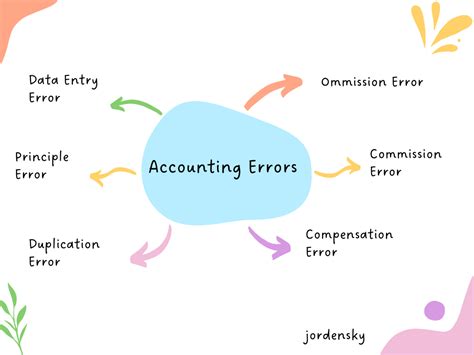
Common general ledger accounting errors include incorrect account coding, incomplete or inaccurate transaction recording, and failure to reconcile accounts. These errors can have significant consequences, including inaccurate financial statements, missed deadlines, and regulatory penalties. By understanding the common causes of general ledger accounting errors, organizations can take steps to prevent them and ensure the accuracy and reliability of their financial data.
General Ledger Accounting and Financial Analysis
General ledger accounting provides a foundation for financial analysis, enabling organizations to assess their financial performance, identify trends and patterns, and make informed decisions about investments and resource allocation. By using financial ratios and other analytical tools, organizations can gain insights into their financial position, liquidity, and profitability, as well as identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth.Gallery of General Ledger Accounting Images
General Ledger Accounting Image Gallery
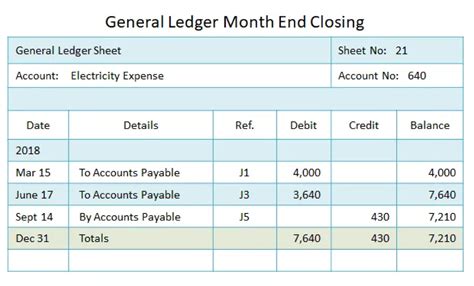

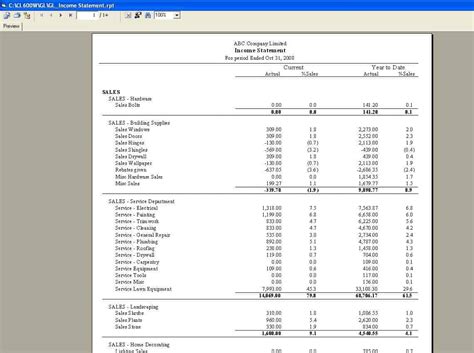

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a general ledger?
+The purpose of a general ledger is to provide a comprehensive and accurate record of all financial transactions within an organization.
What are the key components of a general ledger?
+The key components of a general ledger include accounts, journals, and ledgers.
How do I record transactions in a general ledger?
+Recording transactions in a general ledger involves identifying the transaction, determining the accounts affected, and posting the transaction to the general ledger.
What are the benefits of using general ledger accounting software?
+The benefits of using general ledger accounting software include improved financial management, enhanced decision-making, and increased transparency.
How often should I reconcile my general ledger accounts?
+It is recommended to reconcile your general ledger accounts on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure accuracy and detect any errors or discrepancies.
In conclusion, general ledger accounting is a critical component of financial management, providing a comprehensive and accurate record of all financial transactions within an organization. By understanding the basics of general ledger accounting, including the key components, recording transactions, and benefits of using accounting software, organizations can improve their financial management, enhance decision-making, and increase transparency. Whether you are a seasoned accountant or just starting to learn about accounting principles, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of general ledger accounting, including its importance, principles, and practical applications. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with general ledger accounting in the comments below, and to explore the resources and tools available to support your financial management needs.
