Intro
Discover what wholesalers are, their role in supply chains, and how they connect manufacturers with retailers, distributors, and buyers, facilitating bulk sales and inventory management with wholesale pricing and logistics.
The world of commerce is complex and multifaceted, with various players contributing to the supply chain. One crucial component of this chain is wholesalers, who act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers. Understanding the role of wholesalers is essential for anyone interested in the business world, as they play a significant part in ensuring that products reach consumers efficiently. In this article, we will delve into the world of wholesalers, exploring their importance, benefits, and the mechanisms by which they operate.
Wholesalers are businesses that purchase products in bulk from manufacturers and then resell them to retailers, who ultimately sell these products to end consumers. This process involves significant logistical and financial investments, as wholesalers must manage storage facilities, transportation, and inventory management. Despite these challenges, wholesalers provide a vital service by bridging the gap between producers and retailers, facilitating the smooth flow of goods through the supply chain.
The importance of wholesalers cannot be overstated. They enable manufacturers to focus on production, knowing that their products will be distributed effectively. Similarly, wholesalers provide retailers with access to a wide range of products, allowing them to cater to diverse consumer demands without having to establish direct relationships with numerous manufacturers. This intermediary role simplifies the supply chain, making it more efficient and cost-effective for all parties involved.
Benefits of Wholesalers

The benefits of wholesalers are manifold. Firstly, they offer economies of scale, allowing manufacturers to produce goods in large quantities, which can reduce production costs. Wholesalers also absorb some of the risks associated with holding inventory, as they purchase products upfront and then resell them. This risk absorption is crucial, as it protects manufacturers from fluctuations in demand and ensures that retailers have a consistent supply of products.
Moreover, wholesalers often provide additional services such as packaging, labeling, and transportation, which can be tailored to meet the specific needs of retailers. This customization enhances the overall efficiency of the supply chain, ensuring that products are delivered in the right condition and at the right time. Furthermore, wholesalers can negotiate better prices with manufacturers due to their bulk purchases, which can lead to cost savings for retailers and, ultimately, consumers.
Types of Wholesalers
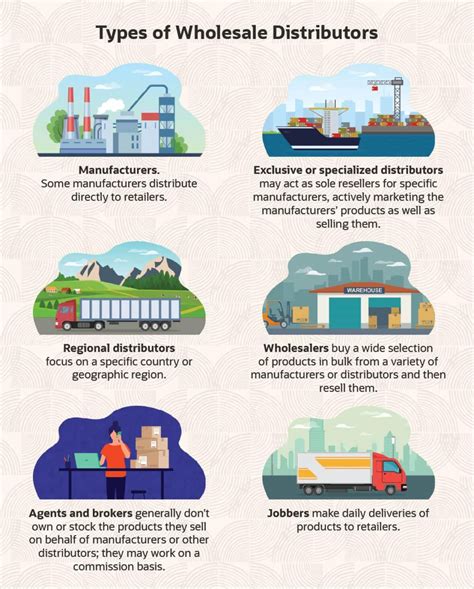
There are several types of wholesalers, each serving different segments of the market. General merchandise wholesalers deal with a broad range of products, from clothing to electronics, and are often the primary source for small and medium-sized retailers. Specialty wholesalers, on the other hand, focus on specific product categories, such as food or pharmaceuticals, and may offer specialized services like refrigerated storage.Another category is that of wholesale merchants, who may either sell to other wholesalers or directly to retailers. These merchants often have significant market power, as they can influence prices and product availability. Lastly, there are agents and brokers who act on behalf of manufacturers or retailers, facilitating transactions without taking ownership of the goods. These intermediaries are especially useful in international trade, where language barriers and legal complexities can hinder direct negotiations.
Working Mechanisms of Wholesalers
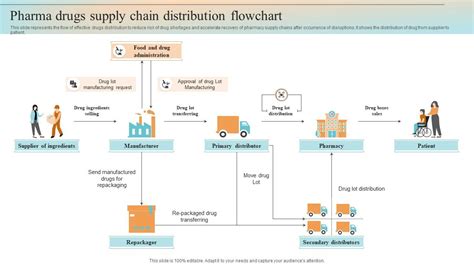
The working mechanisms of wholesalers involve a series of complex steps, from sourcing products to delivering them to retailers. Initially, wholesalers establish relationships with manufacturers, negotiating prices and terms of supply. They then purchase products in bulk, which are stored in warehouses or distribution centers. Inventory management is a critical function, as wholesalers must balance the need to hold sufficient stock with the risk of overstocking, which can lead to waste and financial losses.
Once products are stored, wholesalers may undertake additional tasks such as packaging, labeling, and quality control to ensure that goods meet retailer and consumer standards. They then sell these products to retailers, either through direct sales forces, online platforms, or trade shows. The transaction may involve credit terms, where wholesalers offer financing options to retailers, allowing them to purchase goods without immediate payment.
Steps to Become a Wholesaler
For individuals or businesses interested in becoming wholesalers, several steps must be taken: - **Research the Market**: Identify a niche or product category with demand and relatively low competition. - **Establish Relationships with Manufacturers**: Build trust and negotiate favorable terms, including pricing and payment conditions. - **Secure Financing**: Obtain the necessary capital to purchase initial inventory and cover operational costs. - **Set Up Logistics and Distribution**: Rent or lease a warehouse, and arrange for transportation and inventory management systems. - **Develop a Sales Strategy**: Create a plan to reach and serve retailers, which may include hiring a sales team, developing an e-commerce platform, or participating in industry events.Challenges Faced by Wholesalers

Despite their crucial role in the supply chain, wholesalers face numerous challenges. One of the most significant is the pressure to maintain low prices while ensuring profitability. This can be particularly difficult in competitive markets, where retailers may demand deep discounts to remain competitive. Additionally, wholesalers must manage inventory risks, as holding too much stock can lead to obsolescence and waste, while insufficient stock can result in lost sales.
The rise of e-commerce has also disrupted traditional wholesale models, as manufacturers increasingly sell directly to consumers, bypassing intermediaries. This trend requires wholesalers to adapt, offering value-added services that justify their position in the supply chain. Moreover, regulatory compliance, especially in industries like food and pharmaceuticals, can be complex and costly, necessitating significant investments in quality control and auditing processes.
Future of Wholesaling
The future of wholesaling is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and evolving business models. The integration of digital platforms, artificial intelligence, and data analytics will enhance supply chain visibility, efficiency, and responsiveness. Wholesalers who embrace these technologies will be better positioned to predict demand, manage inventory, and offer personalized services to retailers.Moreover, the trend towards sustainability and environmental responsibility will influence wholesaling practices, with a greater emphasis on reducing waste, using renewable energy, and promoting eco-friendly products. As consumers become more conscious of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions, wholesalers will need to adapt by sourcing products from responsible manufacturers and implementing green logistics practices.
Gallery of Wholesaling Images
Wholesaling Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary role of wholesalers in the supply chain?
+Wholesalers act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers, purchasing products in bulk and reselling them, thus facilitating the flow of goods through the supply chain.
How do wholesalers benefit manufacturers and retailers?
+Wholesalers benefit manufacturers by providing a consistent outlet for their products, allowing them to focus on production. For retailers, wholesalers offer a wide range of products, logistics support, and often, financing options, making it easier for them to stock and sell goods.
What challenges do wholesalers face in the modern market?
+Wholesalers face challenges such as maintaining low prices, managing inventory risks, adapting to e-commerce trends, and complying with regulatory requirements. They must also invest in technology and sustainability to remain competitive and relevant.
As we conclude our exploration of the world of wholesalers, it's clear that their role in the supply chain is multifaceted and indispensable. From facilitating the flow of goods to providing value-added services, wholesalers are the backbone of commerce, enabling manufacturers to produce and retailers to sell. As the business landscape continues to evolve, wholesalers must adapt, embracing technology, sustainability, and innovation to remain vital. We invite readers to share their insights and experiences with wholesaling, and to explore the resources and links provided to delve deeper into this fascinating topic. Whether you're a seasoned business professional or just starting your journey, understanding the importance of wholesalers can offer valuable perspectives on the intricacies of the supply chain and the opportunities that lie within.
