Intro
Discover 5 ways to define a vendor, including supplier management, procurement strategies, and partner relationships, to streamline business operations and improve vendor selection, evaluation, and performance metrics.
The concept of a vendor is crucial in various industries, including business, technology, and everyday commerce. Understanding the role and definition of a vendor can help individuals and organizations navigate complex supply chains, negotiate contracts, and ensure the quality of goods and services. In this article, we will delve into the world of vendors, exploring their definitions, types, and significance in different contexts.
A vendor can be defined as an individual or entity that sells goods or services to another party, often in a business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) setting. Vendors can operate in various sectors, including retail, wholesale, manufacturing, and technology. Their primary goal is to provide products or services that meet the needs of their customers, while also generating revenue and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Vendors play a vital role in the global economy, as they facilitate the exchange of goods and services between different parties. Without vendors, businesses and individuals would struggle to access the products and services they need to operate efficiently. In this sense, vendors are the backbone of commerce, enabling the flow of goods, services, and ideas across different industries and regions.
Definition of a Vendor
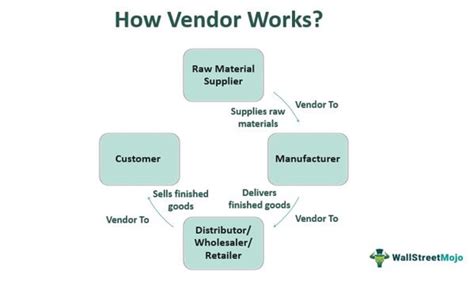
A vendor can be defined in several ways, depending on the context and industry. Here are five possible definitions:
- Supplier: A vendor can be seen as a supplier of goods or services, providing products that meet the needs of their customers. In this sense, vendors are responsible for sourcing, producing, and delivering products to their clients.
- Seller: A vendor can also be defined as a seller of goods or services, engaging in transactions with customers to exchange products for payment. In this context, vendors are focused on marketing, sales, and customer service.
- Partner: In some cases, a vendor can be considered a partner, working closely with clients to understand their needs and provide tailored solutions. This definition emphasizes the collaborative aspect of vendor relationships, where both parties work together to achieve mutual goals.
- Service Provider: A vendor can also be seen as a service provider, offering expertise, support, and maintenance to customers. In this sense, vendors are responsible for delivering high-quality services that meet the needs of their clients.
- Contractor: Finally, a vendor can be defined as a contractor, providing goods or services on a project-by-project basis. In this context, vendors are hired to complete specific tasks or deliver particular products, often working on a freelance or contract basis.
Types of Vendors
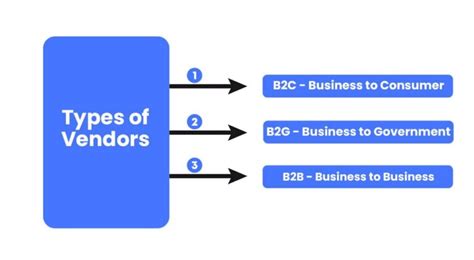
There are various types of vendors, each with their own unique characteristics and specialties. Some common types of vendors include:
- Manufacturing vendors: These vendors produce goods, such as raw materials, components, or finished products.
- Wholesale vendors: These vendors sell products in bulk to retailers, who then resell them to consumers.
- Retail vendors: These vendors sell products directly to consumers, often through brick-and-mortar stores or online platforms.
- Service vendors: These vendors provide intangible products, such as consulting, training, or support services.
- Technology vendors: These vendors provide software, hardware, or other technology solutions to businesses and individuals.
Importance of Vendors

Vendors play a vital role in the global economy, as they facilitate the exchange of goods and services between different parties. The importance of vendors can be seen in several areas:
- Economic growth: Vendors contribute to economic growth by creating jobs, generating revenue, and stimulating innovation.
- Supply chain management: Vendors are critical to supply chain management, as they provide the goods and services needed to keep businesses and industries running smoothly.
- Customer satisfaction: Vendors are responsible for delivering high-quality products and services that meet the needs of their customers, ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Competition: Vendors drive competition in the market, pushing businesses to innovate, improve quality, and reduce prices.
Vendor Management
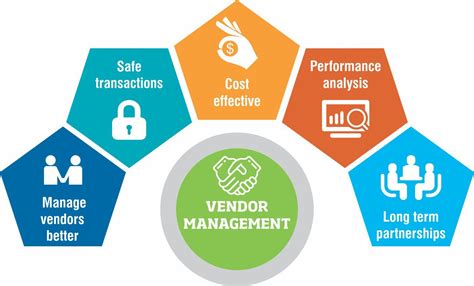
Effective vendor management is crucial for businesses and organizations, as it enables them to build strong relationships with vendors, negotiate contracts, and ensure the quality of goods and services. Some key aspects of vendor management include:
- Vendor selection: Choosing the right vendor is critical, as it can impact the quality of goods and services, as well as the overall cost.
- Contract negotiation: Negotiating contracts with vendors requires careful consideration of terms, conditions, and pricing.
- Performance monitoring: Monitoring vendor performance is essential to ensure that goods and services meet the required standards.
- Communication: Effective communication with vendors is vital to build trust, resolve issues, and ensure smooth collaboration.
Challenges Faced by Vendors

Vendors face various challenges in the market, including:
- Competition: Vendors must compete with other vendors to win contracts and customers.
- Regulatory compliance: Vendors must comply with regulations and laws, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Quality control: Vendors must ensure that their goods and services meet the required standards, which can be challenging in certain industries.
- Payment terms: Vendors often face payment terms that are unfavorable, such as late payments or strict payment schedules.
Future of Vendors

The future of vendors is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and evolving regulatory environments. Some trends that may impact vendors include:
- Digitalization: The increasing use of digital technologies, such as e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces, is likely to change the way vendors operate and interact with customers.
- Sustainability: Vendors may need to prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, as consumers become more conscious of the impact of their purchasing decisions.
- Globalization: The increasing globalization of trade and commerce may create new opportunities for vendors to expand their reach and customer base.
Vendor Image Gallery








What is a vendor?
+A vendor is an individual or entity that sells goods or services to another party, often in a business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-consumer (B2C) setting.
What are the different types of vendors?
+There are various types of vendors, including manufacturing vendors, wholesale vendors, retail vendors, service vendors, and technology vendors.
Why are vendors important?
+Vendors play a vital role in the global economy, as they facilitate the exchange of goods and services between different parties, contributing to economic growth, supply chain management, and customer satisfaction.
How do vendors manage their relationships with customers?
+Vendors manage their relationships with customers through effective communication, contract negotiation, performance monitoring, and quality control.
What challenges do vendors face in the market?
+Vendors face various challenges, including competition, regulatory compliance, quality control, and payment terms.
In conclusion, the concept of a vendor is complex and multifaceted, encompassing various definitions, types, and significance in different contexts. As the global economy continues to evolve, vendors will play an increasingly important role in facilitating the exchange of goods and services between different parties. By understanding the importance of vendors and the challenges they face, businesses and organizations can build strong relationships with their vendors, ensuring the quality of goods and services and driving economic growth. We invite you to share your thoughts on the role of vendors in the economy and how they can be supported to drive innovation and success.
