Intro
Optimize your online presence with 5 DNS settings tips, improving domain name system security, DNS resolver, and network performance, while reducing DNS lookup times and enhancing overall web browsing experience.
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a critical component of the internet, responsible for translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand. DNS settings play a crucial role in ensuring the stability, security, and performance of online applications and websites. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNS settings, exploring the importance of optimizing them for a seamless online experience.
Effective DNS settings can significantly impact the speed and reliability of website loading, email delivery, and online transactions. A well-configured DNS setup can also enhance security, protecting users from cyber threats and data breaches. On the other hand, poorly configured DNS settings can lead to slow loading times, downtime, and increased vulnerability to attacks. As the internet continues to evolve, the importance of DNS settings will only continue to grow, making it essential for individuals and organizations to understand the basics of DNS configuration.
The process of configuring DNS settings can seem daunting, especially for those without extensive technical expertise. However, with the right guidance, anyone can optimize their DNS settings to achieve faster, more secure, and more reliable online experiences. In the following sections, we will provide an in-depth exploration of DNS settings, including tips, best practices, and expert advice. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or a beginner, this article aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to take control of your DNS settings and unlock the full potential of your online presence.
Understanding DNS Settings
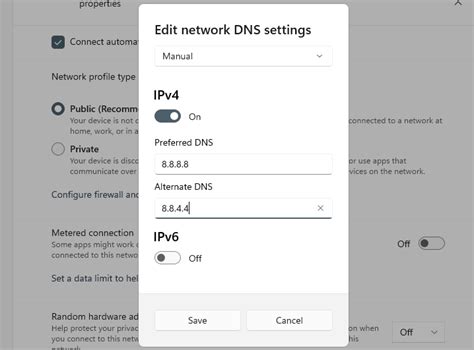
Key Components of DNS Settings
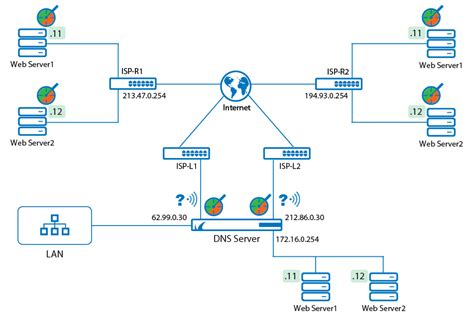
The key components of DNS settings include: * DNS servers: These are the servers responsible for resolving domain names into IP addresses. * DNS records: These provide the necessary information for DNS servers to perform their functions, such as A records, MX records, and CNAME records. * DNS protocols: These include DNSSEC, DNS over HTTPS (DoH), and DNS over TLS (DoT), which ensure the security and integrity of DNS transactions. * DNS caching: This involves storing frequently accessed DNS records in memory to reduce the time it takes to resolve domain names.Optimizing DNS Settings for Performance
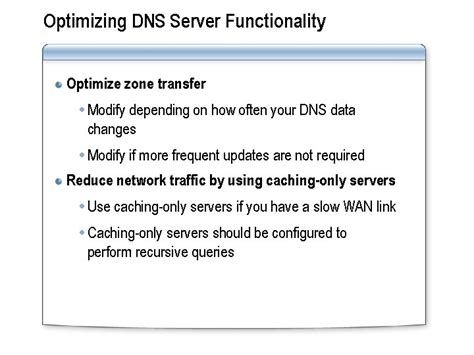
Tips for Optimizing DNS Settings
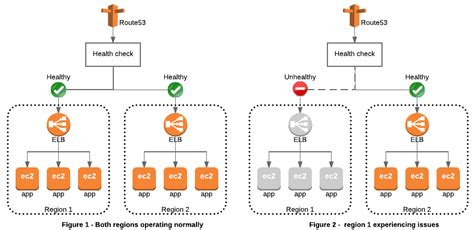
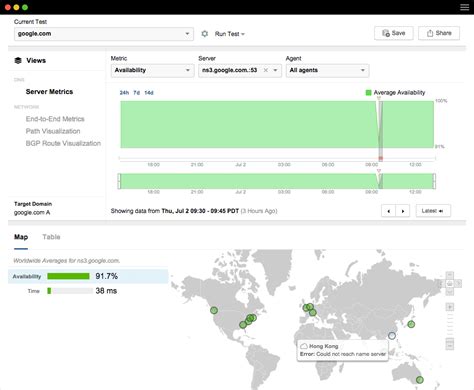
Some additional tips for optimizing DNS settings include: * Monitoring DNS performance: This involves tracking DNS query times, error rates, and other key performance indicators to identify areas for improvement. * Using DNS load balancing: This involves distributing DNS traffic across multiple servers to improve responsiveness and reduce the risk of downtime. * Implementing DNS failover: This involves configuring DNS servers to automatically switch to a backup server in the event of a failure, ensuring minimal disruption to online services.Enhancing DNS Security
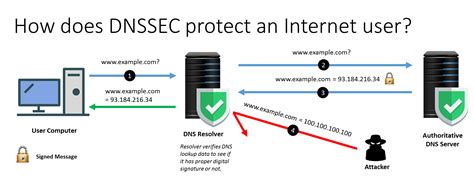
Best Practices for DNS Security
Some additional best practices for DNS security include: * Regularly updating DNS software: This ensures that DNS servers and clients have the latest security patches and features. * Using secure DNS protocols: This includes protocols such as DNS over TLS (DoT) and DNS over HTTPS (DoH), which provide end-to-end encryption for DNS transactions. * Implementing DNS access controls: This involves restricting access to DNS servers and clients to authorized personnel and devices.Common DNS Settings Mistakes
Tips for Avoiding DNS Settings Mistakes
Some additional tips for avoiding DNS settings mistakes include: * Regularly reviewing DNS settings: This involves checking DNS servers, DNS records, and DNS protocols to ensure they are configured correctly. * Using DNS management tools: These tools can help simplify DNS configuration and reduce the risk of errors. * Testing DNS settings: This involves verifying that DNS settings are working as expected and making adjustments as needed.Advanced DNS Settings Techniques
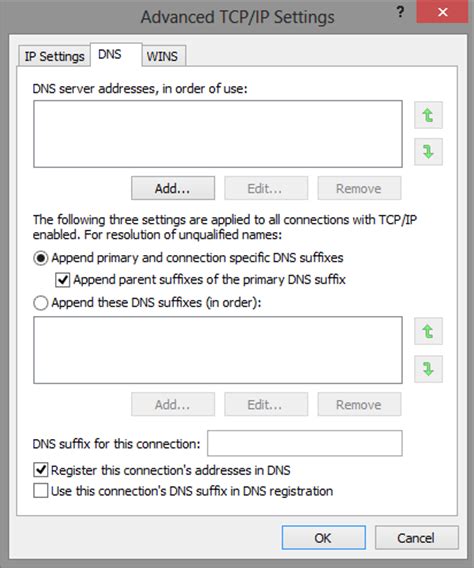
Best Practices for Advanced DNS Settings
Some additional best practices for advanced DNS settings include: * Using automation tools: These tools can help simplify DNS configuration and reduce the risk of errors. * Monitoring DNS performance: This involves tracking DNS query times, error rates, and other key performance indicators to identify areas for improvement. * Testing DNS settings: This involves verifying that DNS settings are working as expected and making adjustments as needed.DNS Settings Image Gallery


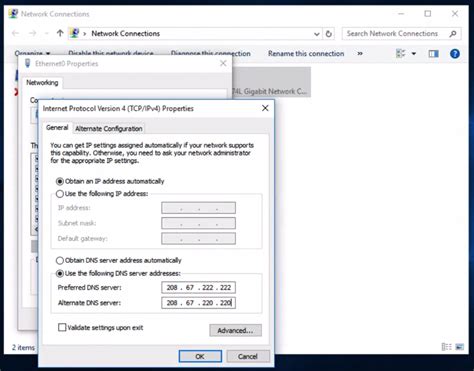

What is DNS and how does it work?
+DNS (Domain Name System) is a system that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand. It works by using a network of DNS servers to resolve domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites and online applications.
Why is DNS security important?
+DNS security is important because it helps protect users from cyber threats such as DNS amplification attacks, DNS tunneling, and DNS spoofing. These attacks can compromise the integrity of online applications and websites, leading to data breaches, downtime, and other security incidents.
How can I optimize my DNS settings for performance?
+You can optimize your DNS settings for performance by using high-performance DNS servers, implementing DNS caching, and using content delivery networks (CDNs). You can also use DNS load balancing and DNS failover to improve responsiveness and reduce the risk of downtime.
What are some common DNS settings mistakes?
+Common DNS settings mistakes include using default DNS settings, failing to monitor DNS activity, not implementing DNSSEC, and using outdated DNS software. These mistakes can leave online applications and websites vulnerable to security threats and performance issues.
How can I avoid DNS settings mistakes?
+You can avoid DNS settings mistakes by regularly reviewing DNS settings, using DNS management tools, and testing DNS settings. You can also use automation tools to simplify DNS configuration and reduce the risk of errors.
In
