Intro
Discover what a General Ledger is, a crucial accounting tool for financial management, featuring ledger accounts, journal entries, and trial balances, to streamline financial reporting and analysis.
General ledger is a crucial component of any organization's accounting system, serving as the primary recording system for all financial transactions. It is a comprehensive and detailed account of every transaction that occurs within a business, providing a clear picture of its financial position and performance. The general ledger is often referred to as the "book of final entry" because it contains the summarised and classified information from the journal entries, which are the initial recordings of transactions.
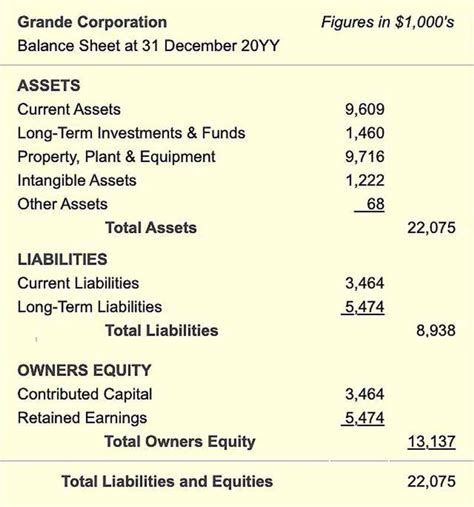
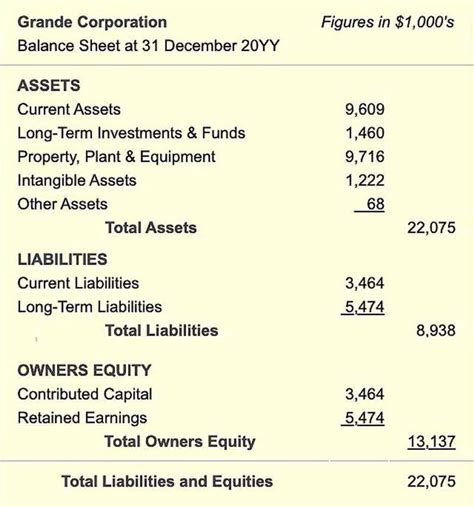
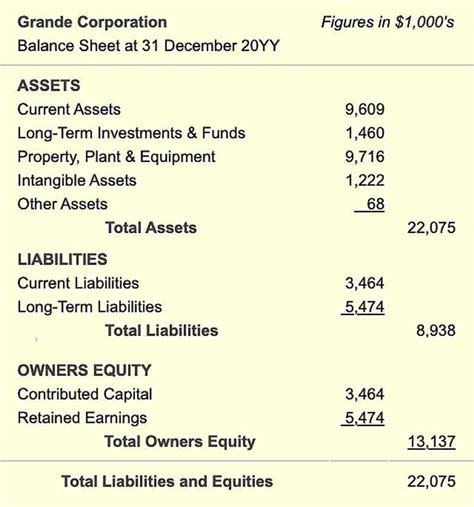
The importance of a general ledger cannot be overstated, as it provides the foundation for preparing financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement. These statements are essential for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, to make informed decisions about the organization. A well-maintained general ledger ensures that financial transactions are accurately recorded, classified, and reported, enabling businesses to comply with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
In today's fast-paced business environment, the general ledger plays a vital role in supporting strategic decision-making. By providing a centralized repository of financial data, it enables organizations to analyze their financial performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. The general ledger is also essential for auditing and financial reporting purposes, as it provides a transparent and auditable record of all financial transactions.
Overview of General Ledger
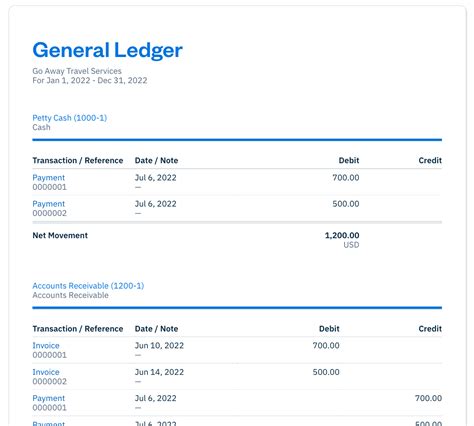
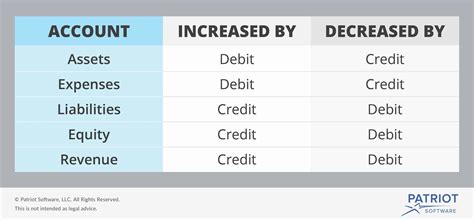
A general ledger typically consists of a set of accounts, each representing a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense. These accounts are categorized into different groups, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses, to facilitate financial reporting and analysis. The general ledger is updated regularly to reflect changes in the organization's financial position, such as the purchase of assets, payment of expenses, or receipt of revenues.
The general ledger is often maintained using accounting software, which provides a range of features and tools to support financial management. These software solutions enable organizations to automate many of the tasks associated with maintaining a general ledger, such as data entry, account reconciliation, and financial reporting. Additionally, they provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling businesses to gain deeper insights into their financial performance and make more informed decisions.
Key Components of General Ledger
The general ledger consists of several key components, including: * Chart of accounts: a list of all accounts used by the organization to record financial transactions * Account balances: the current balance of each account, which is updated regularly to reflect changes in the organization's financial position * Journal entries: the initial recordings of transactions, which are later posted to the general ledger * Ledger accounts: the individual accounts that make up the general ledger, each representing a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expenseTypes of General Ledger Accounts
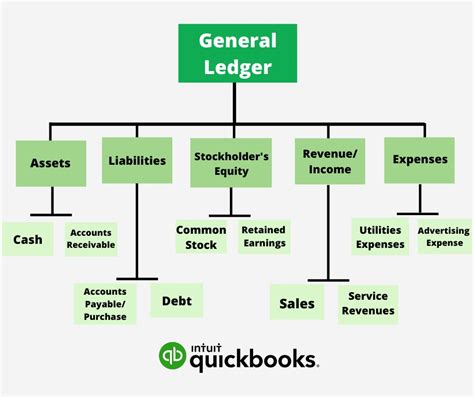
There are several types of general ledger accounts, each serving a specific purpose. These include:
- Asset accounts: represent the organization's assets, such as cash, accounts receivable, and property, plant, and equipment
- Liability accounts: represent the organization's liabilities, such as accounts payable, loans, and taxes owed
- Equity accounts: represent the organization's equity, such as common stock, retained earnings, and dividends
- Revenue accounts: represent the organization's revenues, such as sales, services, and interest income
- Expense accounts: represent the organization's expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities
Benefits of General Ledger
The general ledger provides several benefits to organizations, including: * Improved financial reporting: the general ledger provides a centralized repository of financial data, enabling organizations to prepare accurate and timely financial statements * Enhanced decision-making: the general ledger provides a clear picture of an organization's financial position and performance, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions * Increased efficiency: the general ledger automates many of the tasks associated with financial management, such as data entry and account reconciliation * Better compliance: the general ledger ensures that financial transactions are accurately recorded and reported, enabling organizations to comply with accounting standards and regulatory requirementsGeneral Ledger Accounting Process

The general ledger accounting process involves several steps, including:
- Identifying and recording transactions: the organization identifies and records all financial transactions, such as the purchase of assets, payment of expenses, or receipt of revenues
- Classifying transactions: the organization classifies each transaction into a specific account, such as an asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense
- Posting transactions: the organization posts each transaction to the general ledger, updating the relevant account balances
- Preparing financial statements: the organization uses the general ledger to prepare financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement
Common General Ledger Accounts
Some common general ledger accounts include: * Cash: represents the organization's cash balance * Accounts receivable: represents the amount owed to the organization by its customers * Accounts payable: represents the amount owed by the organization to its suppliers * Salaries expense: represents the organization's salary expenses * Rent expense: represents the organization's rent expensesGeneral Ledger Reconciliation
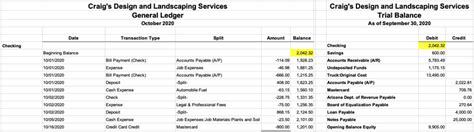
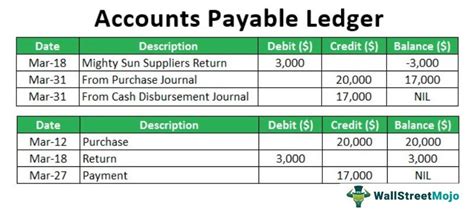
General ledger reconciliation is the process of verifying the accuracy of the general ledger accounts by comparing them with external statements, such as bank statements. This process involves:
- Identifying discrepancies: the organization identifies any discrepancies between the general ledger accounts and the external statements
- Investigating discrepancies: the organization investigates the cause of each discrepancy and makes any necessary adjustments
- Reconciling accounts: the organization reconciles the general ledger accounts with the external statements, ensuring that they are accurate and up-to-date
General Ledger Software
General ledger software is a type of accounting software that is designed to support the general ledger accounting process. These software solutions provide a range of features and tools, including: * Automated data entry: the software automates many of the tasks associated with data entry, such as posting transactions to the general ledger * Account reconciliation: the software provides tools to support account reconciliation, such as automated reconciliation and discrepancy identification * Financial reporting: the software provides advanced financial reporting capabilities, enabling organizations to prepare accurate and timely financial statementsGeneral Ledger Best Practices
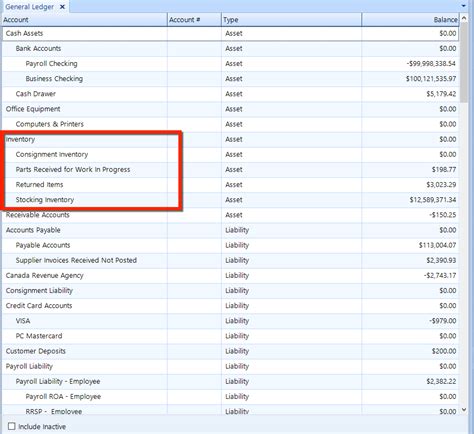
Some best practices for maintaining a general ledger include:
- Regularly reviewing and updating the chart of accounts: the organization regularly reviews and updates the chart of accounts to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date
- Implementing effective internal controls: the organization implements effective internal controls to ensure that financial transactions are accurately recorded and reported
- Providing ongoing training and support: the organization provides ongoing training and support to accounting staff to ensure that they are familiar with the general ledger accounting process
Common General Ledger Errors
Some common general ledger errors include: * Incorrect account classification: the organization incorrectly classifies a transaction, resulting in an inaccurate account balance * Failure to reconcile accounts: the organization fails to reconcile the general ledger accounts with external statements, resulting in inaccurate financial reporting * Insufficient internal controls: the organization fails to implement effective internal controls, resulting in inaccurate or fraudulent financial reportingGeneral Ledger Image Gallery


What is the purpose of a general ledger?
+The purpose of a general ledger is to provide a centralized repository of financial data, enabling organizations to prepare accurate and timely financial statements.
What are the key components of a general ledger?
+The key components of a general ledger include the chart of accounts, account balances, journal entries, and ledger accounts.
What is the difference between a general ledger and a journal?
+A general ledger is a comprehensive and detailed account of every transaction that occurs within a business, while a journal is the initial recording of a transaction.
How often should a general ledger be reconciled?
+A general ledger should be reconciled regularly, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date.
What are some common general ledger errors?
+Some common general ledger errors include incorrect account classification, failure to reconcile accounts, and insufficient internal controls.
In conclusion, a general ledger is a critical component of any organization's accounting system, providing a centralized repository of financial data and enabling the preparation of accurate and timely financial statements. By understanding the key components, benefits, and best practices associated with a general ledger, organizations can ensure that their financial management is effective and efficient. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with general ledger accounting in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available for learning more about this important topic.
