Intro
Master retail math with 5 essential tips, including inventory turnover, gross margin, and sales analysis, to boost profitability and optimize retail operations management.
The world of retail is a complex and ever-changing landscape, where businesses must constantly adapt to stay ahead of the competition. One crucial aspect of retail that can make or break a business is math. Retail math is the backbone of any retail operation, and understanding its concepts is essential for making informed decisions, maximizing profits, and minimizing losses. In this article, we will delve into the world of retail math, exploring its importance, key concepts, and providing valuable tips for retailers to improve their mathematical skills.
Retail math is not just about basic arithmetic operations; it involves a deep understanding of various concepts, such as markup, margin, inventory management, and sales forecasting. These concepts are interconnected and have a significant impact on a retailer's bottom line. For instance, a retailer who fails to accurately calculate their markup and margin may end up pricing their products incorrectly, leading to reduced sales and profits. On the other hand, a retailer who masters retail math can make data-driven decisions, optimize their inventory, and drive business growth.
As we explore the world of retail math, it becomes clear that it is an essential tool for retailers to stay competitive in today's fast-paced market. With the rise of e-commerce and changing consumer behavior, retailers must be able to analyze data, identify trends, and make informed decisions quickly. Retail math provides the foundation for this analysis, enabling retailers to calculate key metrics, such as sales per square foot, inventory turnover, and gross margin return on investment (GMROI). By mastering these concepts, retailers can gain a deeper understanding of their business, identify areas for improvement, and develop strategies to drive growth and profitability.
Understanding Retail Math Concepts

Before we dive into the tips, it's essential to understand some key retail math concepts. These concepts include markup, margin, inventory turnover, and sales forecasting. Markup refers to the amount added to the cost of a product to determine its selling price. Margin, on the other hand, is the difference between the selling price and the cost of the product, expressed as a percentage. Inventory turnover measures how quickly a retailer sells and replaces their inventory, while sales forecasting involves predicting future sales based on historical data and market trends. Understanding these concepts is crucial for retailers, as they provide the foundation for making informed decisions and driving business growth.
Key Retail Math Formulas
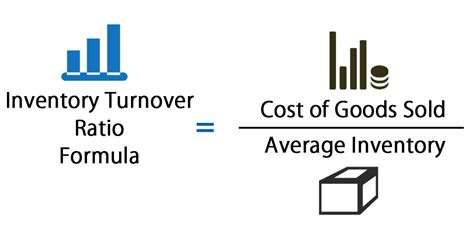
Some essential retail math formulas include: * Markup = (Selling Price - Cost) / Cost * Margin = (Selling Price - Cost) / Selling Price * Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory * Sales Forecasting = (Historical Sales Data + Market Trends) / Time PeriodThese formulas provide the basis for calculating key metrics and making informed decisions. By understanding and applying these formulas, retailers can optimize their pricing, inventory, and sales strategies, driving business growth and profitability.
Tip 1: Calculate Markup and Margin Accurately

Calculating markup and margin accurately is crucial for retailers, as it enables them to determine the optimal selling price for their products. Markup and margin are interconnected, and understanding their relationship is essential for making informed decisions. A retailer who calculates their markup and margin accurately can identify opportunities to increase profits, optimize their pricing strategy, and drive business growth.
To calculate markup and margin accurately, retailers should follow these steps:
- Determine the cost of the product
- Calculate the desired markup and margin
- Determine the selling price based on the markup and margin
- Monitor and adjust the selling price as needed
By following these steps, retailers can ensure that they are calculating their markup and margin accurately, enabling them to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Some common mistakes to avoid when calculating markup and margin include: * Failing to account for all costs, such as labor and overhead * Using incorrect formulas or calculations * Not monitoring and adjusting the selling price regularlyBy avoiding these mistakes, retailers can ensure that they are calculating their markup and margin accurately, driving business growth and profitability.
Tip 2: Optimize Inventory Management
Inventory management is a critical aspect of retail math, as it enables retailers to optimize their inventory levels, reduce waste, and drive business growth. Effective inventory management involves understanding inventory turnover, lead time, and safety stock. By optimizing inventory management, retailers can reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and increase profits.
To optimize inventory management, retailers should follow these steps:
- Calculate inventory turnover regularly
- Determine the optimal inventory levels based on historical data and market trends
- Monitor and adjust inventory levels regularly
- Implement a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system to reduce waste and improve efficiency
By following these steps, retailers can optimize their inventory management, reducing costs and driving business growth.
Benefits of Effective Inventory Management
Some benefits of effective inventory management include: * Reduced waste and obsolescence * Improved customer satisfaction * Increased profits * Better cash flow managementBy optimizing inventory management, retailers can achieve these benefits, driving business growth and profitability.
Tip 3: Analyze Sales Data and Forecast Future Sales
Analyzing sales data and forecasting future sales is essential for retailers, as it enables them to identify trends, optimize their inventory, and drive business growth. Sales forecasting involves predicting future sales based on historical data and market trends. By analyzing sales data and forecasting future sales, retailers can make informed decisions, optimize their pricing strategy, and drive business growth.
To analyze sales data and forecast future sales, retailers should follow these steps:
- Collect and analyze historical sales data
- Identify trends and patterns in the data
- Determine the factors that influence sales, such as seasonality and weather
- Use statistical models or machine learning algorithms to forecast future sales
By following these steps, retailers can analyze sales data and forecast future sales accurately, driving business growth and profitability.
Common Sales Forecasting Methods
Some common sales forecasting methods include: * Naive method * Moving average method * Exponential smoothing method * Regression analysisBy using these methods, retailers can forecast future sales accurately, making informed decisions and driving business growth.
Tip 4: Use Retail Math to Optimize Pricing Strategy
Pricing strategy is a critical aspect of retail math, as it enables retailers to optimize their pricing, drive business growth, and increase profits. Retailers should use retail math to determine the optimal selling price for their products, taking into account factors such as markup, margin, and competition. By optimizing pricing strategy, retailers can drive business growth, increase profits, and improve customer satisfaction.
To optimize pricing strategy, retailers should follow these steps:
- Calculate the cost of the product
- Determine the desired markup and margin
- Research the competition and market trends
- Determine the optimal selling price based on the markup, margin, and competition
By following these steps, retailers can optimize their pricing strategy, driving business growth and profitability.
Benefits of Optimized Pricing Strategy
Some benefits of optimized pricing strategy include: * Increased profits * Improved customer satisfaction * Competitive advantage * Better cash flow managementBy optimizing pricing strategy, retailers can achieve these benefits, driving business growth and profitability.
Tip 5: Monitor and Adjust Retail Math Metrics Regularly

Monitoring and adjusting retail math metrics regularly is essential for retailers, as it enables them to identify areas for improvement, optimize their operations, and drive business growth. Retailers should regularly calculate key metrics, such as markup, margin, inventory turnover, and sales forecasting, and adjust their strategies accordingly. By monitoring and adjusting retail math metrics regularly, retailers can stay ahead of the competition, drive business growth, and increase profits.
To monitor and adjust retail math metrics regularly, retailers should follow these steps:
- Calculate key metrics regularly
- Identify areas for improvement
- Adjust strategies accordingly
- Monitor and adjust metrics regularly to ensure continuous improvement
By following these steps, retailers can monitor and adjust retail math metrics regularly, driving business growth and profitability.
Common Retail Math Metrics to Monitor
Some common retail math metrics to monitor include: * Markup and margin * Inventory turnover * Sales forecasting * Gross margin return on investment (GMROI)By monitoring these metrics, retailers can identify areas for improvement, optimize their operations, and drive business growth.
Retail Math Image Gallery



What is retail math, and why is it important?
+Retail math is the application of mathematical concepts to retail operations, including pricing, inventory management, and sales forecasting. It is essential for retailers to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and drive business growth.
How do I calculate markup and margin?
+Markup is calculated by adding the desired profit to the cost of the product, while margin is calculated by dividing the profit by the selling price. The formulas for markup and margin are: Markup = (Selling Price - Cost) / Cost and Margin = (Selling Price - Cost) / Selling Price.
What is the importance of inventory management in retail?
+Inventory management is critical in retail, as it enables retailers to optimize their inventory levels, reduce waste, and drive business growth. Effective inventory management involves understanding inventory turnover, lead time, and safety stock.
How do I forecast future sales?
+Sales forecasting involves predicting future sales based on historical data and market trends. Retailers can use statistical models or machine learning algorithms to forecast future sales, taking into account factors such as seasonality and weather.
What are some common retail math metrics to monitor?
+Some common retail math metrics to monitor include markup and margin, inventory turnover, sales forecasting, and gross margin return on investment (GMROI). These metrics provide insights into a retailer's operations and enable them to make informed decisions.
In conclusion, retail math is a critical aspect of retail operations, enabling retailers to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and drive business growth. By following the tips outlined in this article, retailers can improve their mathematical skills, optimize their pricing strategy, and drive business growth. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips on retail math in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with their colleagues and friends who may benefit from the information. By working together, we can help retailers master retail math and drive business success.
