Intro
Discover what GL means, exploring General Ledger definitions, accounting concepts, and financial management systems, to understand its role in bookkeeping and ledger accounting processes.
The importance of understanding gluten and its effects on the human body has become a significant topic of discussion in recent years. With the rise of gluten-free diets and the increasing awareness of gluten-related disorders, it's essential to delve into the world of gluten and explore its implications on our health. Gluten, a protein found in certain grains, can have both positive and negative effects on the body, depending on individual circumstances. As we navigate the complexities of gluten, it's crucial to separate fact from fiction and provide a comprehensive understanding of this multifaceted topic.
Gluten is a type of protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, which are commonly consumed grains in many parts of the world. It's responsible for the elasticity and structure of dough, making it a vital component in baking. However, for some individuals, gluten can be detrimental to their health, causing a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to severe reactions. The prevalence of gluten-related disorders has sparked a growing interest in gluten-free diets, with many people adopting this lifestyle choice in hopes of alleviating symptoms or improving overall well-being.
As we explore the world of gluten, it's essential to recognize the different types of gluten-related disorders, including celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and wheat allergy. Each of these conditions has distinct characteristics and requires unique approaches to management and treatment. By understanding the nuances of gluten and its effects on the body, we can better navigate the complexities of gluten-related disorders and make informed decisions about our dietary choices. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a individual with a gluten-related disorder, or simply someone interested in learning more about this topic, this article aims to provide a comprehensive and informative exploration of the world of gluten.
Introduction to Gluten

Types of Gluten-Related Disorders
There are several types of gluten-related disorders, each with distinct characteristics and requirements for management and treatment. These include: * Celiac disease: an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to react to gluten, leading to inflammation and damage in the small intestine. * Non-celiac gluten sensitivity: a condition characterized by symptoms similar to celiac disease, but without the same level of immune system activation and intestinal damage. * Wheat allergy: an immune system reaction to one of the proteins in wheat, which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial in providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.Celiac Disease
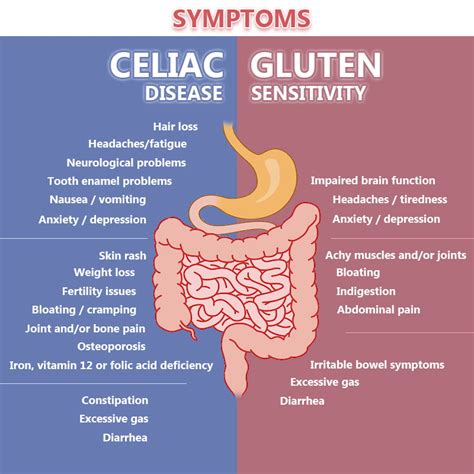
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity is a condition characterized by symptoms similar to celiac disease, but without the same level of immune system activation and intestinal damage. The exact mechanisms behind non-celiac gluten sensitivity are not yet fully understood, but research suggests that it may be related to changes in gut bacteria, inflammation, and immune system function. Symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity can include bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, and may be similar to those experienced by individuals with celiac disease. However, the lack of intestinal damage and immune system activation distinguishes non-celiac gluten sensitivity from celiac disease.Wheat Allergy

Gluten-Free Diets
Gluten-free diets have become increasingly popular in recent years, with many individuals adopting this lifestyle choice in hopes of alleviating symptoms or improving overall well-being. However, it's essential to recognize that gluten-free diets are not suitable for everyone and may be necessary only for those with a diagnosed gluten-related disorder. For individuals with celiac disease, a strict gluten-free diet is the only effective treatment, and even small amounts of gluten can cause significant harm. In contrast, individuals with non-celiac gluten sensitivity may find that a gluten-free diet helps to alleviate symptoms, but the evidence for this is still limited, and more research is needed to fully understand the benefits and risks of gluten-free diets.Benefits and Risks of Gluten-Free Diets

Practical Tips for Following a Gluten-Free Diet
For individuals who require a gluten-free diet, there are several practical tips to help make the transition easier: * Read food labels carefully to identify gluten-containing ingredients. * Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. * Explore gluten-free alternatives to traditional grains, such as rice, quinoa, and corn. * Consider working with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to develop a personalized meal plan.Gallery of Gluten-Related Images
Gluten Image Gallery
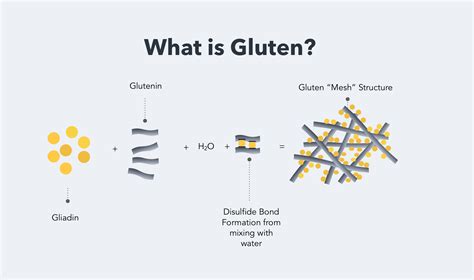









Frequently Asked Questions
What is gluten?
+Gluten is a type of protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, which are commonly consumed grains in many parts of the world.
What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
+The symptoms of celiac disease can include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue, as well as malabsorption of essential nutrients.
Is a gluten-free diet suitable for everyone?
+No, a gluten-free diet is not suitable for everyone and may be necessary only for those with a diagnosed gluten-related disorder.
How can I follow a gluten-free diet?
+To follow a gluten-free diet, read food labels carefully, focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and explore gluten-free alternatives to traditional grains.
What are the benefits and risks of a gluten-free diet?
+A gluten-free diet can have both benefits and risks, depending on individual circumstances, and it's essential to weigh the potential benefits and risks before making any significant changes to your diet.
In conclusion, the world of gluten is complex and multifaceted, with both positive and negative effects on the body. By understanding the different types of gluten-related disorders, the benefits and risks of gluten-free diets, and practical tips for following a gluten-free lifestyle, we can make informed decisions about our dietary choices and improve overall well-being. Whether you're a healthcare professional, an individual with a gluten-related disorder, or simply someone interested in learning more about this topic, we hope this article has provided a comprehensive and informative exploration of the world of gluten. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and engage in a discussion about the complexities of gluten and its effects on our health.
