Intro
Discover how General Ledger works with 5 key methods, utilizing accounting software, financial reporting, and ledger accounts to streamline financial management, accounting processes, and bookkeeping tasks.
The general ledger is a crucial component of any accounting system, serving as the central repository for all financial transactions within an organization. It provides a comprehensive and detailed record of every transaction, allowing businesses to track their financial performance, make informed decisions, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. In this article, we will delve into the five ways the general ledger works, exploring its importance, benefits, and key features.
The general ledger is often referred to as the "book of final entry" because it contains the summary of all transactions recorded in the various journals and sub-ledgers throughout the accounting system. This ledger is typically organized into a series of accounts, each representing a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense. By analyzing the general ledger, businesses can gain valuable insights into their financial position, identify trends and patterns, and make adjustments to optimize their operations.
The importance of the general ledger cannot be overstated, as it provides the foundation for financial reporting, budgeting, and forecasting. By maintaining an accurate and up-to-date general ledger, businesses can ensure that their financial statements are reliable and compliant with accounting standards. Moreover, the general ledger serves as a critical tool for internal control, enabling organizations to detect and prevent errors, irregularities, and fraudulent activities.
Introduction to General Ledger

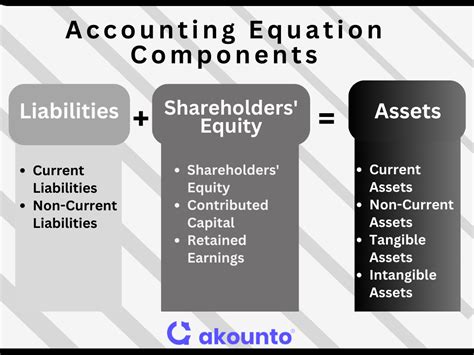
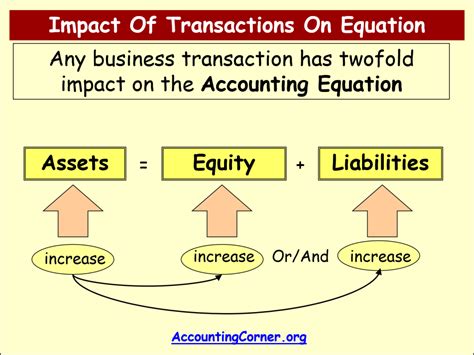
Accounts and Accounting Equations
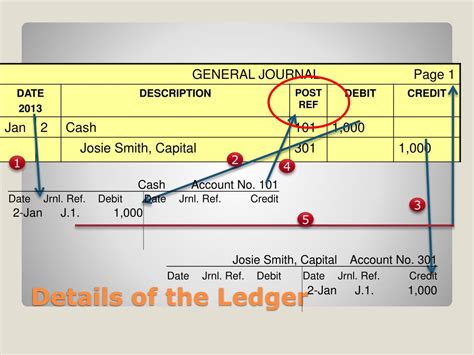
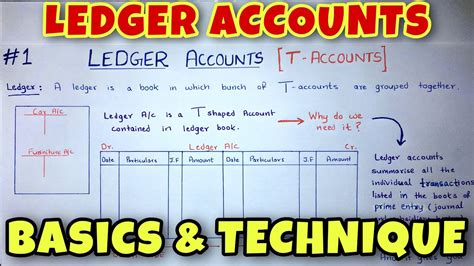
Journal Entries and Ledger Posting
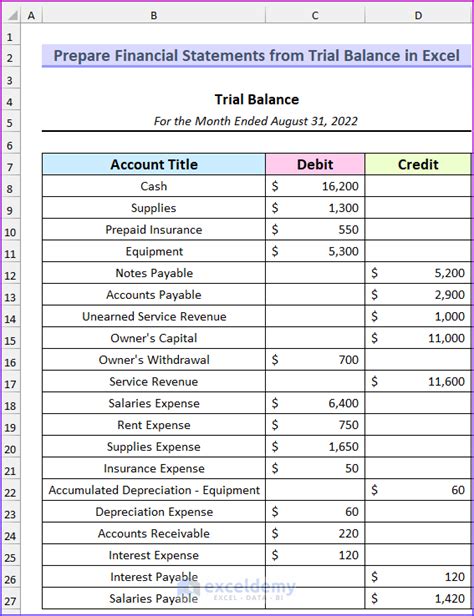
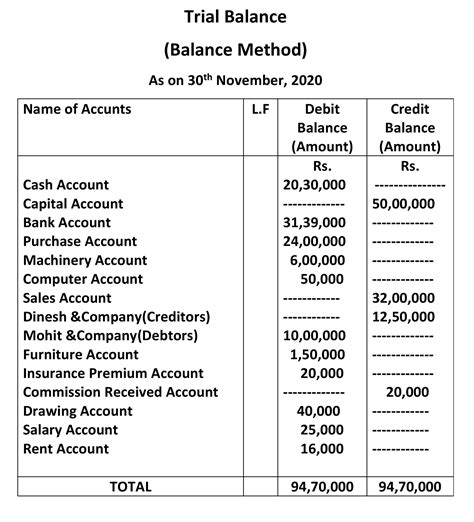
Trail Balance and Financial Statements
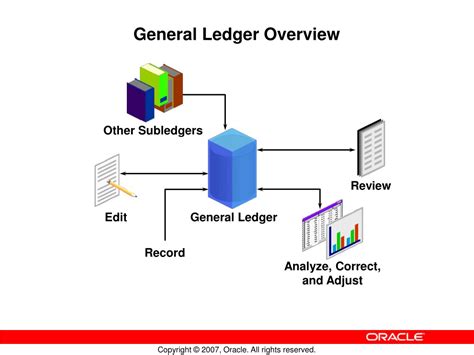
General Ledger Reconciliation

In addition to these key features, the general ledger also provides a range of benefits, including improved financial reporting, enhanced internal control, and increased efficiency. By maintaining an accurate and up-to-date general ledger, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Some of the key benefits of the general ledger include:
- Improved financial reporting: The general ledger provides the foundation for financial reporting, enabling businesses to prepare accurate and reliable financial statements.
- Enhanced internal control: The general ledger serves as a critical tool for internal control, enabling organizations to detect and prevent errors, irregularities, and fraudulent activities.
- Increased efficiency: The general ledger automates many accounting tasks, reducing the risk of errors and increasing the efficiency of the accounting process.
- Better decision-making: The general ledger provides businesses with a comprehensive overview of their financial performance, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
To illustrate the importance of the general ledger, consider the following example: A company has a general ledger that is not properly maintained, resulting in inaccurate financial reporting and poor internal control. As a result, the company is unable to make informed decisions, and its financial performance suffers. By implementing a well-designed general ledger system, the company can improve its financial reporting, enhance its internal control, and increase its efficiency, ultimately leading to better decision-making and improved financial performance.
In conclusion, the general ledger is a critical component of any accounting system, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of all financial transactions. By understanding how the general ledger works, businesses can maintain accurate and reliable financial records, make informed decisions, and achieve their strategic objectives.
Gallery of General Ledger
General Ledger Image Gallery



What is the purpose of the general ledger?
+The general ledger is the central repository for all financial transactions within an organization, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of every transaction.
How does the general ledger work?
+The general ledger works by recording, classifying, and reporting financial transactions, as well as reconciling accounts and preparing financial statements.
What are the benefits of the general ledger?
+The general ledger provides improved financial reporting, enhanced internal control, and increased efficiency, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and achieve their strategic objectives.
How is the general ledger used in financial reporting?
+The general ledger is used to prepare financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which provide stakeholders with a comprehensive overview of the organization's financial performance and position.
What is the importance of reconciling the general ledger?
+Reconciling the general ledger is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting, as well as to detect and prevent errors, irregularities, and fraudulent activities.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the general ledger and its importance in accounting. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with the general ledger, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your colleagues and friends who may benefit from this knowledge.
