Intro
Learn about Inventory Turnover Rate, a key metric for supply chain efficiency, calculating sales, costs, and asset management to optimize logistics and boost business performance.
The inventory turnover rate is a crucial metric for businesses, particularly those in the retail and manufacturing sectors. It measures the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period, typically a year. This metric is essential for understanding a company's efficiency in managing its inventory, as well as its overall financial health. In this article, we will delve into the world of inventory turnover rates, exploring their importance, calculation methods, and the factors that influence them.
The inventory turnover rate is a key performance indicator (KPI) that helps businesses evaluate their inventory management strategies. A high inventory turnover rate indicates that a company is selling its products quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased revenue and profitability. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover rate may suggest that a company is holding onto inventory for too long, resulting in unnecessary storage costs, waste, and potential losses. By monitoring their inventory turnover rates, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about their inventory management practices.
As we explore the concept of inventory turnover rates, it is essential to understand the various factors that influence them. These factors include the type of products being sold, the target market, the pricing strategy, and the level of competition. For instance, a company that sells perishable goods, such as food or cosmetics, will typically have a higher inventory turnover rate than a company that sells non-perishable goods, such as electronics or furniture. Similarly, a company that operates in a highly competitive market may need to maintain a higher inventory turnover rate to stay ahead of its competitors.
Understanding Inventory Turnover Rate
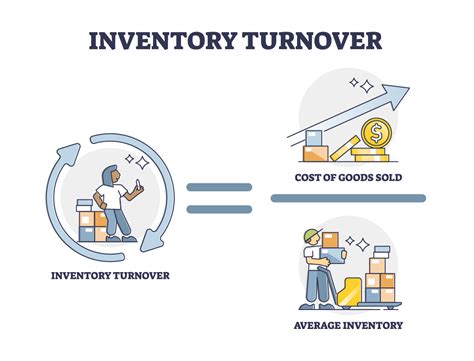
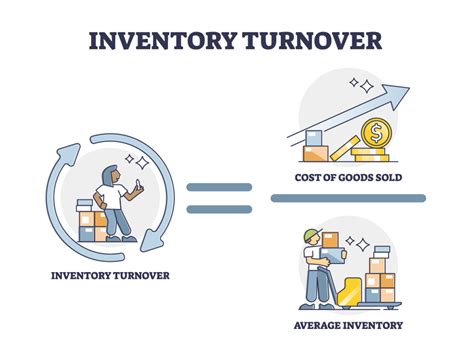
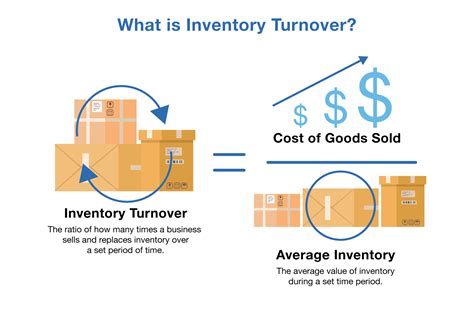
To calculate the inventory turnover rate, businesses use the following formula: inventory turnover rate = cost of goods sold / average inventory. The cost of goods sold represents the total cost of producing or purchasing the products sold during a given period, while the average inventory represents the average value of the inventory held during that period. By dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory, businesses can determine how many times they have sold and replaced their inventory.
For example, let's say a company has a cost of goods sold of $100,000 and an average inventory of $25,000. Using the formula, we can calculate the inventory turnover rate as follows: inventory turnover rate = $100,000 / $25,000 = 4. This means that the company has sold and replaced its inventory four times during the given period.
Factors Influencing Inventory Turnover Rate
The inventory turnover rate is influenced by various factors, including the type of products being sold, the target market, the pricing strategy, and the level of competition. Businesses that sell perishable goods, such as food or cosmetics, will typically have a higher inventory turnover rate than businesses that sell non-perishable goods, such as electronics or furniture. Similarly, businesses that operate in a highly competitive market may need to maintain a higher inventory turnover rate to stay ahead of their competitors.Other factors that can influence the inventory turnover rate include the level of demand, the availability of products, and the efficiency of the supply chain. Businesses that experience high demand for their products will typically have a higher inventory turnover rate, as they need to replenish their inventory more frequently to meet customer demand. On the other hand, businesses that experience low demand may have a lower inventory turnover rate, as they may not need to replenish their inventory as frequently.
Calculating Inventory Turnover Rate
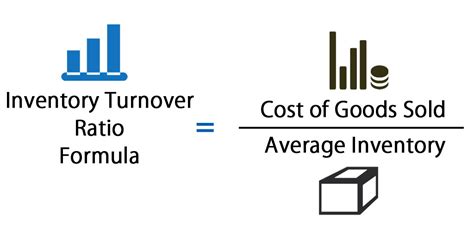
To calculate the inventory turnover rate, businesses need to follow these steps:
- Determine the cost of goods sold: This represents the total cost of producing or purchasing the products sold during a given period.
- Determine the average inventory: This represents the average value of the inventory held during the given period.
- Divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory: This will give you the inventory turnover rate.
For example, let's say a company has a cost of goods sold of $100,000 and an average inventory of $25,000. Using the formula, we can calculate the inventory turnover rate as follows: inventory turnover rate = $100,000 / $25,000 = 4.
Interpreting Inventory Turnover Rate Results
Once you have calculated the inventory turnover rate, you need to interpret the results. A high inventory turnover rate indicates that a company is selling its products quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased revenue and profitability. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover rate may suggest that a company is holding onto inventory for too long, resulting in unnecessary storage costs, waste, and potential losses.Here are some general guidelines for interpreting inventory turnover rate results:
- High inventory turnover rate (above 5): This indicates that a company is selling its products quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased revenue and profitability.
- Medium inventory turnover rate (between 3 and 5): This indicates that a company is selling its products at a moderate pace, which may be suitable for businesses that sell non-perishable goods.
- Low inventory turnover rate (below 3): This indicates that a company is holding onto inventory for too long, resulting in unnecessary storage costs, waste, and potential losses.
Improving Inventory Turnover Rate

To improve the inventory turnover rate, businesses can implement the following strategies:
- Optimize inventory levels: This involves determining the optimal level of inventory to hold, based on factors such as demand, lead time, and storage costs.
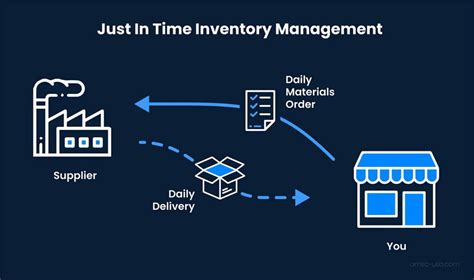
- Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management: This involves ordering and receiving inventory just in time to meet customer demand, rather than holding excess inventory.
- Improve supply chain efficiency: This involves streamlining the supply chain to reduce lead times, improve quality, and increase reliability.
- Enhance product demand forecasting: This involves using data and analytics to predict demand for products, and adjusting inventory levels accordingly.
- Consider drop shipping or third-party logistics: This involves partnering with a third-party provider to manage inventory and fulfill orders, rather than holding inventory in-house.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can improve their inventory turnover rate, reduce waste and costs, and increase revenue and profitability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating and interpreting the inventory turnover rate, businesses should avoid the following common mistakes:- Failing to account for seasonal fluctuations: This can result in inaccurate calculations and interpretations of the inventory turnover rate.
- Not considering the type of products being sold: This can result in comparisons between businesses that sell different types of products, which can be misleading.
- Failing to adjust for changes in pricing or costs: This can result in inaccurate calculations and interpretations of the inventory turnover rate.
- Not monitoring inventory turnover rate regularly: This can result in missed opportunities to improve inventory management and increase revenue and profitability.
By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can ensure that they are accurately calculating and interpreting their inventory turnover rate, and making informed decisions about their inventory management practices.
Inventory Turnover Rate and Business Performance
The inventory turnover rate is closely linked to business performance, as it can impact revenue, profitability, and cash flow. A high inventory turnover rate can indicate that a business is selling its products quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased revenue and profitability. On the other hand, a low inventory turnover rate can indicate that a business is holding onto inventory for too long, resulting in unnecessary storage costs, waste, and potential losses.
Here are some ways in which the inventory turnover rate can impact business performance:
- Revenue: A high inventory turnover rate can lead to increased revenue, as businesses are selling their products quickly and efficiently.
- Profitability: A high inventory turnover rate can lead to increased profitability, as businesses are reducing waste and costs associated with holding excess inventory.
- Cash flow: A high inventory turnover rate can lead to improved cash flow, as businesses are receiving payment from customers more quickly.
- Competitive advantage: A high inventory turnover rate can provide a competitive advantage, as businesses are able to respond quickly to changes in demand and stay ahead of their competitors.
By monitoring and improving their inventory turnover rate, businesses can improve their overall performance and increase their revenue, profitability, and cash flow.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of businesses that have improved their inventory turnover rate and achieved significant benefits:- Walmart: Walmart has implemented a range of strategies to improve its inventory turnover rate, including just-in-time inventory management and supply chain optimization. As a result, the company has reduced its inventory levels by 10% and improved its inventory turnover rate by 20%.
- Amazon: Amazon has implemented a range of strategies to improve its inventory turnover rate, including the use of data and analytics to predict demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. As a result, the company has improved its inventory turnover rate by 30% and reduced its inventory levels by 15%.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola has implemented a range of strategies to improve its inventory turnover rate, including the use of just-in-time inventory management and supply chain optimization. As a result, the company has reduced its inventory levels by 12% and improved its inventory turnover rate by 25%.
These examples demonstrate the importance of monitoring and improving the inventory turnover rate, and the significant benefits that can be achieved by doing so.
Inventory Turnover Rate Image Gallery





What is the inventory turnover rate, and why is it important?
+The inventory turnover rate is a metric that measures the number of times a company sells and replaces its inventory within a given period. It is important because it can indicate a company's efficiency in managing its inventory, as well as its overall financial health.
How is the inventory turnover rate calculated?
+The inventory turnover rate is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory. This can be expressed as: inventory turnover rate = cost of goods sold / average inventory.
What are some strategies for improving the inventory turnover rate?
+Some strategies for improving the inventory turnover rate include optimizing inventory levels, implementing just-in-time inventory management, improving supply chain efficiency, enhancing product demand forecasting, and considering drop shipping or third-party logistics.
How can the inventory turnover rate impact business performance?
+The inventory turnover rate can impact business performance by affecting revenue, profitability, and cash flow. A high inventory turnover rate can indicate that a company is selling its products quickly and efficiently, which can lead to increased revenue and profitability.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating and interpreting the inventory turnover rate?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when calculating and interpreting the inventory turnover rate include failing to account for seasonal fluctuations, not considering the type of products being sold, failing to adjust for changes in pricing or costs, and not monitoring the inventory turnover rate regularly.
In conclusion, the inventory turnover rate is a crucial metric for businesses, particularly those in the retail and manufacturing sectors. By understanding the importance of the inventory turnover rate, calculating it accurately, and interpreting the results correctly, businesses can make informed decisions about their inventory management practices and improve their overall performance. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences on inventory turnover rates in the comments section below, and to explore other articles on our website for more information on inventory management and business performance.
