Intro
Learn the 5 steps of long division with ease, mastering division methods, partial quotients, and multi-digit calculations for accurate math solutions.
The process of long division is a fundamental concept in mathematics that involves dividing a large number, known as the dividend, by a smaller number, known as the divisor, to find the quotient and remainder. Mastering long division is essential for various mathematical operations, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. In this article, we will delve into the 5 steps of long division, providing a comprehensive guide on how to perform this mathematical operation with ease.
Long division is a multi-step process that requires attention to detail, patience, and practice. It is a method used to divide a large number by a smaller number, and it involves a series of calculations to find the quotient and remainder. The process of long division is used in various real-world applications, including finance, engineering, and science. Whether you are a student, teacher, or professional, understanding the 5 steps of long division is crucial for solving complex mathematical problems.
The importance of long division cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental concept that builds upon basic arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Long division helps to develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and analytical reasoning. It also enhances numerical literacy, which is essential for making informed decisions in various aspects of life. By mastering the 5 steps of long division, individuals can improve their mathematical proficiency, boost their confidence, and achieve academic and professional success.
Introduction to Long Division
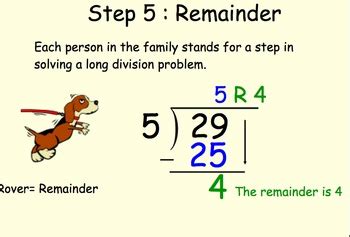
Long division is a step-by-step process that involves dividing a large number by a smaller number. The process begins with the division of the first digit of the dividend by the divisor, followed by a series of calculations to find the quotient and remainder. The 5 steps of long division are: divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, and repeat. These steps are repeated until the dividend is completely divided, and the remainder is obtained.
Step 1: Divide
The first step in long division is to divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor. This involves estimating how many times the divisor fits into the first digit of the dividend. The result of this division is the first digit of the quotient. For example, if we are dividing 432 by 12, we start by dividing 4 by 12, which gives us 0 with a remainder of 4.
Step 2: Multiply
The second step in long division is to multiply the divisor by the quotient obtained in the first step. This involves multiplying the entire divisor by the first digit of the quotient. The result of this multiplication is subtracted from the dividend to obtain the remainder. For example, if we are dividing 432 by 12, and we obtained 0 as the first digit of the quotient, we multiply 12 by 0, which gives us 0.
Step 3: Subtract
The third step in long division is to subtract the result of the multiplication from the dividend. This involves subtracting the product of the divisor and the quotient from the dividend to obtain the remainder. For example, if we are dividing 432 by 12, and we obtained 0 as the first digit of the quotient, we subtract 0 from 4, which gives us 4.
Step 4: Bring Down

The fourth step in long division is to bring down the next digit of the dividend. This involves adding the next digit of the dividend to the remainder obtained in the previous step. For example, if we are dividing 432 by 12, and we obtained 4 as the remainder, we bring down the next digit, which is 3, to obtain 43.
Step 5: Repeat

The fifth and final step in long division is to repeat the process until the dividend is completely divided. This involves repeating steps 1-4 until the remainder is 0 or less than the divisor. For example, if we are dividing 432 by 12, we repeat the process until we obtain a quotient of 36 with a remainder of 0.
Benefits of Long Division
The benefits of long division are numerous. It helps to develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and analytical reasoning. Long division also enhances numerical literacy, which is essential for making informed decisions in various aspects of life. By mastering the 5 steps of long division, individuals can improve their mathematical proficiency, boost their confidence, and achieve academic and professional success.Common Challenges in Long Division
Despite its importance, long division can be challenging for many individuals. Common challenges include difficulty in understanding the concept, making mistakes in calculations, and struggling with multi-digit numbers. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to practice regularly, use visual aids, and seek help from teachers or tutors.Real-World Applications of Long Division
Long division has numerous real-world applications. It is used in finance to calculate interest rates, investments, and loans. In engineering, long division is used to calculate distances, velocities, and accelerations. In science, it is used to calculate quantities, concentrations, and rates. By mastering the 5 steps of long division, individuals can develop a strong foundation in mathematics and improve their problem-solving skills.Long Division Image Gallery
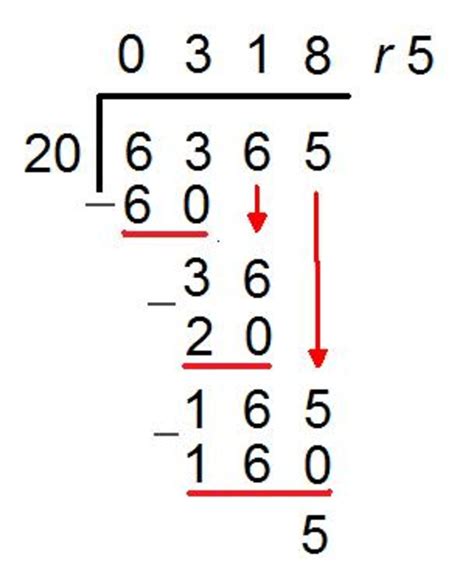
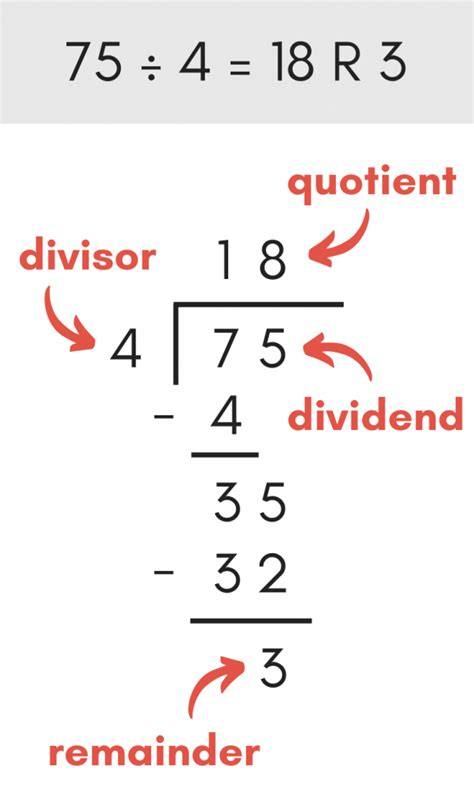

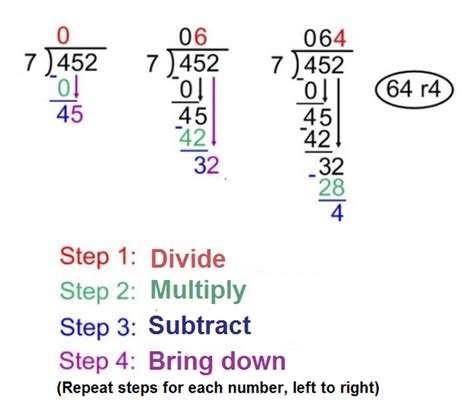




What is long division?
+Long division is a mathematical operation that involves dividing a large number by a smaller number to find the quotient and remainder.
What are the 5 steps of long division?
+The 5 steps of long division are: divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, and repeat.
Why is long division important?
+Long division is important because it helps to develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and analytical reasoning. It also enhances numerical literacy, which is essential for making informed decisions in various aspects of life.
How can I improve my long division skills?
+You can improve your long division skills by practicing regularly, using visual aids, and seeking help from teachers or tutors.
What are some real-world applications of long division?
+Long division has numerous real-world applications, including finance, engineering, and science. It is used to calculate interest rates, investments, loans, distances, velocities, accelerations, quantities, concentrations, and rates.
In conclusion, the 5 steps of long division are a fundamental concept in mathematics that involves dividing a large number by a smaller number to find the quotient and remainder. By mastering these steps, individuals can develop problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and analytical reasoning. Long division has numerous real-world applications, and it is essential for making informed decisions in various aspects of life. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide on how to perform long division with ease. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
