Intro
Discover 5 ways printable metal revolutionizes manufacturing with additive technology, metal 3D printing, and laser cutting, enhancing precision, durability, and innovation in metal fabrication, engineering, and design applications.
The world of manufacturing and engineering has witnessed a significant transformation with the advent of printable metal technology. This innovative method has opened up new avenues for creating complex metal structures with unprecedented precision and speed. The importance of printable metal cannot be overstated, as it has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the world of printable metal and explore its benefits, applications, and future prospects.
Printable metal technology has been gaining traction in recent years, and its importance can be gauged from the fact that it has been adopted by several leading companies and research institutions. The technology involves the use of 3D printing techniques to create metal structures with complex geometries and properties. This has enabled the creation of lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant metal parts that can be used in a wide range of applications. The benefits of printable metal are numerous, and we will discuss them in detail in the following sections.
The printable metal technology has several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. For instance, it allows for the creation of complex structures with internal cavities and channels, which cannot be produced using conventional methods. Additionally, printable metal enables the production of parts with customized properties, such as texture, density, and conductivity. This has opened up new possibilities for the development of advanced materials and devices. Furthermore, the technology has the potential to reduce production costs and lead times, making it an attractive option for industries that require rapid prototyping and production.
Introduction to Printable Metal

The printable metal technology involves the use of 3D printing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) and electron beam melting (EBM), to create metal structures. These techniques involve the layer-by-layer deposition of metal powders or wires, which are then fused together using a high-energy source, such as a laser or electron beam. The resulting structure can be tailored to have specific properties, such as strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Benefits of Printable Metal
The benefits of printable metal are numerous and can be summarized as follows: * Rapid prototyping and production * Creation of complex structures with internal cavities and channels * Customized properties, such as texture, density, and conductivity * Reduced production costs and lead times * Increased design flexibility and freedomApplications of Printable Metal

The applications of printable metal are diverse and can be found in various industries, including:
- Aerospace: creation of lightweight, high-strength structures for aircraft and spacecraft
- Automotive: production of complex engine components, such as cylinder blocks and piston heads
- Healthcare: creation of customized implants, such as hip and knee replacements, and surgical instruments
- Energy: production of advanced materials and devices for energy storage and conversion
Future Prospects of Printable Metal
The future prospects of printable metal are promising, with several research institutions and companies working on developing new technologies and applications. Some of the potential areas of research include: * Development of new metal alloys and composites with enhanced properties * Creation of complex structures with multiple materials and functions * Integration of printable metal with other technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligenceChallenges and Limitations of Printable Metal
Despite the benefits and applications of printable metal, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. Some of the key challenges include:
- High production costs and limited scalability
- Limited availability of metal powders and wires with consistent properties
- Need for advanced software and hardware for design and production
- Limited understanding of the mechanical and thermal properties of printed metal structures
Current Research and Development in Printable Metal
Several research institutions and companies are working on developing new technologies and applications for printable metal. Some of the current research areas include: * Development of new metal alloys and composites with enhanced properties * Creation of complex structures with multiple materials and functions * Integration of printable metal with other technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligencePrintable Metal in Aerospace Industry

The aerospace industry is one of the key beneficiaries of printable metal technology. The creation of lightweight, high-strength structures with complex geometries has enabled the development of advanced aircraft and spacecraft components. Some of the potential applications of printable metal in aerospace include:
- Creation of lightweight engine components, such as turbine blades and compressor vanes
- Production of complex structural components, such as fuselage and wing sections
- Development of advanced materials and devices for thermal management and radiation protection
Printable Metal in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is another key beneficiary of printable metal technology. The creation of complex engine components, such as cylinder blocks and piston heads, has enabled the development of advanced vehicles with improved performance and fuel efficiency. Some of the potential applications of printable metal in automotive include: * Production of complex engine components, such as cylinder blocks and piston heads * Creation of lightweight structural components, such as chassis and suspension systems * Development of advanced materials and devices for thermal management and radiation protectionPrintable Metal in Healthcare Industry

The healthcare industry is also a key beneficiary of printable metal technology. The creation of customized implants, such as hip and knee replacements, and surgical instruments has enabled the development of advanced medical devices with improved performance and safety. Some of the potential applications of printable metal in healthcare include:
- Creation of customized implants, such as hip and knee replacements, and surgical instruments
- Production of complex structural components, such as dental implants and surgical guides
- Development of advanced materials and devices for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
Printable Metal in Energy Industry
The energy industry is another key beneficiary of printable metal technology. The creation of advanced materials and devices for energy storage and conversion has enabled the development of advanced systems for renewable energy generation and storage. Some of the potential applications of printable metal in energy include: * Production of complex structural components, such as fuel cells and solar panels * Creation of advanced materials and devices for thermal management and radiation protection * Development of advanced systems for energy storage and conversion, such as batteries and supercapacitorsPrintable Metal Image Gallery

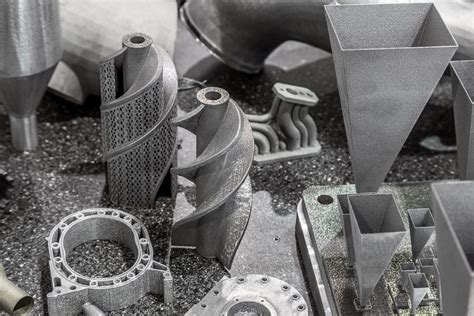






What is printable metal technology?
+Printable metal technology involves the use of 3D printing techniques to create metal structures with complex geometries and properties.
What are the benefits of printable metal?
+The benefits of printable metal include rapid prototyping and production, creation of complex structures with internal cavities and channels, and customized properties, such as texture, density, and conductivity.
What are the applications of printable metal?
+The applications of printable metal include aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and energy industries, where it is used to create complex structures, customized implants, and advanced materials and devices.
In summary, printable metal technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries by enabling the creation of complex structures with customized properties. The benefits of printable metal include rapid prototyping and production, creation of complex structures with internal cavities and channels, and customized properties, such as texture, density, and conductivity. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with printable metal technology and its applications. Please comment below or share this article with others who may be interested in this topic.

