Intro
Discover the meaning of retail price, including its calculation, market value, and pricing strategies, to understand how manufacturers and retailers determine prices for consumer goods and services.
The retail price is the amount that a customer pays for a product or service at a retail store or online platform. It is the final price that the consumer sees and pays, and it includes all the costs, markups, and margins that the retailer has added to the product. The retail price is an important aspect of the retail industry, as it directly affects the profitability of the business and the purchasing decisions of the customers.
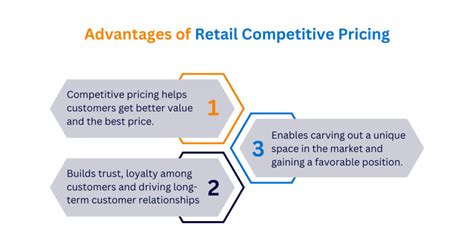
In today's competitive market, retailers need to carefully set their retail prices to stay ahead of the competition and attract price-conscious customers. The retail price is influenced by various factors, including the cost of goods, market conditions, competition, and target audience. Retailers use various pricing strategies, such as discount pricing, premium pricing, and price anchoring, to influence customer perceptions and drive sales.
The retail price is not just a simple number; it is a complex calculation that involves various costs, including the cost of goods, shipping, handling, storage, and marketing. Retailers need to balance their pricing strategy with their profit margins, as high prices can drive away customers, while low prices can erode profits. The retail price is a critical component of the retail mix, and it plays a significant role in determining the success or failure of a retail business.
Understanding Retail Price

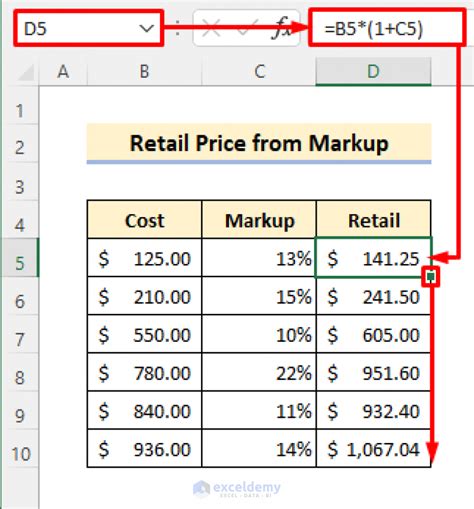
Understanding the retail price is essential for retailers, as it helps them to make informed decisions about their pricing strategy. The retail price is calculated by adding the cost of goods, markup, and other expenses to the product. The markup is the difference between the cost of goods and the selling price, and it is expressed as a percentage of the cost of goods. Retailers use various markup percentages, depending on the product, market conditions, and target audience.
For example, a retailer buys a product for $10 and sells it for $15. The markup is $5, which is 50% of the cost of goods. The retail price of $15 includes the cost of goods, markup, and other expenses, such as shipping, handling, and storage. Retailers need to carefully calculate their markup to ensure that they are making a profit while staying competitive in the market.
Factors Influencing Retail Price
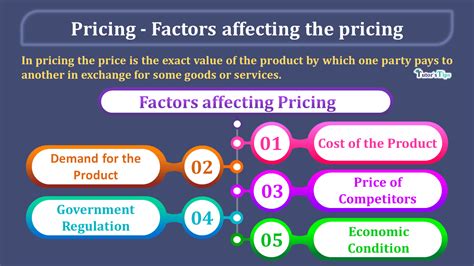
Several factors influence the retail price, including the cost of goods, market conditions, competition, and target audience. The cost of goods is the most significant factor, as it directly affects the retail price. Retailers need to consider the cost of production, shipping, handling, and storage when calculating the retail price.
Market conditions, such as demand and supply, also influence the retail price. During periods of high demand, retailers can charge higher prices, while during periods of low demand, they may need to reduce prices to stimulate sales. Competition is another significant factor, as retailers need to stay competitive in the market. They may need to adjust their prices to match or beat the prices of their competitors.
The target audience is also an essential factor, as retailers need to consider the willingness of their customers to pay a certain price. For example, a luxury brand may charge a higher price for its products, as its target audience is willing to pay a premium for high-quality products.
Retail Pricing Strategies

Retailers use various pricing strategies to influence customer perceptions and drive sales. Some common pricing strategies include:
- Discount pricing: This involves offering products at a lower price than the regular price to stimulate sales.
- Premium pricing: This involves charging a higher price for products that are perceived as high-quality or unique.
- Price anchoring: This involves displaying a higher price next to a lower price to make the lower price appear more attractive.
- Bundle pricing: This involves offering multiple products together at a discounted price.
- Dynamic pricing: This involves adjusting prices in real-time based on demand and supply.
Retailers need to carefully choose their pricing strategy to achieve their business objectives. They need to consider their target audience, market conditions, and competition when selecting a pricing strategy.
Benefits of Effective Retail Pricing
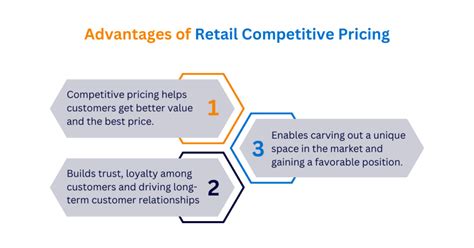
Effective retail pricing can bring several benefits to retailers, including:
- Increased sales: A well-designed pricing strategy can stimulate sales and drive revenue growth.
- Improved profitability: A pricing strategy that balances revenue and costs can improve profitability.
- Competitive advantage: A unique pricing strategy can differentiate a retailer from its competitors and attract price-conscious customers.
- Customer loyalty: A pricing strategy that offers value to customers can build loyalty and retention.
Retailers need to continuously monitor their pricing strategy and adjust it as needed to stay competitive in the market. They need to consider various factors, including market conditions, competition, and target audience, when designing their pricing strategy.
Challenges of Retail Pricing

Retail pricing can be challenging, as retailers need to balance their pricing strategy with their business objectives. Some common challenges of retail pricing include:
- Price transparency: The internet has made it easy for customers to compare prices, making it challenging for retailers to maintain price consistency.
- Price competition: Retailers need to compete with other retailers on price, making it challenging to maintain profit margins.
- Price elasticity: Retailers need to understand how price changes affect demand, making it challenging to design an effective pricing strategy.
Retailers need to use data and analytics to overcome these challenges and design an effective pricing strategy. They need to consider various factors, including market conditions, competition, and target audience, when designing their pricing strategy.
Gallery of Retail Price Images
Retail Price Image Gallery




What is retail price?
+Retail price is the amount that a customer pays for a product or service at a retail store or online platform.
What factors influence retail price?
+Factors that influence retail price include the cost of goods, market conditions, competition, and target audience.
What are the benefits of effective retail pricing?
+Benefits of effective retail pricing include increased sales, improved profitability, competitive advantage, and customer loyalty.
What are the challenges of retail pricing?
+Challenges of retail pricing include price transparency, price competition, and price elasticity.
How can retailers overcome the challenges of retail pricing?
+Retailers can overcome the challenges of retail pricing by using data and analytics to design an effective pricing strategy.
In conclusion, retail price is a critical component of the retail mix, and it plays a significant role in determining the success or failure of a retail business. Retailers need to carefully design their pricing strategy to achieve their business objectives, considering various factors, including market conditions, competition, and target audience. By understanding the benefits and challenges of retail pricing, retailers can make informed decisions about their pricing strategy and stay competitive in the market. We invite you to share your thoughts on retail pricing and its impact on the retail industry. Please comment below and share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about retail pricing.
