Intro
Discover 5 general ledger examples, illustrating accounting principles, financial reporting, and ledger management, with key entries, trial balances, and journal entries for accurate financial tracking and analysis.
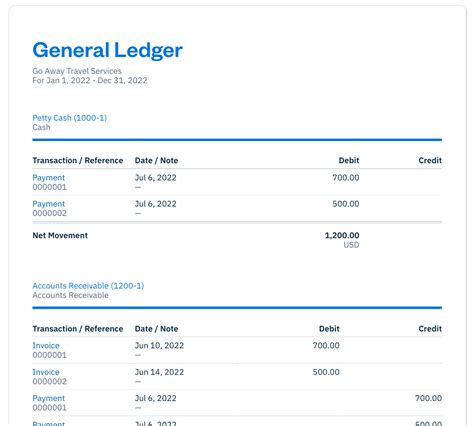
The general ledger is a crucial component of a company's accounting system, serving as a centralized repository for all financial transactions. It provides a comprehensive and detailed record of a company's financial activities, enabling businesses to track their income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. In this article, we will delve into the world of general ledger examples, exploring their significance, types, and applications.
The general ledger is essential for businesses of all sizes, as it facilitates financial reporting, budgeting, and decision-making. By analyzing the general ledger, companies can identify trends, detect anomalies, and make informed decisions about investments, funding, and resource allocation. Moreover, the general ledger helps businesses to prepare financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement, which are vital for stakeholders, investors, and regulatory bodies.
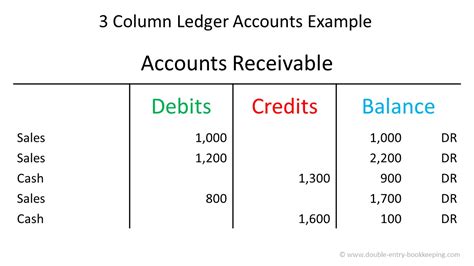
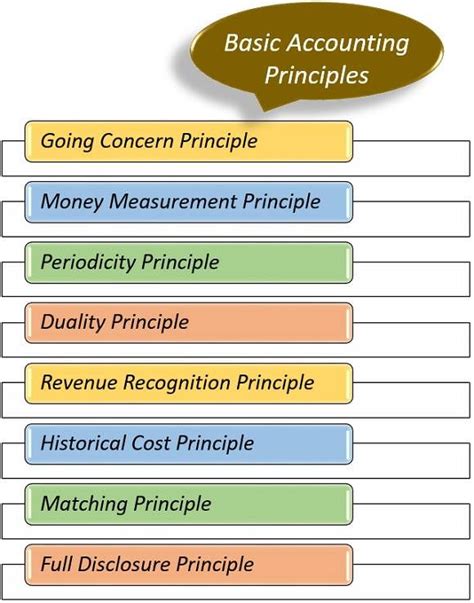
A general ledger typically consists of a chart of accounts, which is a list of all the accounts used by a company to record its financial transactions. The chart of accounts is organized into various categories, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses. Each account has a unique number and name, making it easier to identify and track specific transactions. The general ledger also includes journal entries, which are used to record transactions and update the account balances.
Introduction to General Ledger Examples
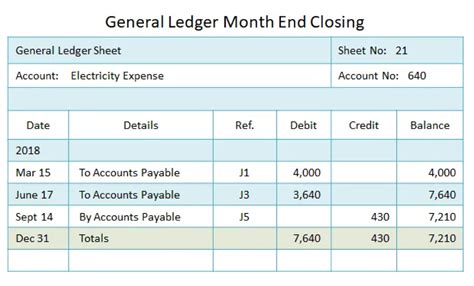
General ledger examples are numerous and varied, reflecting the diverse needs and operations of different businesses. For instance, a retail company's general ledger might include accounts for sales, cost of goods sold, inventory, and accounts payable. In contrast, a manufacturing company's general ledger might include accounts for production costs, raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
Types of General Ledger Examples
There are several types of general ledger examples, each serving a specific purpose or industry. Some common examples include:- Asset accounts: These accounts record the company's assets, such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property, plant, and equipment.
- Liability accounts: These accounts record the company's liabilities, such as accounts payable, loans, and taxes owed.
- Equity accounts: These accounts record the company's equity, including common stock, retained earnings, and dividends.
- Revenue accounts: These accounts record the company's revenues, such as sales, services, and interest income.
- Expense accounts: These accounts record the company's expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
General Ledger Example for a Small Business
A small business general ledger example might include the following accounts:
- Cash: This account records the company's cash transactions, including deposits, withdrawals, and payments.
- Accounts receivable: This account records the company's sales on credit, including invoices and payments from customers.
- Inventory: This account records the company's inventory levels, including purchases, sales, and adjustments.
- Accounts payable: This account records the company's purchases on credit, including invoices and payments to suppliers.
- Sales: This account records the company's sales revenue, including cash and credit sales.
General Ledger Example for a Non-Profit Organization
A non-profit organization's general ledger example might include the following accounts:- Donations: This account records the organization's donations, including cash, grants, and in-kind contributions.
- Grants: This account records the organization's grants, including government and private funding.
- Program expenses: This account records the organization's program expenses, including salaries, materials, and travel.
- Administrative expenses: This account records the organization's administrative expenses, including salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Fundraising expenses: This account records the organization's fundraising expenses, including event costs, marketing, and donor outreach.
General Ledger Example for a Manufacturing Company
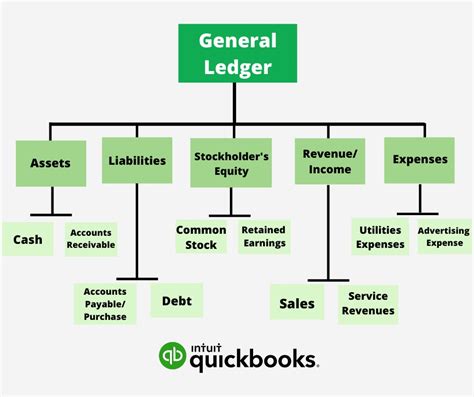
A manufacturing company's general ledger example might include the following accounts:
- Raw materials: This account records the company's raw materials inventory, including purchases and usage.
- Work-in-progress: This account records the company's work-in-progress inventory, including production costs and labor.
- Finished goods: This account records the company's finished goods inventory, including production costs and sales.
- Production costs: This account records the company's production costs, including labor, materials, and overhead.
- Cost of goods sold: This account records the company's cost of goods sold, including production costs and inventory adjustments.
General Ledger Example for a Retail Company
A retail company's general ledger example might include the following accounts:- Sales: This account records the company's sales revenue, including cash and credit sales.
- Cost of goods sold: This account records the company's cost of goods sold, including inventory purchases and adjustments.
- Inventory: This account records the company's inventory levels, including purchases, sales, and adjustments.
- Accounts payable: This account records the company's purchases on credit, including invoices and payments to suppliers.
- Accounts receivable: This account records the company's sales on credit, including invoices and payments from customers.
General Ledger Example for a Service-Based Company
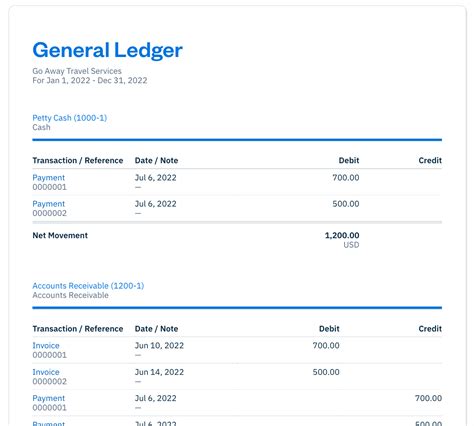
A service-based company's general ledger example might include the following accounts:
- Service revenue: This account records the company's service revenue, including cash and credit sales.
- Labor costs: This account records the company's labor costs, including salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes.
- Operating expenses: This account records the company's operating expenses, including rent, utilities, and marketing.
- Accounts receivable: This account records the company's sales on credit, including invoices and payments from customers.
- Accounts payable: This account records the company's purchases on credit, including invoices and payments to suppliers.
Benefits of Using General Ledger Examples
Using general ledger examples can provide several benefits, including:- Improved financial reporting: General ledger examples can help companies to prepare accurate and comprehensive financial statements, including the balance sheet and income statement.
- Enhanced decision-making: General ledger examples can provide companies with valuable insights into their financial performance, enabling them to make informed decisions about investments, funding, and resource allocation.
- Increased efficiency: General ledger examples can help companies to streamline their accounting processes, reducing errors and improving productivity.
- Better budgeting: General ledger examples can help companies to prepare realistic budgets, including projected revenues, expenses, and cash flows.
Best Practices for Creating General Ledger Examples
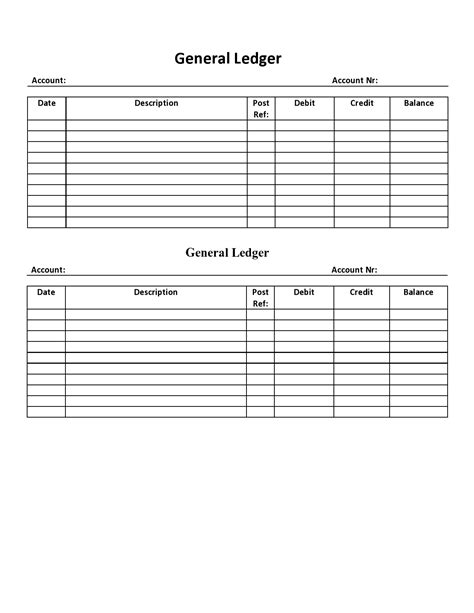
To create effective general ledger examples, companies should follow best practices, including:
- Using a standardized chart of accounts: A standardized chart of accounts can help companies to ensure consistency and accuracy in their financial reporting.
- Implementing robust accounting controls: Robust accounting controls can help companies to prevent errors, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Providing regular training: Regular training can help companies to ensure that their accounting staff is knowledgeable and skilled in using general ledger examples.
- Reviewing and updating regularly: Regular reviews and updates can help companies to ensure that their general ledger examples remain accurate and relevant.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating General Ledger Examples
When creating general ledger examples, companies should avoid common mistakes, including:- Inconsistent accounting practices: Inconsistent accounting practices can lead to errors, inaccuracies, and confusion.
- Insufficient documentation: Insufficient documentation can make it difficult to understand and interpret general ledger examples.
- Lack of standardization: Lack of standardization can make it challenging to compare and analyze general ledger examples.
- Inadequate training: Inadequate training can lead to errors, mistakes, and misunderstandings when using general ledger examples.
General Ledger Image Gallery





What is a general ledger?
+A general ledger is a centralized repository for all financial transactions, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of a company's financial activities.
What are the benefits of using general ledger examples?
+The benefits of using general ledger examples include improved financial reporting, enhanced decision-making, increased efficiency, and better budgeting.
How can I create effective general ledger examples?
+To create effective general ledger examples, follow best practices, including using a standardized chart of accounts, implementing robust accounting controls, providing regular training, and reviewing and updating regularly.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating general ledger examples?
+Common mistakes to avoid when creating general ledger examples include inconsistent accounting practices, insufficient documentation, lack of standardization, and inadequate training.
How can I use general ledger examples to improve my financial reporting?
+General ledger examples can help you to prepare accurate and comprehensive financial statements, including the balance sheet and income statement, by providing a detailed record of your financial transactions and account balances.
In conclusion, general ledger examples are essential tools for businesses, providing a comprehensive and detailed record of financial transactions and account balances. By understanding the different types of general ledger examples, including those for small businesses, non-profit organizations, manufacturing companies, retail companies, and service-based companies, businesses can create effective financial reporting systems, enhance decision-making, and improve their overall financial performance. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with general ledger examples, and to explore the many resources available to help you create and implement effective financial reporting systems.
