Intro
Master 5 dosage calculations with ease, covering medication math, pharmacology, and measurement conversions, to ensure accurate drug administration and patient safety.
The importance of accurate dosage calculations in the medical field cannot be overstated. Medication errors can have serious consequences, including patient harm, prolonged hospital stays, and even death. Healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, are responsible for administering medications to patients, making it crucial for them to have a strong foundation in dosage calculations. In this article, we will delve into the world of dosage calculations, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, steps, and key information related to this critical topic.
Dosage calculations are a fundamental aspect of pharmacology, requiring healthcare professionals to calculate the correct amount of medication to administer to patients. This involves understanding various units of measurement, such as milligrams, milliliters, and grams, as well as being familiar with different medication formulations, including tablets, capsules, and liquids. The ability to perform accurate dosage calculations is essential for ensuring patient safety and preventing medication errors.
The consequences of medication errors can be severe, ranging from mild side effects to life-threatening complications. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), medication errors are a leading cause of adverse events in healthcare settings, resulting in significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burden. Therefore, it is essential for healthcare professionals to develop strong dosage calculation skills to minimize the risk of medication errors and provide high-quality patient care.
Dosage Calculation Basics

To perform dosage calculations, healthcare professionals need to understand the basic principles of pharmacology, including the concept of units of measurement, medication formulations, and dosing regimens. The first step in dosage calculation is to identify the medication order, which includes the medication name, dose, route of administration, and frequency of administration. Next, the healthcare professional must determine the patient's weight, as this is often used to calculate medication doses. The medication label or packaging provides essential information, including the medication's strength, concentration, and dosage instructions.
Units of Measurement
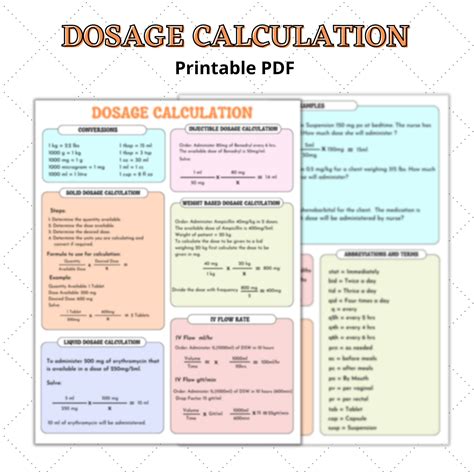
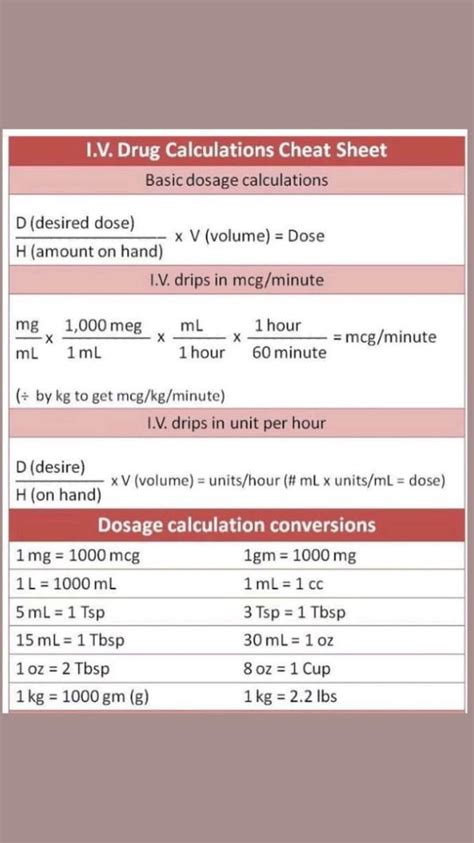
Understanding units of measurement is critical in dosage calculations. The most commonly used units of measurement in pharmacology include milligrams (mg), milliliters (mL), and grams (g). Healthcare professionals must be able to convert between these units, using conversion factors such as 1 gram = 1000 milligrams or 1 milliliter = 1 cubic centimeter (cm³). Accurate conversion is essential to prevent medication errors, as incorrect conversions can result in overdosing or underdosing.Dosage Calculation Methods

There are several dosage calculation methods, including the ratio and proportion method, the formula method, and the dimensional analysis method. The ratio and proportion method involves setting up a ratio of the medication's strength to the desired dose, while the formula method uses a formula to calculate the dose. The dimensional analysis method involves canceling out units of measurement to arrive at the final dose. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and healthcare professionals should be familiar with all three methods to ensure accurate dosage calculations.
Ratio and Proportion Method
The ratio and proportion method is a simple and straightforward method for calculating medication doses. This method involves setting up a ratio of the medication's strength to the desired dose, using the following formula: dose on hand / dose needed = amount to administer. For example, if a medication has a strength of 100 mg per 5 mL and the desired dose is 50 mg, the calculation would be: 100 mg / 5 mL = 50 mg / x mL, where x is the amount to administer.Common Dosage Calculation Errors

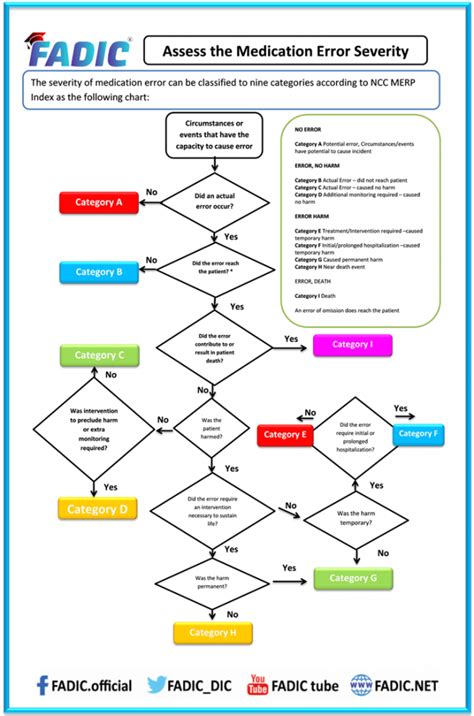
Despite the importance of accurate dosage calculations, errors can still occur. Common dosage calculation errors include incorrect unit conversions, miscalculations, and misunderstandings of medication orders. Healthcare professionals must be vigilant and double-check their calculations to prevent these errors. Additionally, the use of technology, such as electronic medication administration records (e-MARs) and automated dispensing cabinets, can help reduce the risk of medication errors.
Prevention Strategies
To prevent dosage calculation errors, healthcare professionals can use several strategies, including: * Double-checking calculations * Using a second checker or calculator * Reading medication labels carefully * Understanding medication orders and dosing regimens * Using technology, such as e-MARs and automated dispensing cabinets By implementing these strategies, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of medication errors and ensure accurate dosage calculations.Real-World Applications

Dosage calculations have numerous real-world applications, including in hospitals, clinics, and community pharmacies. Healthcare professionals use dosage calculations to administer medications to patients, monitor their effects, and adjust dosing regimens as needed. Accurate dosage calculations are essential in various medical specialties, including pediatrics, gerontology, and oncology, where medication dosing can be complex and critical.
Case Studies
To illustrate the importance of accurate dosage calculations, consider the following case studies: * A pediatric patient requires a dose of 10 mg of medication per kilogram of body weight. If the patient weighs 20 kg, the calculation would be: 10 mg/kg x 20 kg = 200 mg. * A gerontologic patient requires a dose of 50 mg of medication per day. If the medication has a strength of 25 mg per tablet, the calculation would be: 50 mg / 25 mg per tablet = 2 tablets per day.Gallery of Dosage Calculations
Dosage Calculations Image Gallery




Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of medication errors?
+The most common cause of medication errors is incorrect dosage calculations.
How can I improve my dosage calculation skills?
+You can improve your dosage calculation skills by practicing with sample problems, using online resources and calculators, and seeking feedback from instructors or peers.
What is the importance of double-checking dosage calculations?
+Double-checking dosage calculations is crucial to prevent medication errors, which can have serious consequences for patients.
Can technology help reduce medication errors?
+Yes, technology such as electronic medication administration records (e-MARs) and automated dispensing cabinets can help reduce medication errors by improving dosage calculation accuracy and reducing human error.
How often should I review and update my dosage calculation skills?
+You should review and update your dosage calculation skills regularly, ideally every 6-12 months, to ensure you stay current with best practices and guidelines.
In conclusion, accurate dosage calculations are essential for ensuring patient safety and preventing medication errors. By understanding the basics of pharmacology, using various dosage calculation methods, and implementing prevention strategies, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of medication errors and provide high-quality patient care. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for improving dosage calculation skills, and to explore the resources and tools available for healthcare professionals to enhance their knowledge and practice in this critical area.
