Intro
Discover a comprehensive printable low GI food list, featuring glycemic index, glucose control, and balanced diet tips for weight management and healthy eating.
The importance of maintaining a healthy diet cannot be overstated, and one of the key ways to achieve this is by managing the glycemic index (GI) of the foods we consume. The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels, with foods having a low GI being digested more slowly, causing a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar. For individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels, lose weight, or simply adopt a healthier eating habit, understanding and incorporating low GI foods into their diet is crucial. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to printable low GI food lists, explaining the benefits of low GI diets, how to identify low GI foods, and offering practical tips for incorporating these foods into your daily meals.
A low GI diet has been associated with numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar control, weight management, and a reduced risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can naturally lower the GI of their diet. These foods include vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Understanding the GI of common foods can help in making informed choices at the grocery store and when planning meals. Moreover, having a printable low GI food list can serve as a handy reference, making it easier to stick to a low GI diet, even when eating out or shopping for groceries.
The concept of the glycemic index was first introduced to help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels more effectively. However, its application extends far beyond diabetes management, offering a useful tool for anyone seeking to improve their overall health and well-being. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. Foods with a high GI (above 70) cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while those with a low GI (below 55) result in a slower and more gradual increase. Medium GI foods fall between 55 and 69. Knowing the GI of foods can help in planning meals that are balanced and less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar levels.
Benefits of a Low GI Diet

Key Components of a Low GI Diet
A low GI diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, including a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are naturally rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and tend to have a lower GI compared to processed and packaged foods. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, are good sources of fiber and have a lower GI than refined grains. Fruits and vegetables are also low in GI, with the exception of some tropical fruits like mangoes and pineapples, which have a higher GI due to their higher sugar content. Lean proteins, including poultry, fish, and legumes, do not have a GI since they do not contain carbohydrates, but they are an essential part of a balanced diet.Identifying Low GI Foods
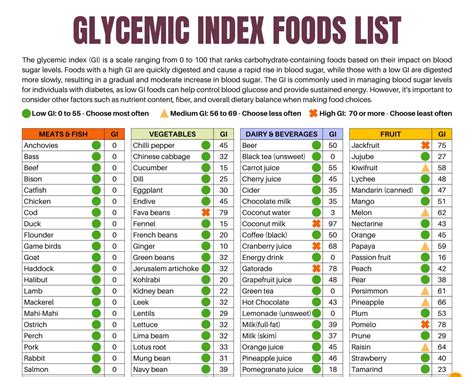
Practical Tips for Incorporating Low GI Foods
Incorporating low GI foods into your diet can be easy and delicious. Here are some practical tips to get you started: - Start your day with a low GI breakfast, such as oatmeal with fruits and nuts, or whole grain toast with avocado and eggs. - Include a variety of vegetables in your meals, aiming for at least five servings a day. - Choose whole grains over refined grains for your carbohydrate sources. - Incorporate lean proteins, such as poultry, fish, and legumes, into your meals. - Healthy fats, like those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, are also essential for a balanced diet.Printable Low GI Food List
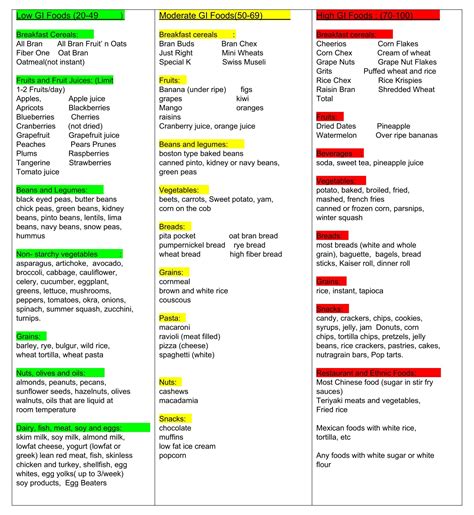
Creating Your Own Low GI Meal Plan
Creating your own low GI meal plan can be tailored to your dietary preferences and lifestyle. Here are some steps to follow: 1. **Identify your dietary needs:** Consider your calorie requirements, any dietary restrictions, and your health goals. 2. **Plan your meals:** Use your printable low GI food list to plan your meals for the week. Include a variety of foods from all food groups. 3. **Make a grocery list:** Based on your meal plan, make a list of the groceries you need to buy. 4. **Shop smart:** When shopping, choose whole, unprocessed foods as much as possible. Read labels to ensure that the products you choose are low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. 5. **Cook at home:** Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes of your meals, making it easier to stick to your low GI diet.Gallery of Low GI Foods
Low GI Food Gallery










Frequently Asked Questions
What is the glycemic index?
+The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100.
What are the benefits of a low GI diet?
+A low GI diet has been associated with improved blood sugar control, weight management, and a reduced risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
How can I identify low GI foods?
+Low GI foods tend to be high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Whole, unprocessed foods generally have a lower GI than processed and packaged foods.
In conclusion, adopting a low GI diet can have a significant impact on your health and well-being. By understanding the glycemic index, identifying low GI foods, and incorporating these foods into your diet, you can manage your blood sugar levels, lose weight, and reduce your risk of chronic diseases. Remember, the key to a successful low GI diet is balance and variety, ensuring that you get a wide range of nutrients from whole, unprocessed foods. With the right approach and a little planning, you can enjoy the benefits of a low GI diet and improve your overall health. We invite you to share your experiences with low GI diets, ask questions, and explore more resources on healthy eating and nutrition. Together, let's embark on a journey towards healthier living, one meal at a time.
