Intro
Discover the 5 ways chargebacks work, including dispute resolution, payment reversals, and fraud protection, to understand credit card chargeback processes and prevent transaction disputes, errors, and merchant losses.
The world of e-commerce and online transactions has made it easier for consumers to purchase goods and services from the comfort of their own homes. However, with the rise of online transactions, there has also been an increase in disputes and chargebacks. Chargebacks are a crucial aspect of consumer protection, allowing individuals to dispute transactions and recover their funds in cases of fraud, error, or dissatisfaction. In this article, we will delve into the world of chargebacks, exploring what they are, how they work, and the various ways they can be utilized.
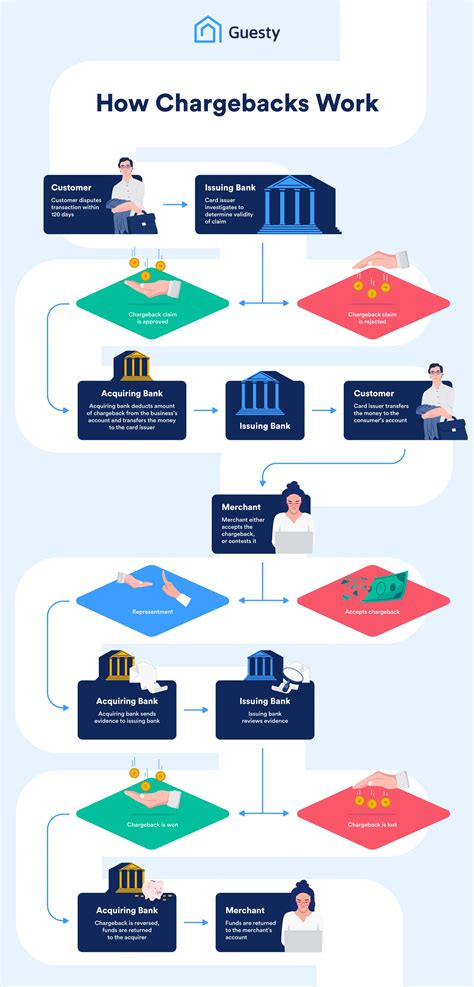
Chargebacks are a mechanism that enables consumers to request a reversal of a transaction, typically due to a dispute or issue with the purchase. This can be due to a variety of reasons, such as a transaction being unauthorized, a product or service not being delivered, or a customer being dissatisfied with their purchase. The chargeback process involves the consumer, the merchant, and the issuing bank, and can be a complex and time-consuming procedure. Understanding how chargebacks work is essential for both consumers and merchants, as it can help to prevent disputes and ensure a smooth transaction process.
The chargeback process typically begins when a consumer contacts their issuing bank to dispute a transaction. The bank will then investigate the claim and may request additional information or evidence from the consumer to support their dispute. If the bank determines that the dispute is valid, they will initiate a chargeback, which involves reversing the transaction and refunding the consumer's account. The merchant will then be notified of the chargeback and will have the opportunity to respond and provide evidence to support their case.
Understanding Chargebacks

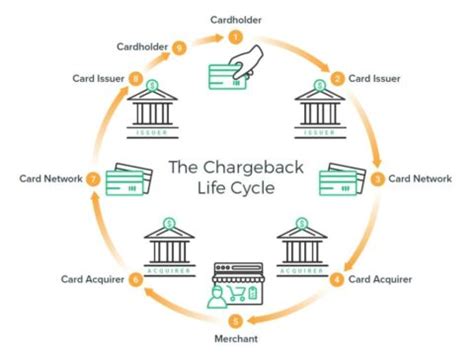
To fully comprehend the chargeback process, it is essential to understand the various parties involved and their roles. The consumer, merchant, and issuing bank all play critical roles in the chargeback process. The consumer is the individual who initiates the dispute, while the merchant is the party that sold the goods or services. The issuing bank is the financial institution that issued the consumer's credit or debit card and is responsible for handling the dispute.
Key Players in the Chargeback Process
The chargeback process involves several key players, including: * The consumer: The individual who initiates the dispute and requests a chargeback. * The merchant: The party that sold the goods or services and is responsible for fulfilling the transaction. * The issuing bank: The financial institution that issued the consumer's credit or debit card and is responsible for handling the dispute. * The acquiring bank: The financial institution that processes the transaction on behalf of the merchant.The Chargeback Process

The chargeback process can be complex and involves several steps. The process typically begins when a consumer contacts their issuing bank to dispute a transaction. The bank will then investigate the claim and may request additional information or evidence from the consumer to support their dispute. If the bank determines that the dispute is valid, they will initiate a chargeback, which involves reversing the transaction and refunding the consumer's account.
Steps in the Chargeback Process
The chargeback process involves the following steps: 1. The consumer initiates a dispute by contacting their issuing bank. 2. The issuing bank investigates the claim and requests additional information or evidence from the consumer. 3. The issuing bank determines whether the dispute is valid and initiates a chargeback if necessary. 4. The merchant is notified of the chargeback and has the opportunity to respond and provide evidence to support their case. 5. The acquiring bank reviews the evidence and makes a final decision regarding the chargeback.Types of Chargebacks

There are several types of chargebacks, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements. The most common types of chargebacks include:
- Unauthorized transactions: These occur when a consumer's credit or debit card is used without their permission.
- Merchandise not received: These occur when a consumer does not receive the goods or services they purchased.
- Merchandise not as described: These occur when the goods or services received are not as described by the merchant.
- Duplicate transactions: These occur when a consumer is charged multiple times for the same transaction.
Preventing Chargebacks
Preventing chargebacks is essential for merchants, as they can result in significant losses and damage to a company's reputation. There are several steps that merchants can take to prevent chargebacks, including: * Clearly describing goods and services: Merchants should ensure that their goods and services are clearly described, including any terms and conditions. * Providing excellent customer service: Merchants should provide excellent customer service, including responding to customer inquiries and resolving issues promptly. * Obtaining authorization: Merchants should obtain authorization from consumers before processing transactions. * Keeping records: Merchants should keep accurate records of transactions, including receipts and invoices.Chargeback Fees and Penalties

Chargebacks can result in significant fees and penalties for merchants. These fees can include:
- Chargeback fees: These are fees charged by the acquiring bank for processing chargebacks.
- Penalty fees: These are fees charged by the acquiring bank for excessive chargebacks.
- Fines: These are fines imposed by the card networks for non-compliance with their rules and regulations.
Minimizing Chargeback Fees and Penalties
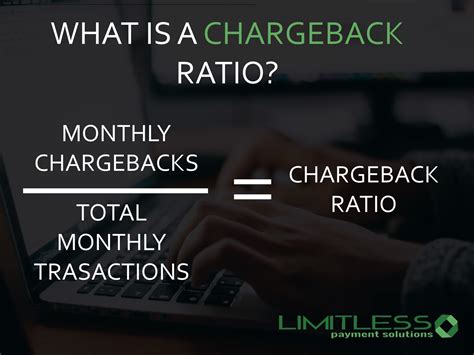
Merchants can minimize chargeback fees and penalties by taking several steps, including: * Responding to chargebacks promptly: Merchants should respond to chargebacks promptly, providing evidence to support their case. * Providing excellent customer service: Merchants should provide excellent customer service, including responding to customer inquiries and resolving issues promptly. * Keeping records: Merchants should keep accurate records of transactions, including receipts and invoices. * Monitoring chargeback ratios: Merchants should monitor their chargeback ratios, taking steps to prevent excessive chargebacks.Best Practices for Chargebacks
There are several best practices that merchants can follow to manage chargebacks effectively, including:
- Responding to chargebacks promptly: Merchants should respond to chargebacks promptly, providing evidence to support their case.
- Providing excellent customer service: Merchants should provide excellent customer service, including responding to customer inquiries and resolving issues promptly.
- Keeping records: Merchants should keep accurate records of transactions, including receipts and invoices.
- Monitoring chargeback ratios: Merchants should monitor their chargeback ratios, taking steps to prevent excessive chargebacks.
Chargeback Management Tools
There are several chargeback management tools available to help merchants manage chargebacks effectively. These tools include: * Chargeback software: This software helps merchants to manage chargebacks, including responding to chargebacks and providing evidence to support their case. * Chargeback services: These services provide merchants with expert advice and support, helping them to manage chargebacks and prevent excessive chargebacks.Chargeback Image Gallery







What is a chargeback?
+A chargeback is a mechanism that enables consumers to request a reversal of a transaction, typically due to a dispute or issue with the purchase.
How do chargebacks work?
+Chargebacks work by allowing consumers to dispute transactions and recover their funds in cases of fraud, error, or dissatisfaction. The chargeback process involves the consumer, the merchant, and the issuing bank.
What are the types of chargebacks?
+The most common types of chargebacks include unauthorized transactions, merchandise not received, merchandise not as described, and duplicate transactions.
How can merchants prevent chargebacks?
+Merchants can prevent chargebacks by clearly describing goods and services, providing excellent customer service, obtaining authorization, and keeping records.
What are the consequences of excessive chargebacks?
+Excessive chargebacks can result in significant fees and penalties for merchants, including chargeback fees, penalty fees, and fines.
In conclusion, chargebacks are a crucial aspect of consumer protection, allowing individuals to dispute transactions and recover their funds in cases of fraud, error, or dissatisfaction. Understanding how chargebacks work is essential for both consumers and merchants, as it can help to prevent disputes and ensure a smooth transaction process. By following best practices and utilizing chargeback management tools, merchants can minimize chargeback fees and penalties, while also providing excellent customer service and preventing excessive chargebacks. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of chargebacks and how they work. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with chargebacks, please don't hesitate to comment below.
