Intro
Master 5 EKG rhythms, including normal sinus, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia, to improve cardiac diagnosis and treatment with electrocardiogram interpretation skills.
The importance of understanding EKG rhythms cannot be overstated, particularly in the medical field where accurate diagnoses and timely interventions are crucial for patient care. Electrocardiography (EKG or ECG) is a tool used to monitor the electrical activity of the heart, providing valuable insights into its functioning and potential abnormalities. For healthcare professionals, being proficient in interpreting EKG rhythms is essential for identifying various heart conditions, guiding treatment decisions, and improving patient outcomes. The complexity of EKG interpretations necessitates a thorough understanding of normal and abnormal heart rhythms, which can be achieved through comprehensive training and practice.
Understanding EKG rhythms is not limited to medical professionals; it also extends to individuals interested in health and wellness. Knowing how to read an EKG can empower individuals to take a more active role in their health, especially those with pre-existing heart conditions or a family history of cardiac diseases. Moreover, advancements in technology have made EKG devices more accessible, allowing for personal use and real-time monitoring. This accessibility underscores the need for broader awareness and education on EKG rhythms, ensuring that individuals can make informed decisions about their health.
The field of EKG interpretation is vast and intricate, requiring a detailed approach to understand the nuances of different rhythms. From the basic understanding of P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves to the identification of complex arrhythmias, each element plays a critical role in diagnosing cardiac conditions. Furthermore, the ability to distinguish between benign and pathological rhythms is paramount, as it directly influences treatment strategies and patient management. As such, delving into the specifics of common EKG rhythms, their characteristics, and clinical implications is essential for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge of cardiac health.
Introduction to EKG Rhythms
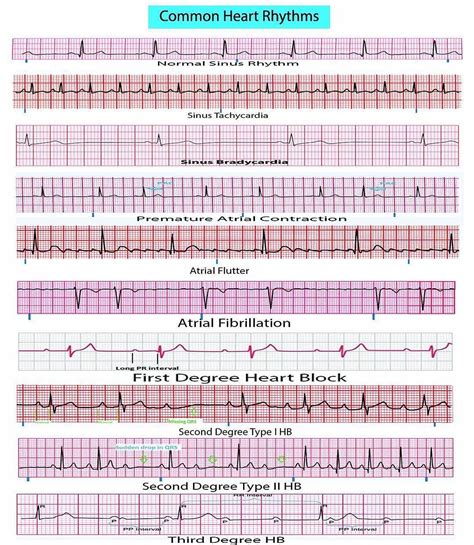
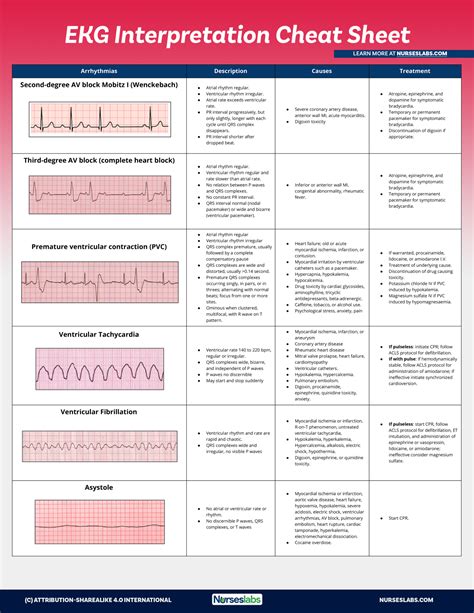
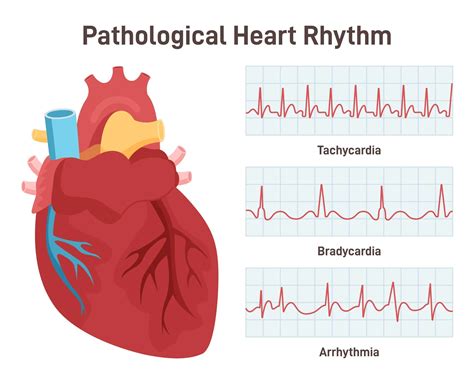
EKG rhythms are categorized based on their origin, rate, and regularity, among other factors. Normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular (AV) block, and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are among the commonly encountered rhythms in clinical practice. Each of these rhythms has distinct features on an EKG tracing, which, when correctly interpreted, can lead to accurate diagnoses and appropriate management strategies.
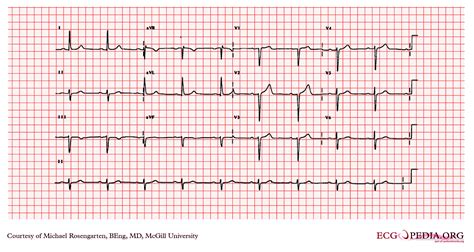
Understanding Normal Sinus Rhythm
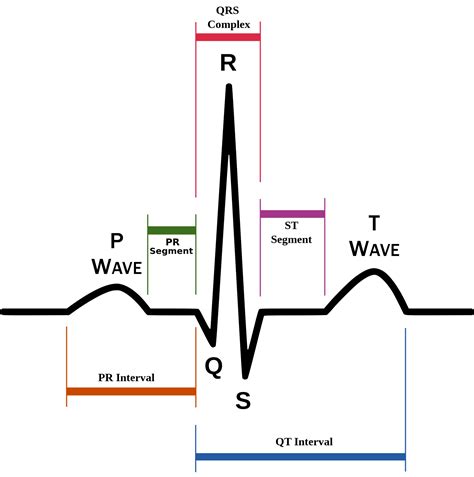
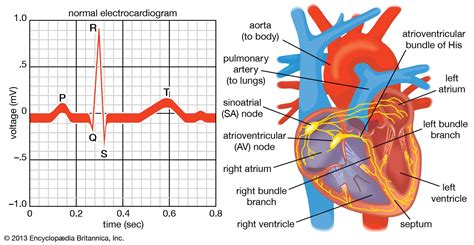
Normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute (bpm), with a regular rhythm originating from the sinoatrial (SA) node. The EKG tracing shows a P wave preceding each QRS complex, indicating atrial depolarization before ventricular depolarization. This rhythm is considered the standard for a healthy heart, and any deviation from this pattern may indicate an underlying cardiac issue.
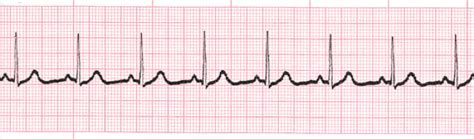
Atrial Fibrillation
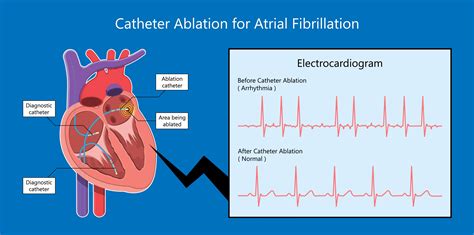
Atrial fibrillation is the most common type of serious arrhythmia, characterized by rapid and irregular atrial impulses. On an EKG, it is identified by the absence of P waves and the presence of fibrillatory waves, with an irregularly irregular ventricular response. This condition increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications, necessitating prompt medical evaluation and treatment.
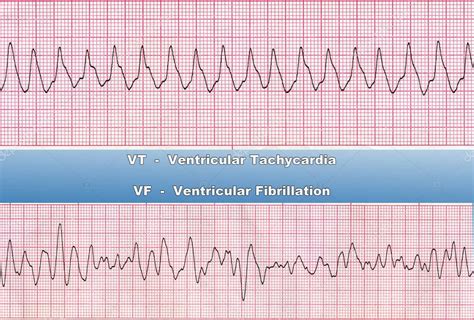
Ventricular Tachycardia
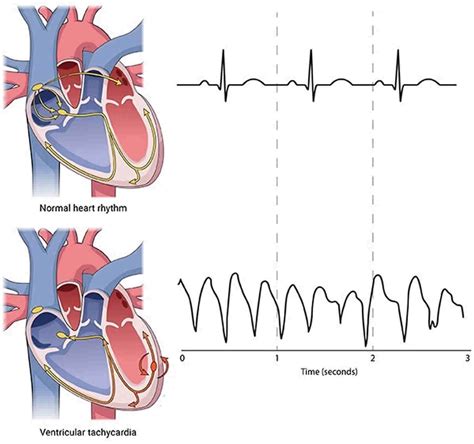
Ventricular tachycardia is a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia characterized by three or more consecutive premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) at a rate greater than 100 bpm. The EKG shows a wide QRS complex tachycardia, which may or may not be monomorphic. This rhythm can degenerate into ventricular fibrillation, making immediate recognition and intervention critical.
Atrioventricular (AV) Block
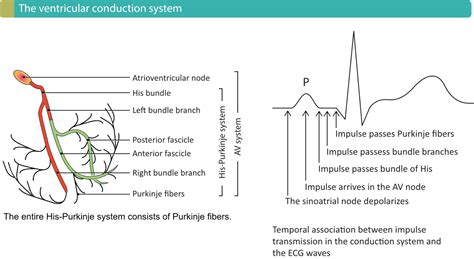
AV block refers to a delay or interruption in the electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles. It is classified into first, second, and third degrees, based on the severity of the block. First-degree AV block shows a prolonged PR interval, second-degree AV block is characterized by intermittent dropped beats, and third-degree AV block exhibits complete dissociation between atrial and ventricular activity. The clinical significance and management of AV block depend on its degree and the patient's symptoms.
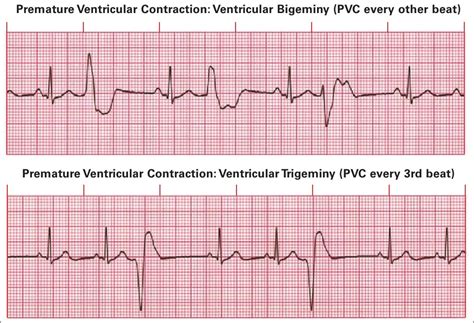
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
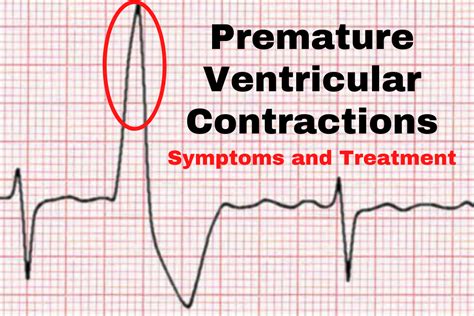
PVCs are early electrical impulses originating in the ventricles, causing the heart to contract prematurely. On an EKG, PVCs are recognized by their wide QRS complex appearance, often followed by a compensatory pause. While usually benign, frequent PVCs can be a sign of underlying heart disease or electrolyte imbalance, warranting further investigation.
Interpretation of EKG Rhythms
The interpretation of EKG rhythms involves a systematic approach, starting with the assessment of the heart rate, rhythm regularity, P wave morphology, PR interval, QRS complex duration, and the presence of any additional waves or pauses. This comprehensive evaluation allows for the identification of normal and abnormal rhythms, facilitating timely and appropriate interventions.Clinical Implications of EKG Rhythms
The clinical implications of EKG rhythms are diverse and significant. Accurate interpretation of these rhythms can lead to the diagnosis of various cardiac conditions, guide the selection of appropriate treatments, and influence patient outcomes. Furthermore, understanding EKG rhythms is essential for risk stratification, particularly in patients with known or suspected heart disease, as certain rhythms can predict adverse events.EKG Rhythms Image Gallery
What is the significance of understanding EKG rhythms in patient care?
+Understanding EKG rhythms is crucial for accurate diagnoses, guiding treatment decisions, and improving patient outcomes, especially in individuals with cardiac conditions.
How can individuals without a medical background learn about EKG rhythms?
+Individuals can learn about EKG rhythms through online courses, health education programs, and by consulting with healthcare professionals. Basic understanding of heart anatomy and function is a good starting point.
What are the common types of EKG rhythms and their clinical implications?
+Common EKG rhythms include normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, AV block, and premature ventricular contractions. Each has distinct clinical implications, ranging from benign to life-threatening conditions, and requires appropriate management strategies.
In conclusion, the study and interpretation of EKG rhythms are fundamental aspects of cardiac care, offering insights into the heart's electrical activity and facilitating the diagnosis of various cardiac conditions. As technology continues to evolve, making EKG devices more accessible, the importance of understanding these rhythms extends beyond the medical field, empowering individuals to take a more proactive role in their heart health. By delving into the complexities of EKG rhythms and their clinical implications, both healthcare professionals and the general public can work towards better heart health outcomes. We invite readers to share their thoughts, experiences, or questions regarding EKG rhythms and cardiac health, and to explore further resources for a deeper understanding of this vital topic.
